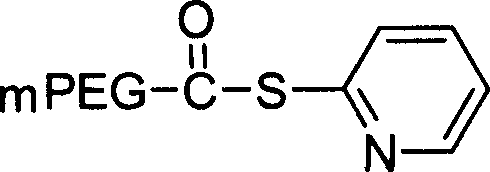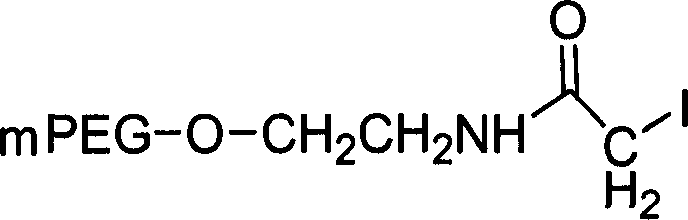Patents
Literature
55 results about "Pathogenicity Factors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
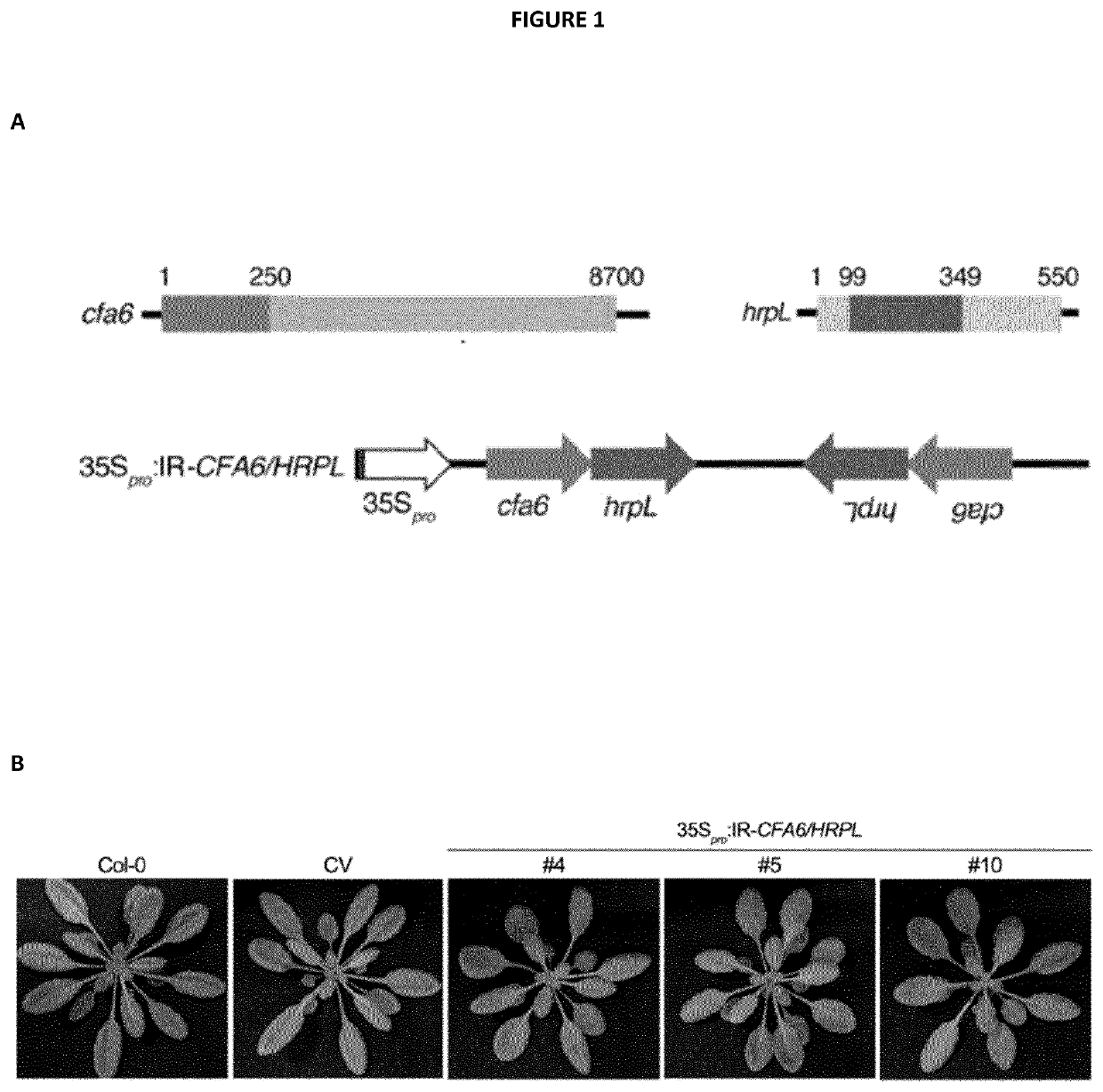
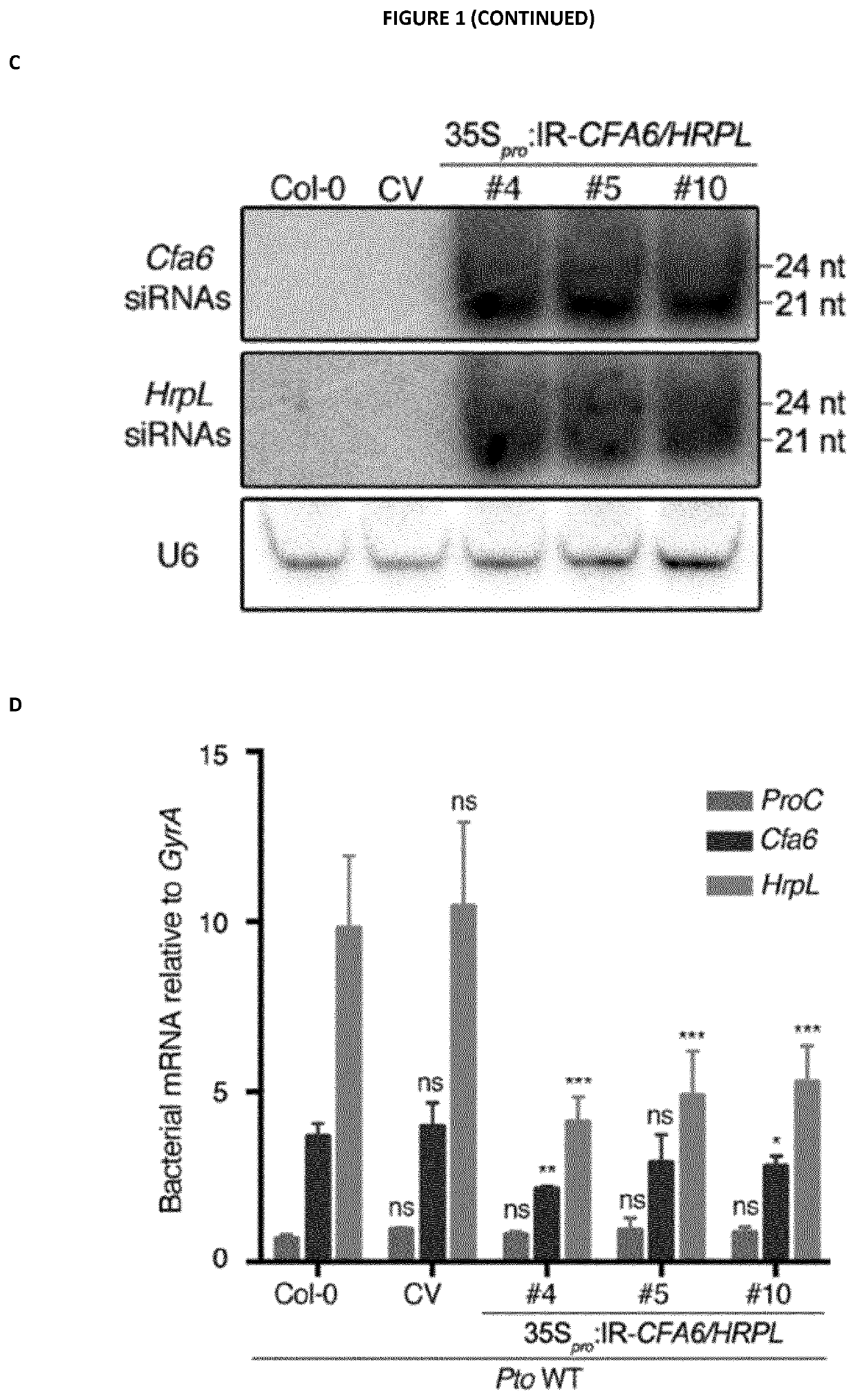
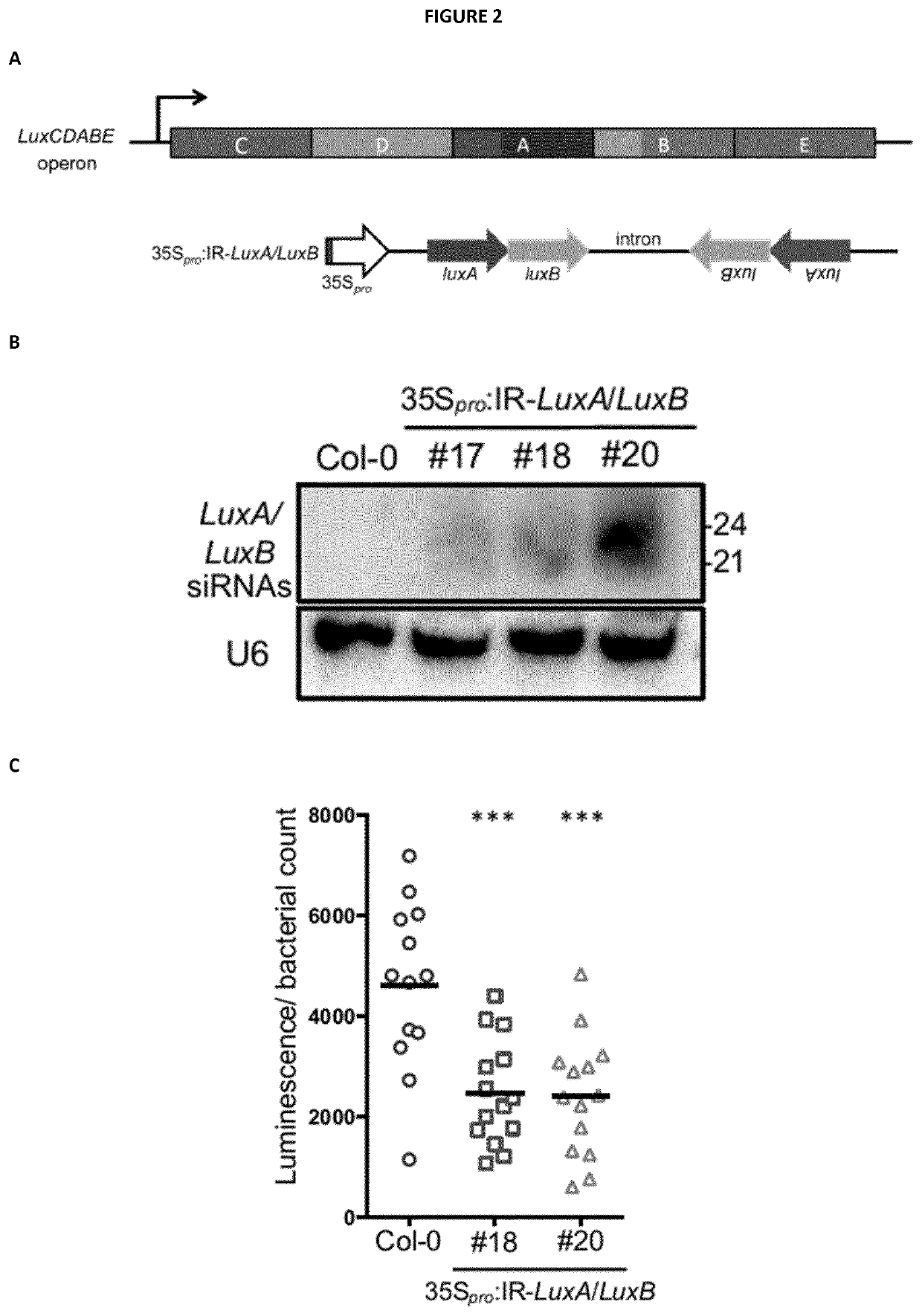
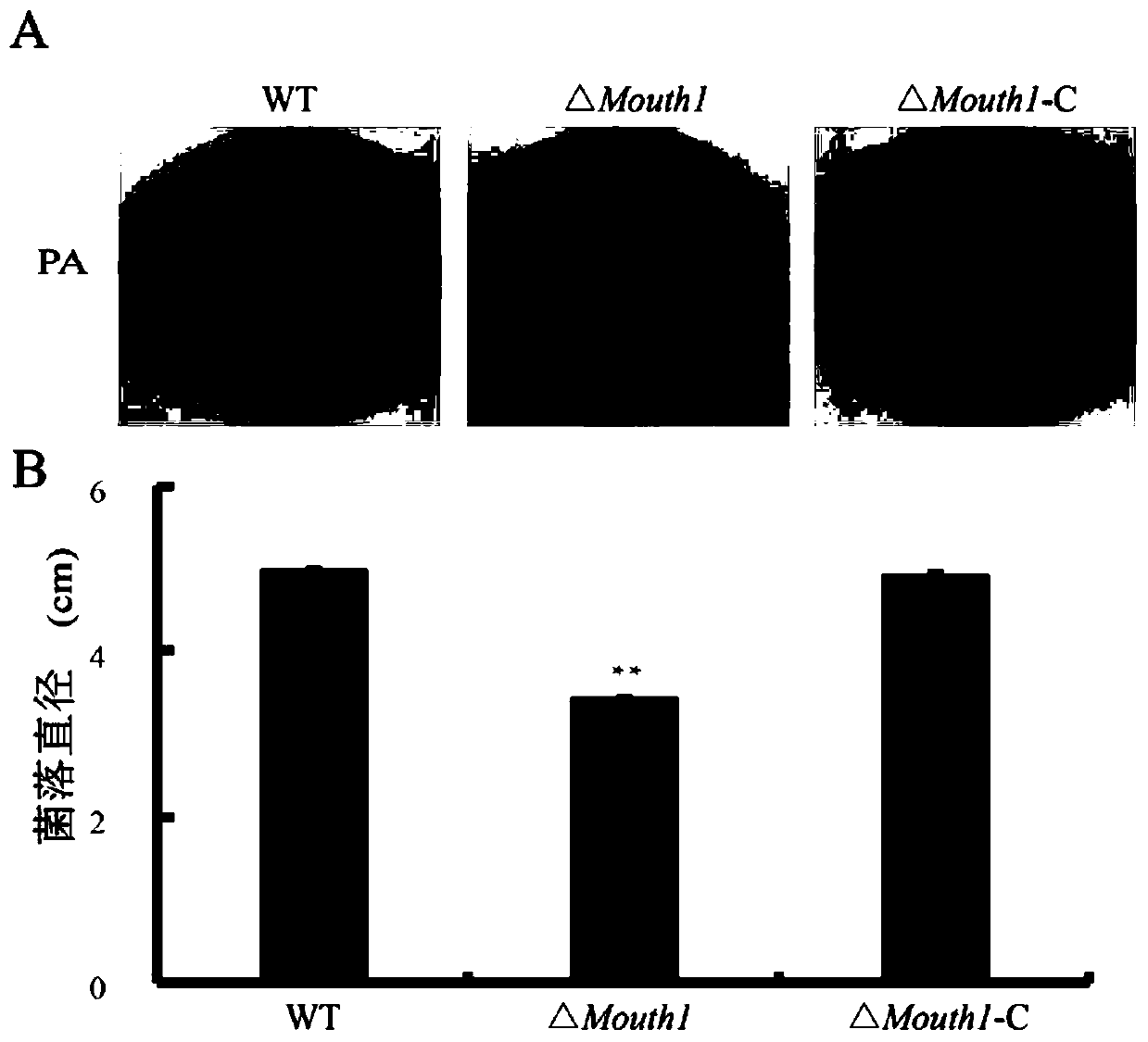
Pathogenicity Factor. Pathogenicity factors are under control of two cell-density–dependent quorum sensing systems controlled by different signal molecules, 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester and acylhomoserine lactone, that interact in complex ways (Von Bodman et al., 2003).
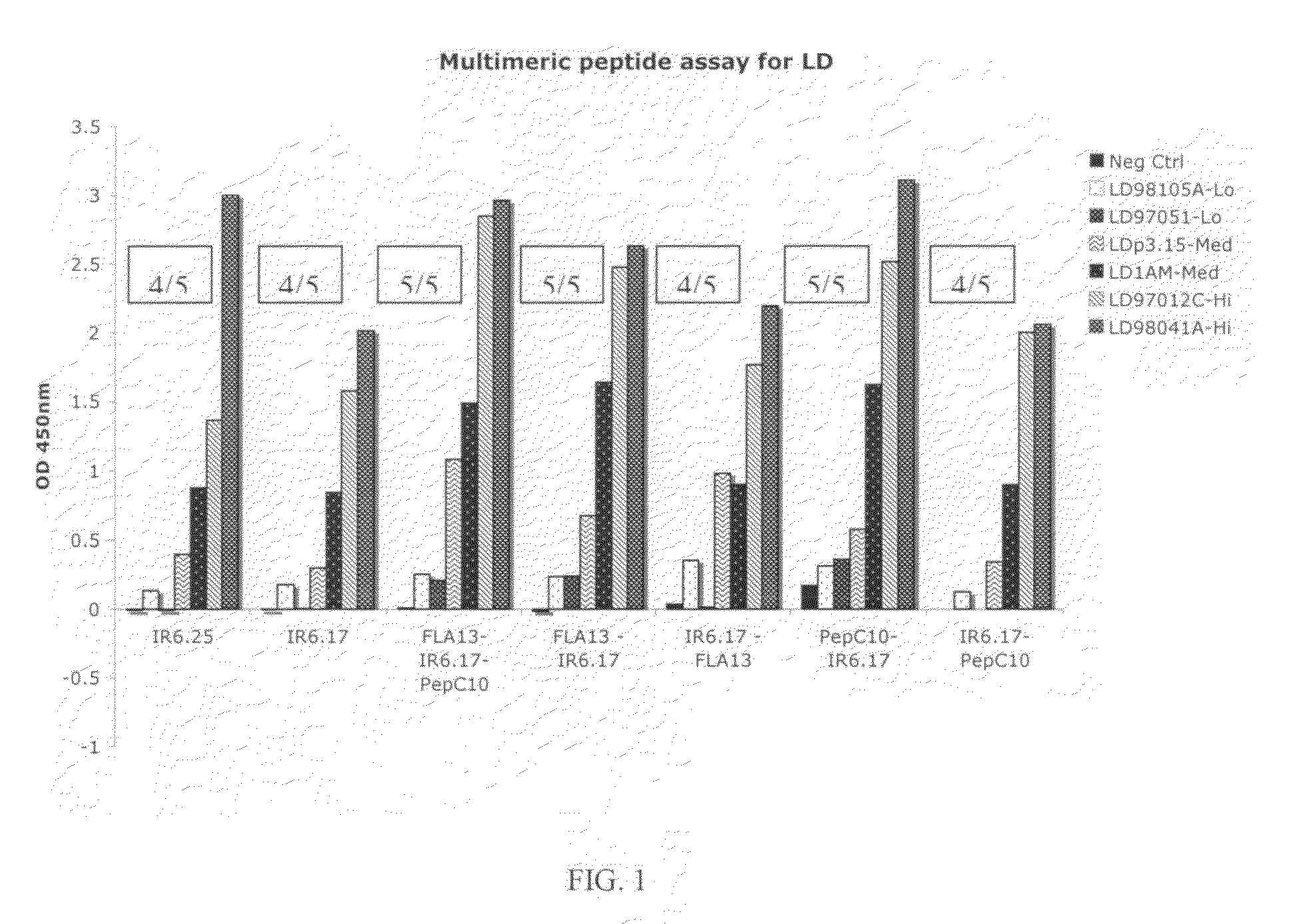
Peptide diagnostic agent for lyme disease
The present invention relates, e.g., to an isolated peptide consisting of the sequence MKKDDQIAAAIALRGMA (SEQ ID NO:1) or an active variant thereof, wherein the peptide or active variant can bind specifically to an antibody induced by a causative agent of Lyme disease (a pathogenic Borrelia), e.g. in a sample from a subject having Lyme disease. Also disclosed are linear multimeric peptides that contain the peptide represented by SEQ ID NO:1 as well as one or more additional peptide epitopes from other Borrelia proteins that can also bind specifically to an antibody as above. Compositions and diagnostic kits comprising a peptide of the invention are described, as are diagnostic assays using the peptide(s).
