Pyricularia grisea mitophagy related pathogenic factor, gene and application thereof
A technology of mitophagy and rice blast fungus, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as incomplete mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Isolation and cloning of the MoUTH1 gene.
[0030] The amino acid sequence of the rice blast fungus pathogenic factor MoUTH1 protein is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The nucleotide sequence (coding region) of the Magnaporthe grisea MoUTH1 gene is shown in SEQ ID No.2.
[0031] In order to elucidate the biological function of MoUTH1 in the growth, development and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe grisea, we constructed a knockout mutant of Magnaporthe grisea MoUTH1 gene. Follow the steps below to construct the knockout vector:
[0032] The MoUTH1 gene knockout vector was constructed by homologous recombination gene knockout method. The length of the MoUTH1 gene was about 1.5kb, and it was replaced by the hygromycin B gene by homologous recombination method to obtain the MoUTH1 knockout mutant. Specific steps are as follows:
[0033] Using the genome of the wild strain B157 of Magnaporthe grisea (a gift from Naqvi Laboratory, Temasek Academy of Life Sciences, Singapore) as a templa...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Identification of a MoUTH1 knockout mutant of Magnaporthe grisea.
[0047] Design a forward primer MoUth1-5tF (MoSun4-5tF: 5'-TGGGACTAGACCAGAAGAGAGGC-3') in front of the upstream flanking sequence, and design a reverse primer pFGL820-5R (5'-TCGACCAAGTCCCTCCACACA-3') on the resistance gene, Use this pair of primers to detect knockout positive transformants, and the detection system is:
[0048]
[0049] The reaction conditions are:
[0050] Pre-denaturation at 95°C for 30s;
[0051] Denaturation at 95°C for 7s, annealing at 63°C for 20s, extension at 72°C, the extension time was determined according to the size of the amplified fragment (30s / kb), a total of 34 cycles, and the annealing temperature decreased by 0.2°C for each cycle;
[0052] Extend at 72°C for 2 min.
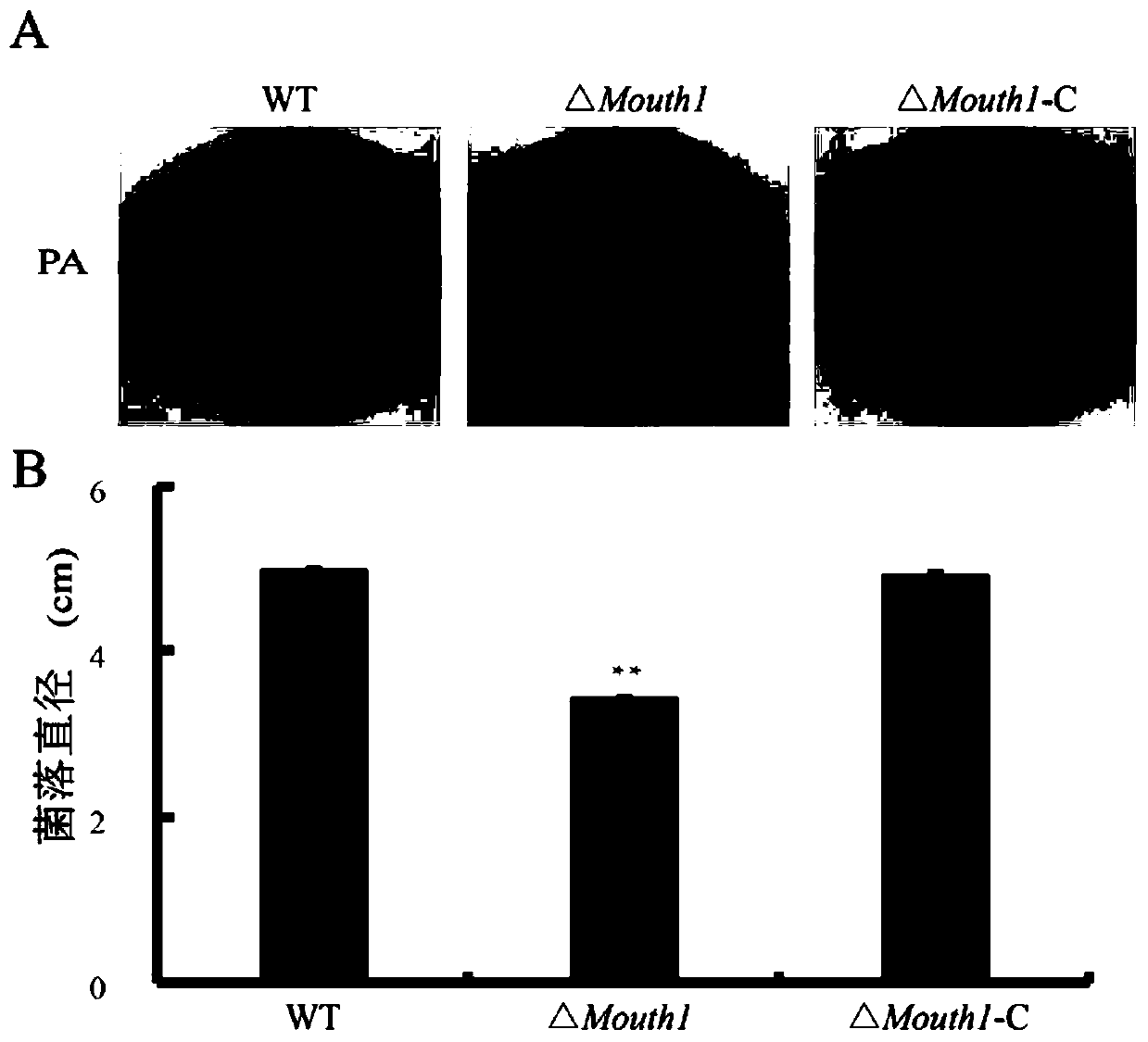