Owner:BIOPEPTIDES LLC
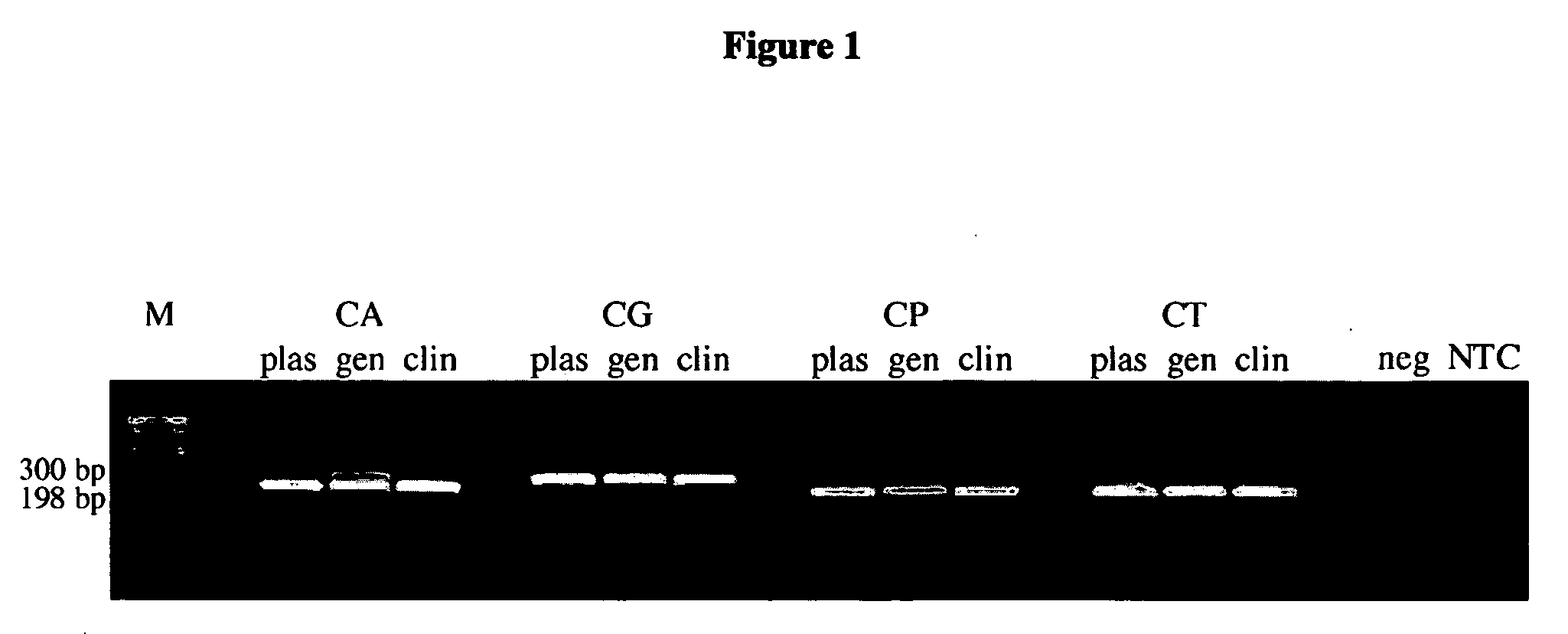
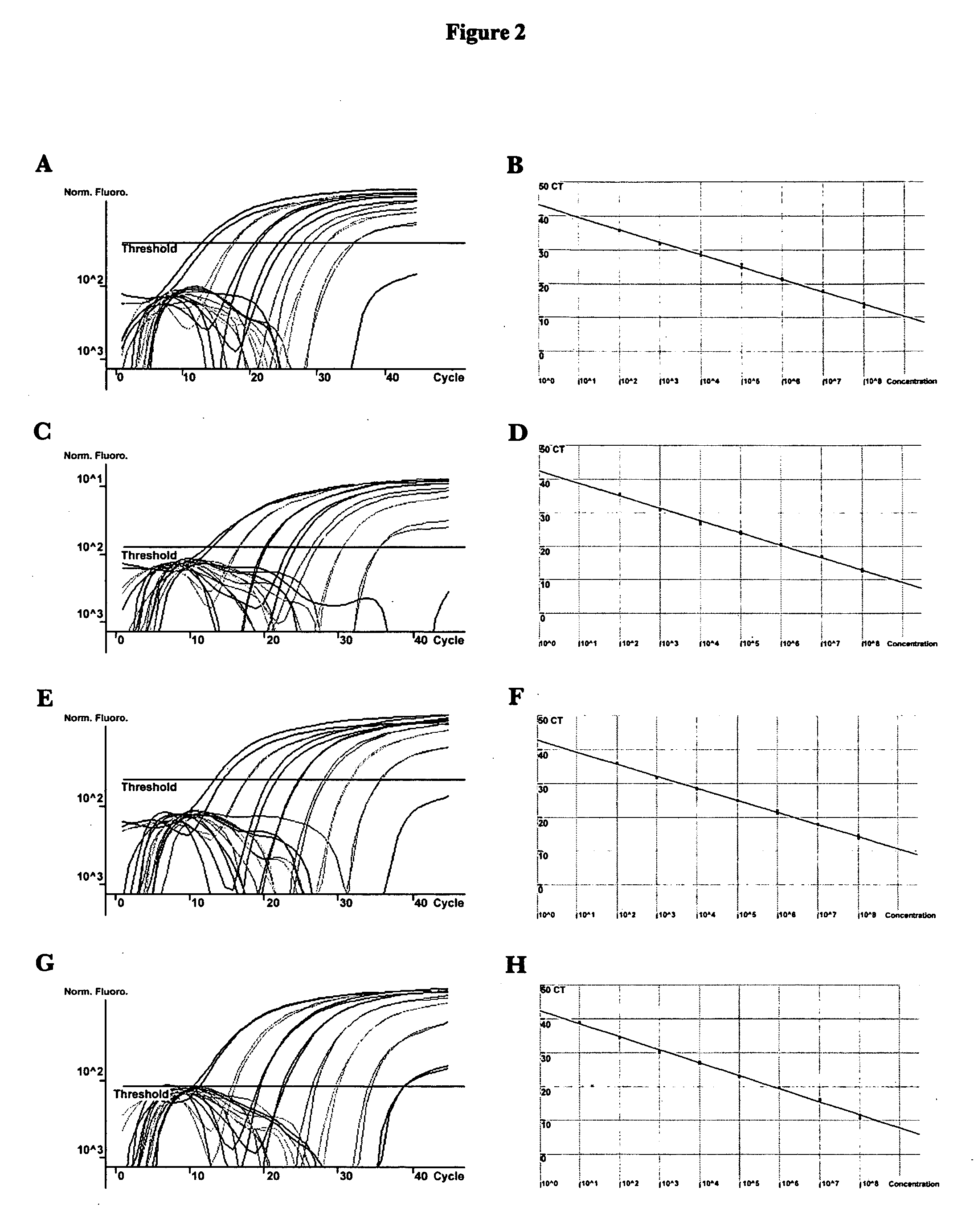
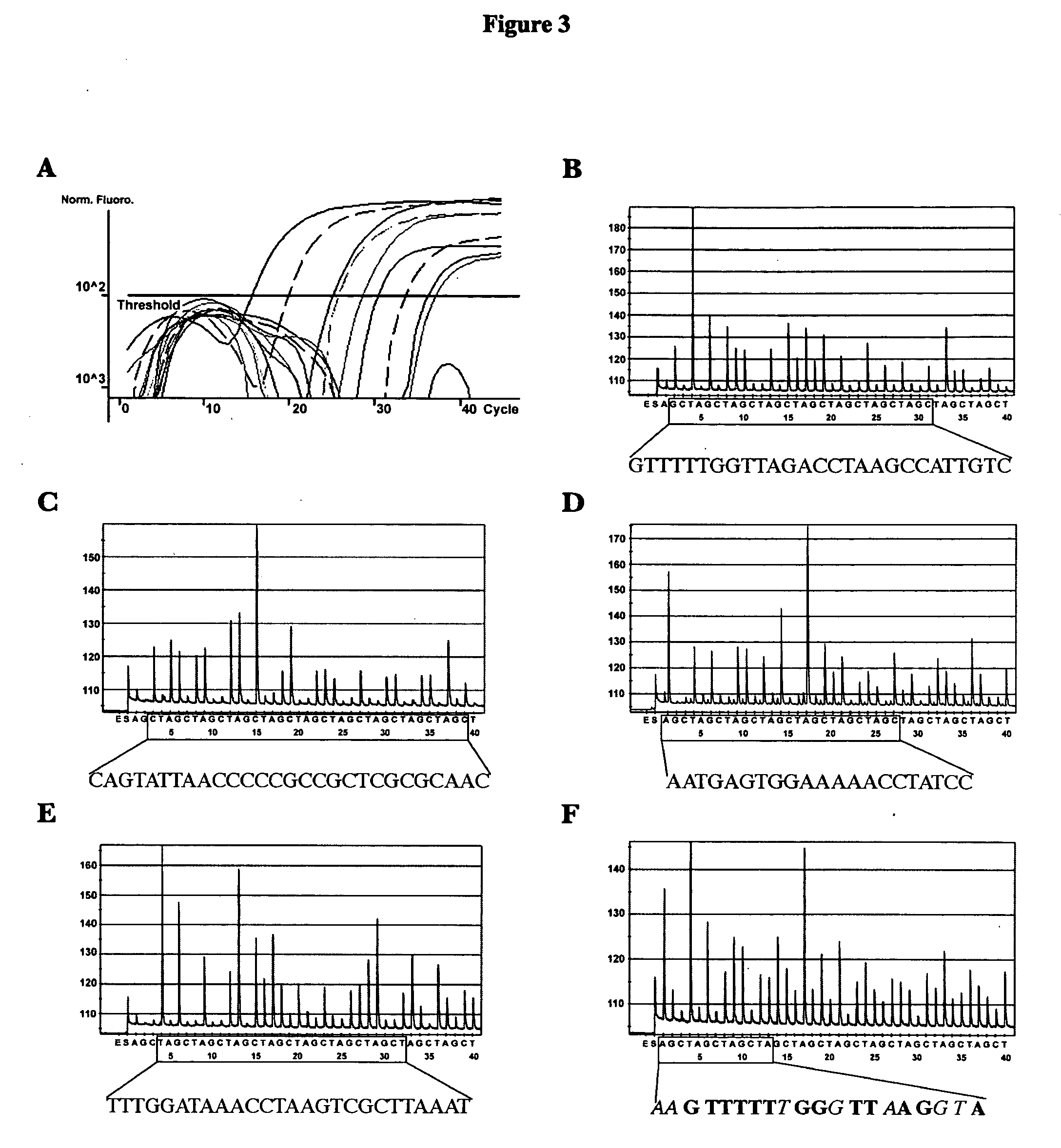
Methods and compositions for detecting and identifying species of Candida
ActiveUS20080102449A1Avoid disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerNucleotide
Methods and compositions useful in the detection and identification of species of Candida are disclosed. These species include Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, each of which is a causative agent for vaginal candidiasis. The compositions of the invention are combinations of oligonucleotides. These oligonucleotides include pairs of forward and reverse primers for polymerase chain reactions, wherein each primer pair is capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to one of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, but preferably is not capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to any of the other three species. In preferred embodiments, the forward primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each reverse primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other reverse primers; or the reverse primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each forward primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other forward primers. These unique primer sequences account for the species specificity of the resultant amplicons. The oligonucleotides also include probes capable of detecting these amplicons, and sequencing primers for determining, in primer extension reactions, the nucleotide sequences contained within the amplicons. In preferred methods of the invention, a biological sample is tested for the presence of at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis by isolating nucleic acid from the sample, attempting a polymerase chain reaction in a mixture containing this nucleic acid and a plurality of these primer pairs, ascertaining whether any amplicon is produced in the mixture using an oligonucleotide probe, and determining the sequence of any resultant amplicon using the sequencing primers. The detection of an amplicon indicates that the sample contains at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, or Candida tropicalis, and the nucleotide sequence data is used to determine which of these four Candida species is present.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
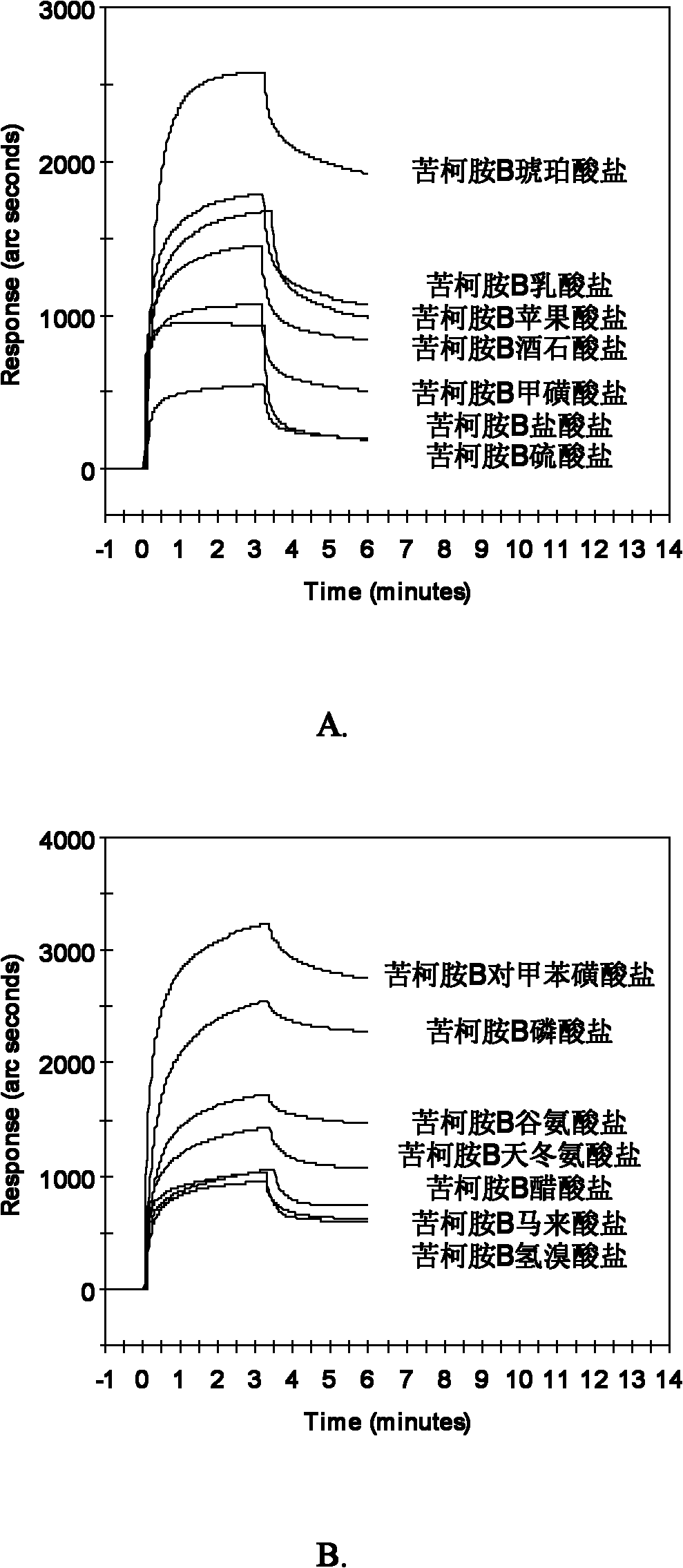
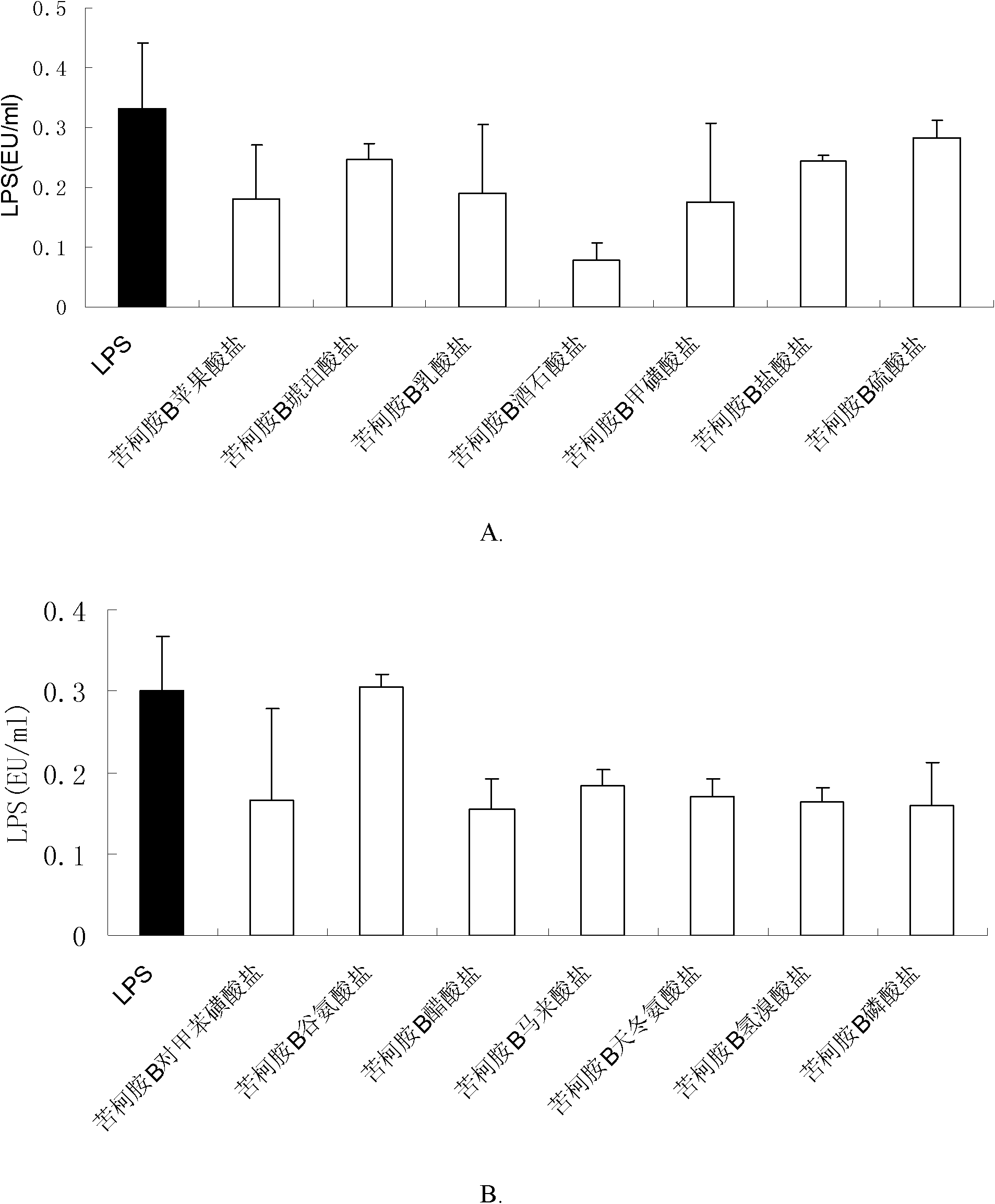
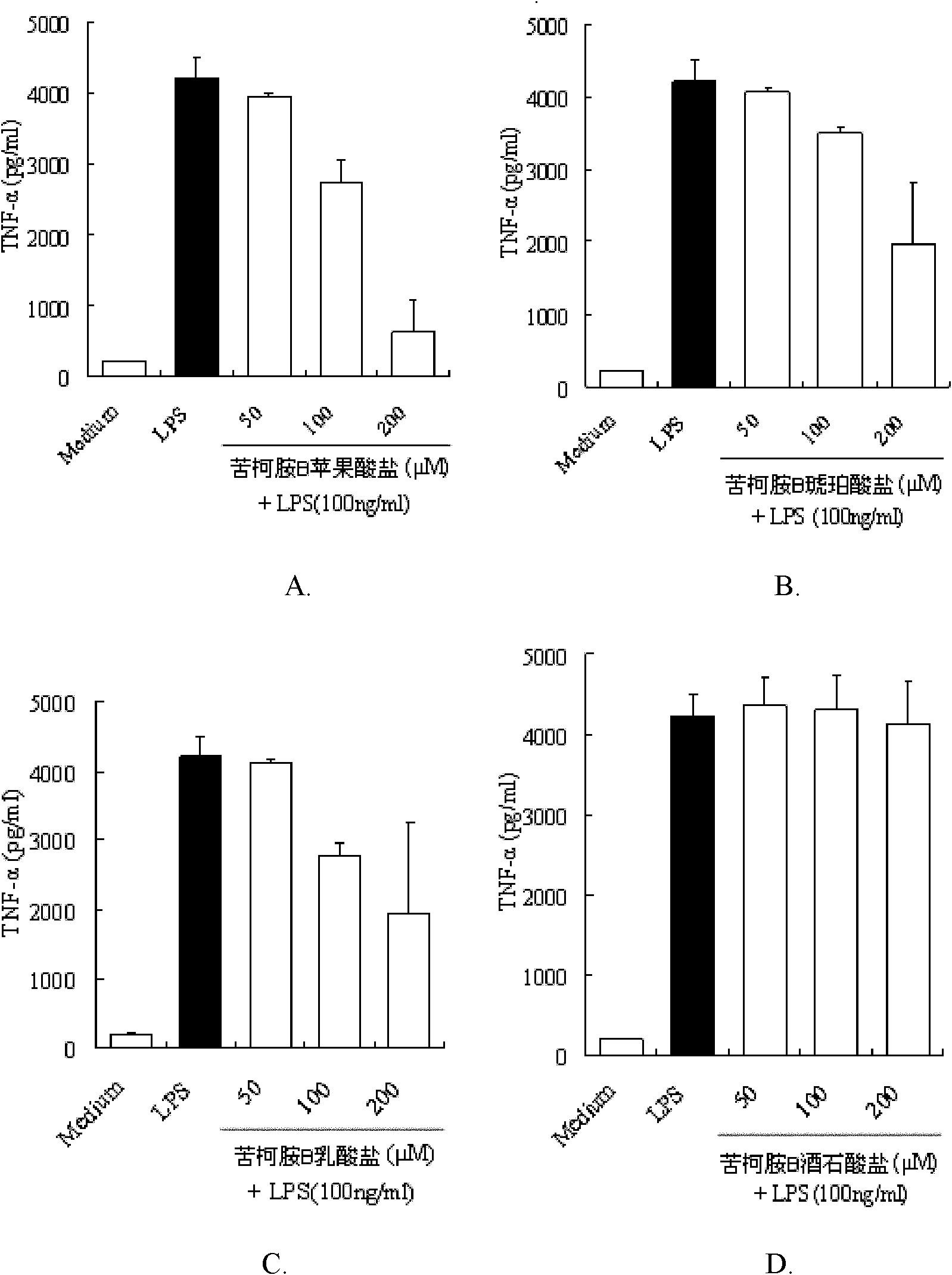
Kukoamine B salt, preparation method thereof and purpose thereof
ActiveCN102464591AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugPharmaceutical medicine
The invention relates to a kukoamine B salt, a preparation method thereof and a purpose of the kukoamine B salt in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating sepsis. Experiments show that the kukoamine B salt has a good inhibition effect on main pathogenic factors mediating the sepsis and can be used to prepare medicines for preventing and treating the sepsis. The kukoamine B salt and various pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and / or diluents can be prepared into various preparations, so an efficient control means is provided for such intractable diseases on condition that definite and effective sepsis treatment measures are clinically lacked at present.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Construction of a comparative database and identification of virulence factors through comparison of polymorphic regions in clinical isolates of infectious organisms
InactiveCN101421415AReduce new targetsImprove protectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsVirulent characteristicsDrug target
The present invention is directed to novel nucleotide sequences to be used for diagnosis, identification of the strain, typing of the strain and giving orientation to its potential degree of virulence, infectivity and / or latency for all infectious diseases more particularly tuberculosis. The present invention also includes method for the identification and selection of polymorphisms associated with the virulence' and / or infectivity in infectious diseases more particularly in tuberculosis by a comparative genomic analysis of the sequences of different clinical isolates / strains of infectious organisms. The regions of polymorphisms, can also act as potential drug targets and vaccine targets.; More particularly, the invention also relates to identifying virulence factors of M. tuberculosis strains and other infectious organisms to be included in a diagnostic DNA chip allowing identification of the strain, typing of the strain and finally giving orientation to its potential degree of virulence. Although the present invention has been illustrated with specific reference to the polymorphic region in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the said invention is not to be understood and construed as being limited to Tuberculosis but is applicable to all infectious diseases.