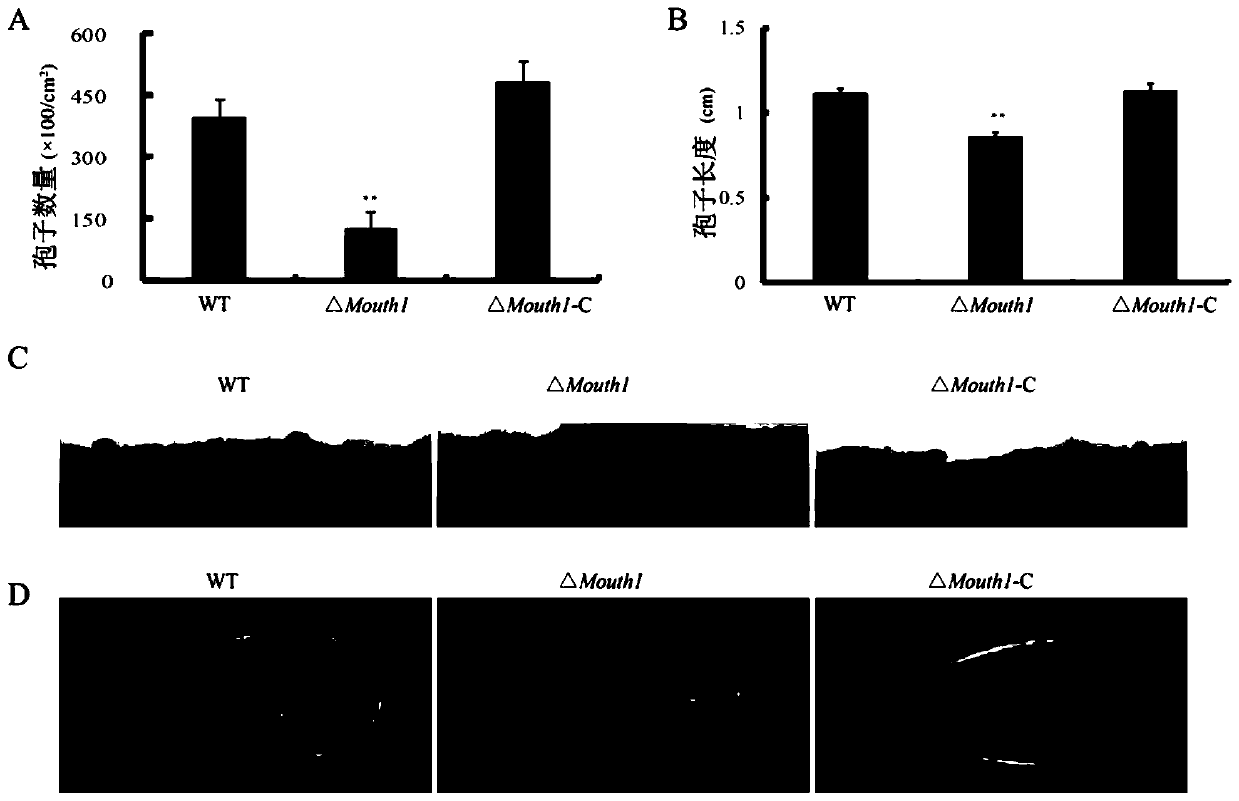
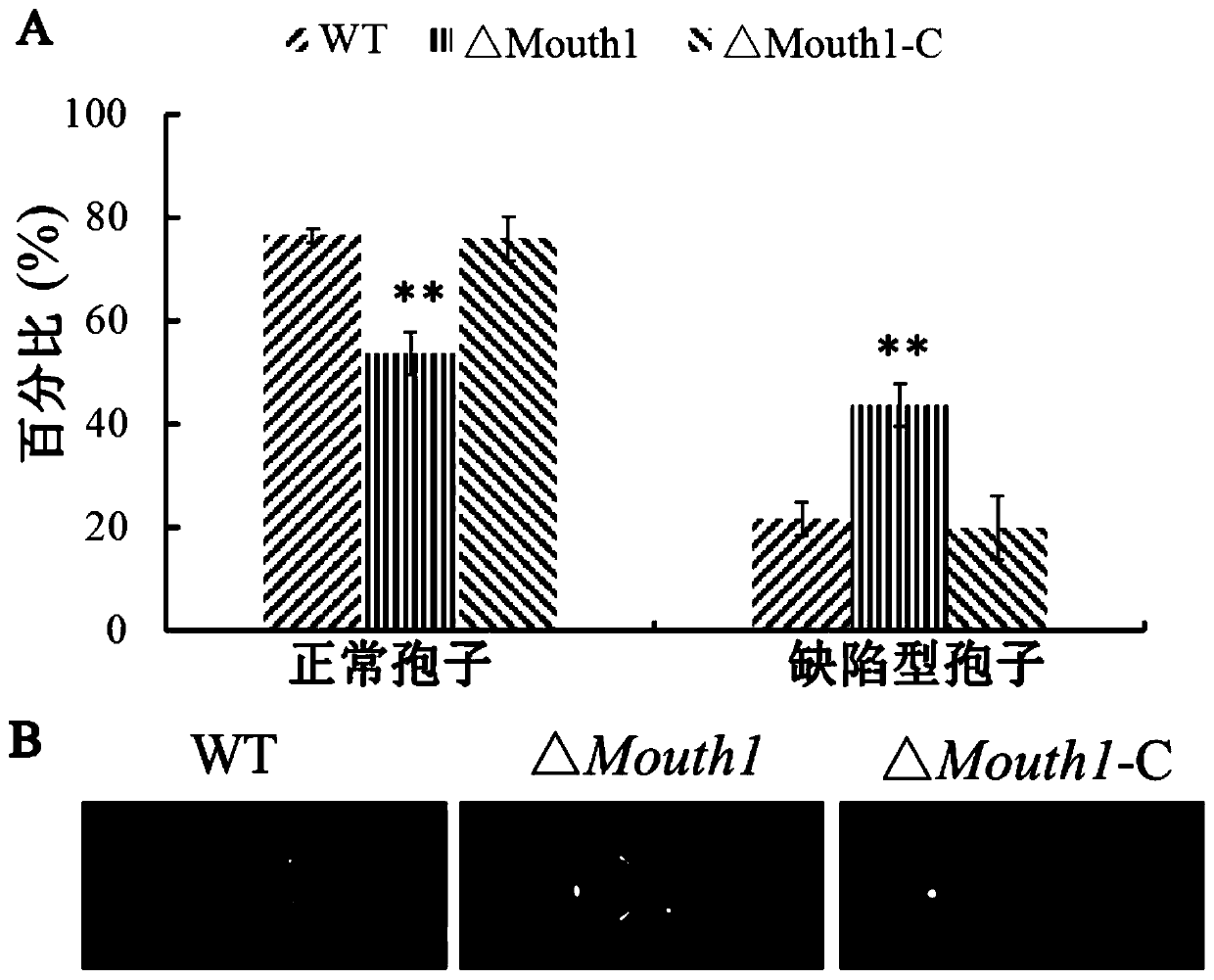
[0053] A total of 7 mutant strains were identified, and one knockout mutant was selected for subsequent analysis and named ΔMouth1.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Construction of MoUTH1 gene complementation vector and acquisition of complementation strain.
[0056] In order to verify that the phenotype of the mutant is caused by the deletion of MoUTH1, we constructed the complementary vector pMouth1-C, used the wild-type B157 genome as a template, and used primers MoUTH1-cF / cR to amplify the MoUTH1 gene (sequence as SEQ ID No. 5), using T4 ligase to connect to the EcoRI and KpnI restriction sites on the linearized vector pFGL822 (addgene ID: 58225).
[0057] MoUTH1-cF: 5'-AGAAACTCGAGAATTCATGGCGTTCAGGAGGTGGTTCG-3';
[0058] MoUTH1-cR: 5'-TCGCCCTTGCTCACGGTACCGCTGCCCTTGCTGAAAACAATG-3'.
[0059] The completed complementation vector was transformed into the knockout mutant ΔMouth1 strain, which was named Mouth1-C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com