Owner:阿维斯塔金格兰技术有限公司 +1
Fusion of multiple enterotoxin genes of escherichia coli and application thereof
ActiveCN101914564AImproving immunogenicityImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliInfant animal
The invention relates to an escherichia coli (E. coli) trivalent enterotoxin fusion gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering subunit vaccines. The enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) is a main pathogen causing baby-animal and infantile diarrhea. Aiming at the defects that the conventional TEC vaccine has narrow protection range and cannot induce high-level antitoxin, the invention designs a trivalent E. coli enterotoxin fusion with the fusion mode of 5'-STa-LT-STb-3' or 5'-STb-LT-STa-3'. After the multivalent enterotoxin gene or protein immunizes animals, high-level STa, STb and LT resistant antibodies can be induced to be generated. Therefore, the escherichia coli (E. coli) trivalent enterotoxin fusion gene can neutralize the toxicity of a key pathogenic factor enterotoxin, improve the immunity protection rate and widen the protection range without being limited by E. coli pilus types so as to effectively control ETEC diarrhea.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Antagonists of the bradykinin b1 receptor
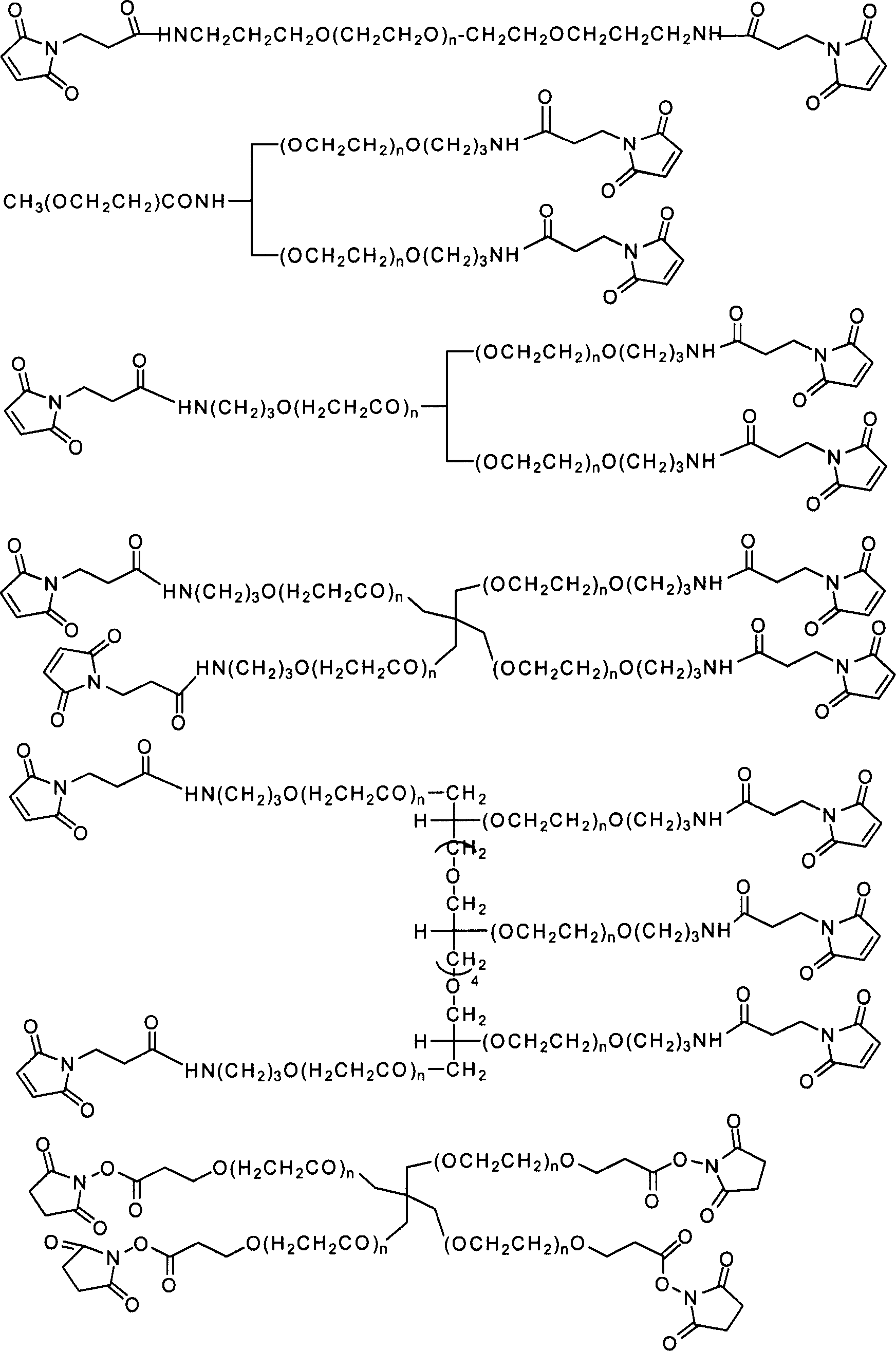
The present invention relates to biologically active peptides and conjugated peptides useful as therapeutic or prophylactic agents against diseases or conditions associated with pathogenic factor B1. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, biologically active PEG-conjugated peptides are provided. In one aspect of the invention, the pharmaceutically active PEG-conjugated peptides of the invention are useful in the treatment of inflammation or pain.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Biochemical detection liquid for calcium in urine
InactiveCN1570635AAchieving self-monitoringQuick checkMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingCalcium metabolismCalcium EDTA
This is a biochemistry detection liquid of urine calcium comprising 1.5-2w / v percents oxalic acid, 1.5-2w / v percents oxalic acid amine, 3.2- 3.5v / v percents glacial acetic acid and distilled water. This invention offers biochemistry detection liquid and self-checking method of urine calcium for the mass scoutting and checking dynamically. Through the recording curve diagram in accordance with series detecting color result one can self-judge something: 1, warning signal of health and pathogenic factor; 2, forepart detectable rate of calcium metabolism overbalancing; 3, the synchronous tracking monitoring of curative effect during the treating course. The above liquid offers the likelihood of carrying out all this function.
Owner:赵青华
Application of mycoplasma bovis secretory protein MbovP274
The invention discloses application of mycoplasma bovis secretory protein MbovP274 in preparation of mycoplasma bovis diagnostic reagents, drugs or vaccines, and belongs to the technical field of animal infectious disease prevention and treatment. The mycoplasma bovis secretory protein MbovP274 has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; gene annotation information shows that the amino acid sequence is a functionally-unknown protein; and experiments show that the MbovP274 protein has antigenicity and can react with mycoplasma bovis positive serum instead of mycoplasma bovis negative serum; the MbovP274 protein is identified as a secretory protein through western blot; it is further verified that the protein can induce bovine macrophages to highly express IL-8 and IFN-gamma, the IL-8 is an important neutrophil activating factor, and the IFN-gamma is a wide immunomodulatory factor. According to the research, the MbovP274 is considered to be an important pathogenic factor of mycoplasma bovis and can activate host immunity, and has important potential in research and development of new drugs and vaccines.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Antimicrobial therapy for bacterial infections
InactiveCN101198252ASuppress generationInhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideHeterologousStaphylococcus aureus
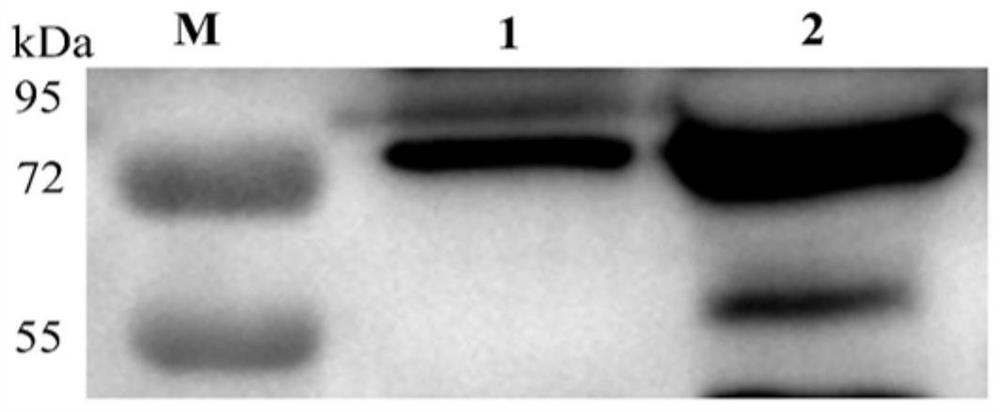
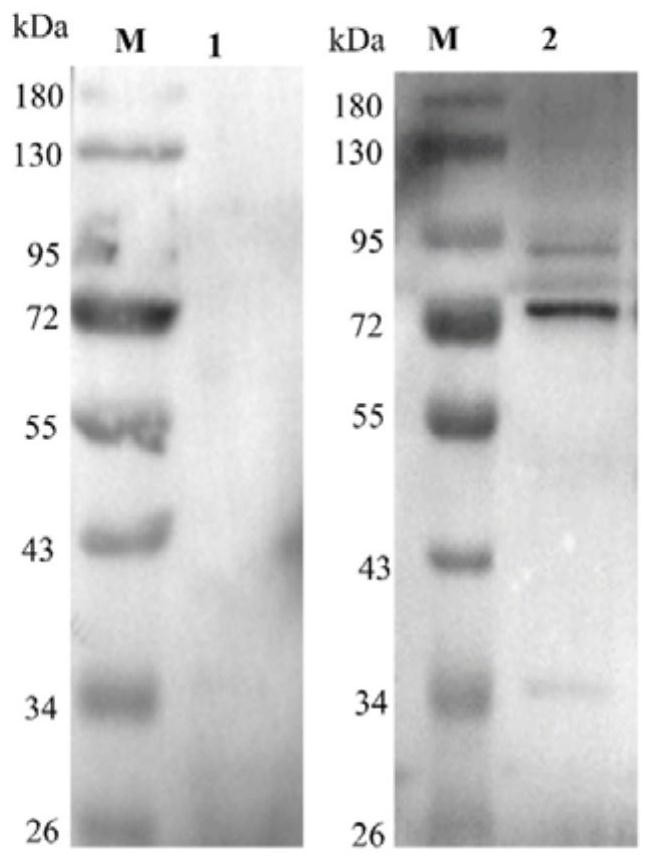
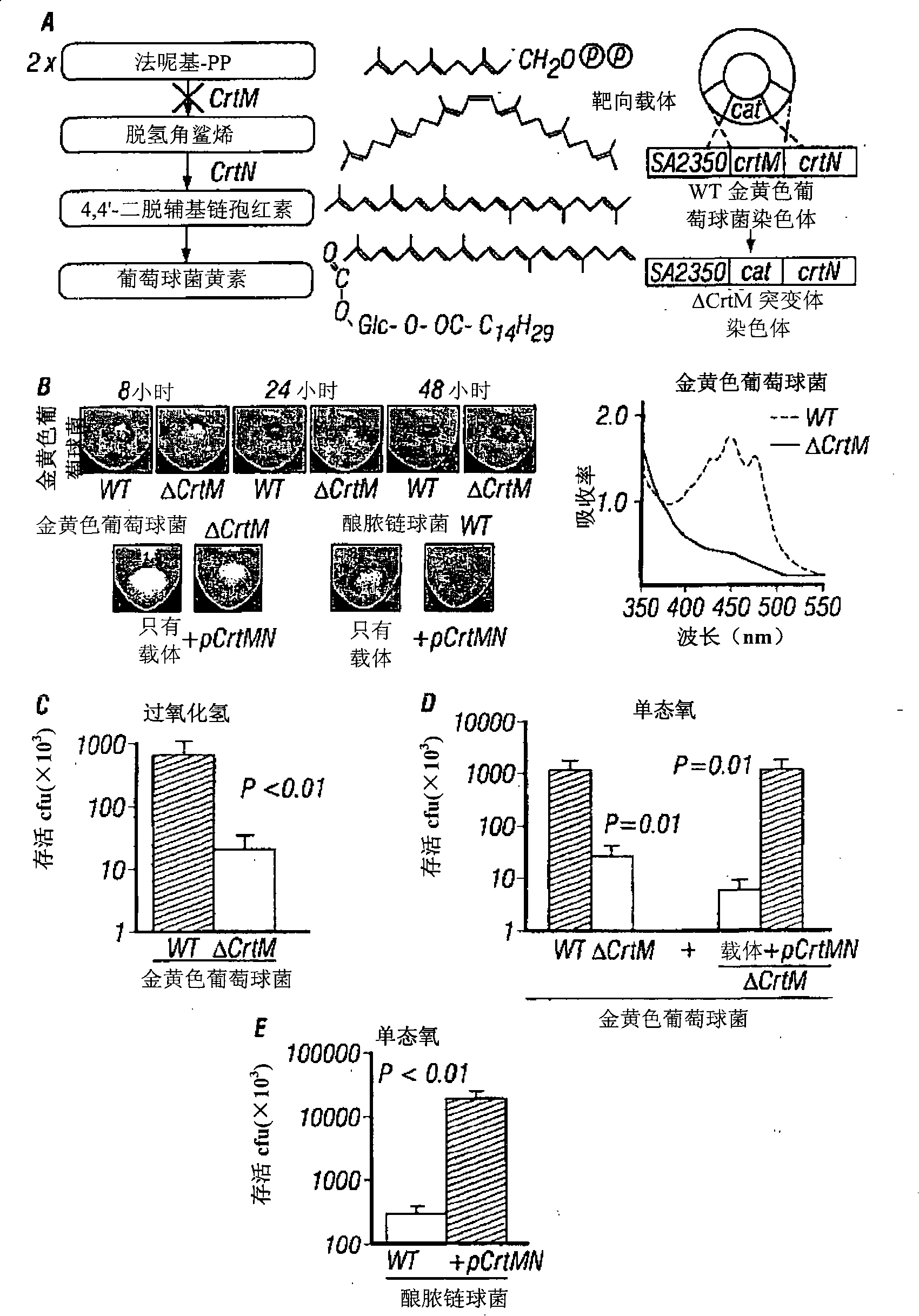
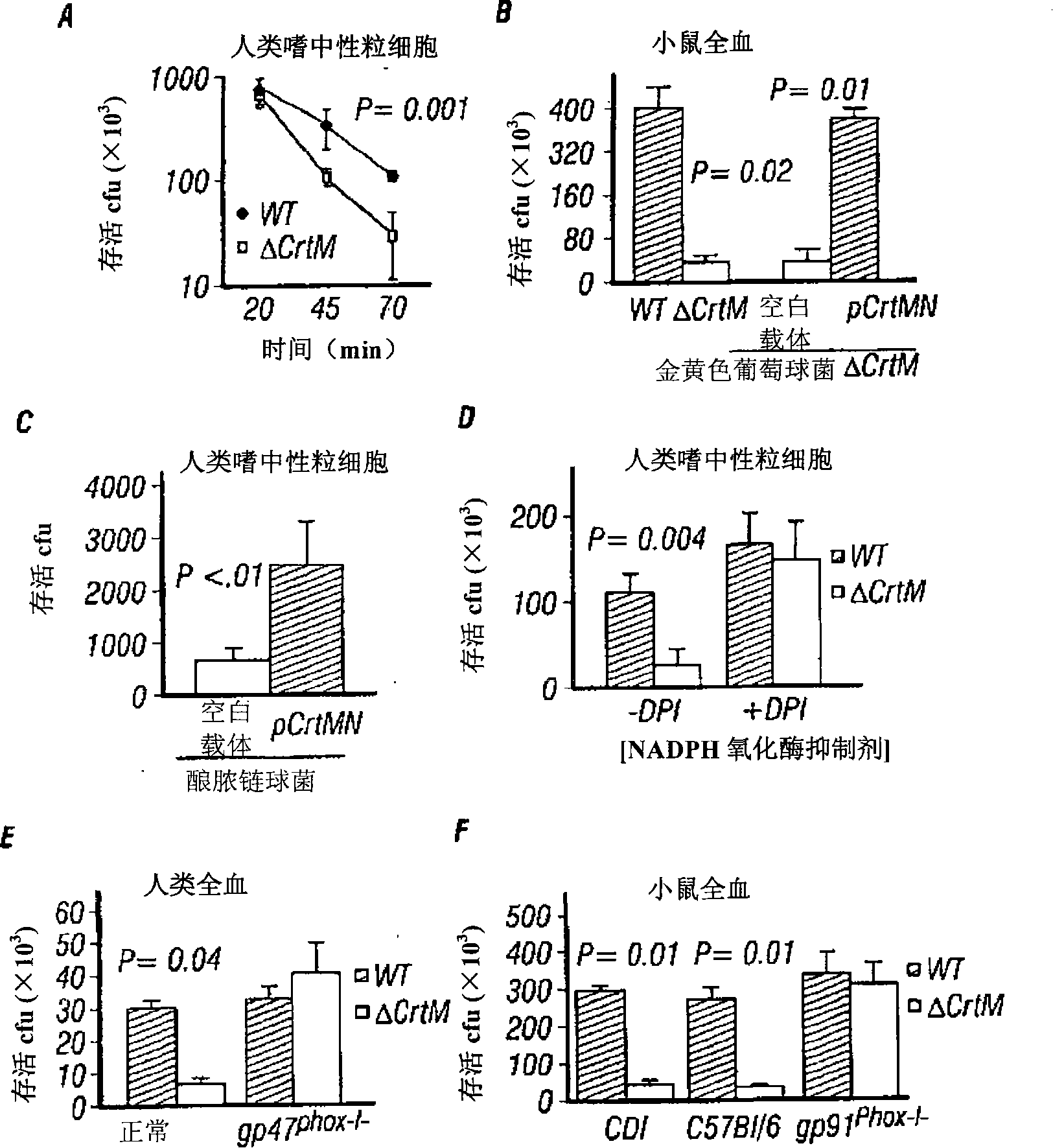
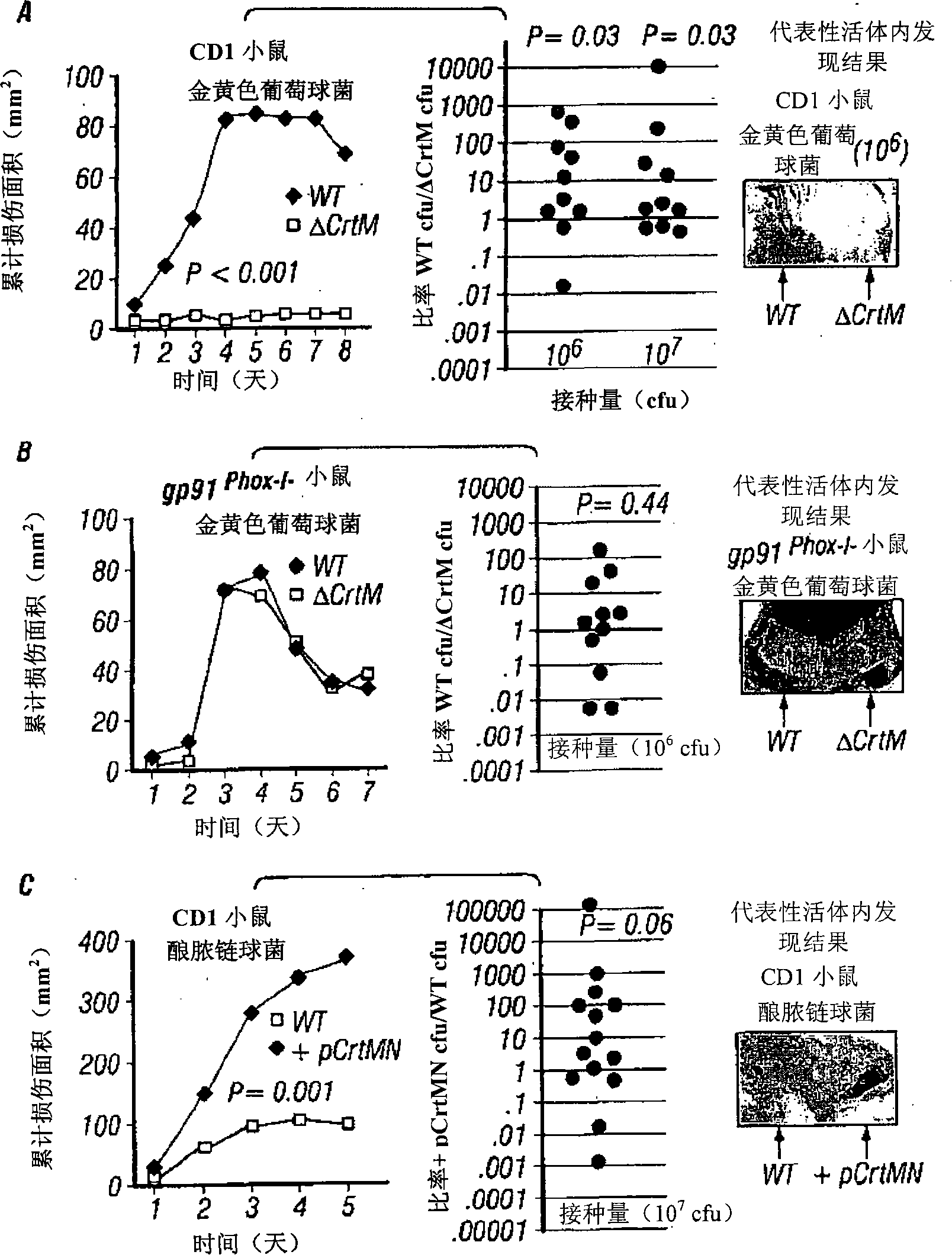
The disclosure provides a molecular genetic approach of targeted mutagenesis and heterologous expression, coupled with in vitro and in vivo models of bacterial pathogenesis, to demonstrate that the S. aureus pigment is a virulence factor and potential novel target for antimicrobial therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biochemical detection liquid for nitrite in urine
InactiveCN1570636AQuick Self-Test MethodFit closelyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingAcetic acidSulfanilic acid
This is a biochemistry detection liquid of urine nitrate comprising 0.35-0.45w / v percents sulfanilic acid, 0.2-0.3mgw / v percents alpha-naphthylamine, 20-40v / v percents glacial acetic acid, 1 -2v / v percents carbinol and distilled water. This invention offers biochemistry detection liquid and self-checking method of urine nitrate for the mass scoutting and checking dynamically. Through the recording curve diagram in accordance with series detecting color result one can self-estimate something: 1, warning signal of health and pathogenic factor; 2, forepart detectable rate of bacterial urine; 3, the synchronous tracking monitoring of curative effect during the treating course. The above liquid offer the likelihood of carrying out all this function.
Owner:赵青华
Immunoadsorbent, preparation method thereof and adsorber for blood perfusion
ActiveCN110975842ARemissionLower resistanceOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesCellulosePolyvinyl alcohol
The present invention provides an immunoadsorbent. The immunoadsorbent comprises a carrier, a grafting connection arm and a ligand, the carrier and the grafting connection arm are covalently connected, and the grafting connection arm is connected to the ligand through a connection group; and the carrier is selected from polystyrene-divinylbenzene or a composition of polystyrene-divinylbenzene andone or more of crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol, polypropylene, chitosan, cellulose, agarose and glucan, and the ligand is selected from tripterygium wilfordii extract and a derivative thereof. The invention also provides a preparation method of the immunoadsorbent and an adsorber for blood perfusion by adopting the immunoadsorbent. Compared with a traditional administration mode, blood circulation makes pathogenic factors in blood directly removed, triptolide can play a role in an in-vitro hemoperfutor, toxic damage to organs and tissues of a patient in the mode of entering the human body is avoided, drug resistance of the patient is avoided, and convenience is brought to use of medical staff.
Owner:JAFRON BIOMEDICAL
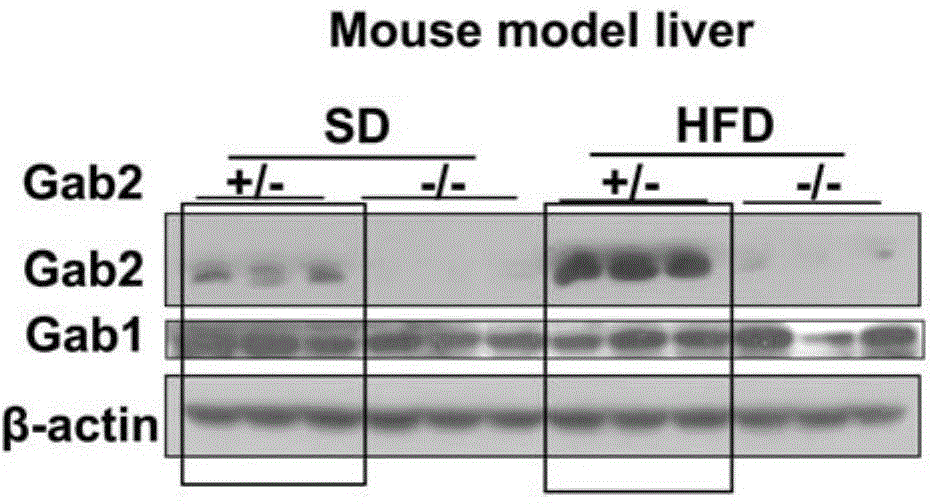
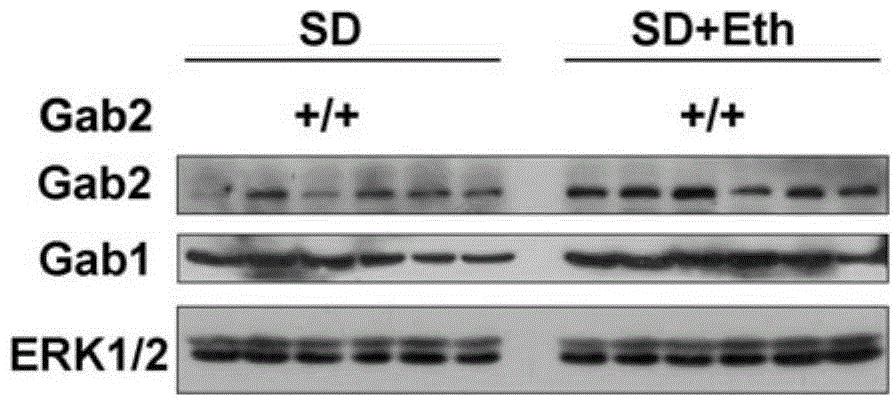
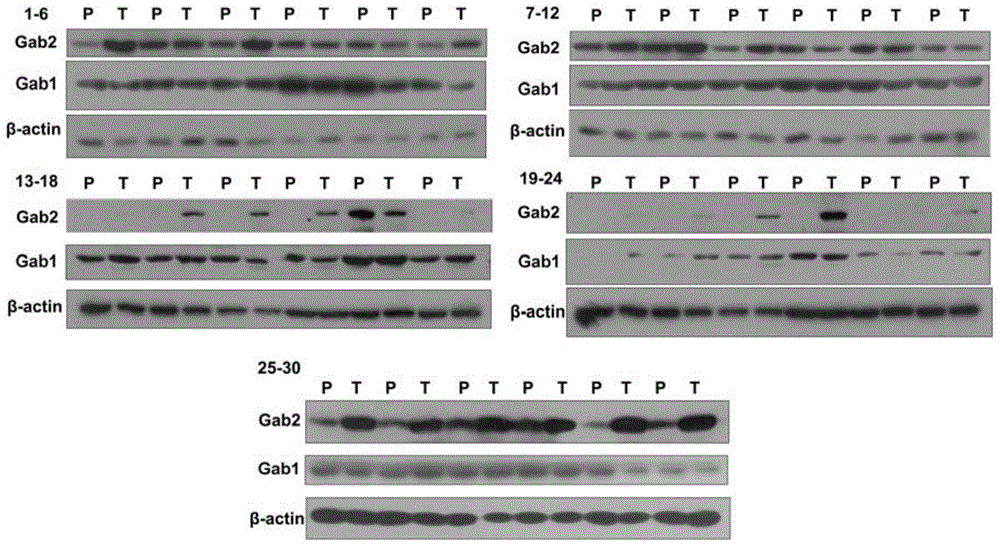
Molecular target Gab2 and application thereof in preparing medicines and health care food for preventing and treating fatty liver and liver cancer
The invention discloses molecular target Gab2 and application thereof in preparing medicines and health care food for preventing and treating fatty liver and liver cancer, and relates to a molecular target. The molecular target Gab2 is cytoplasm signal scaffolding protein mediating pathogenic factor-induced fatty liver and liver cancer; multiple disease animal models prove that in fatty liver and related diseases, the expression of the Gab2 can be induced by pathogenic factor; by collecting and integrating various signals by virtue of the Gab2, a comprehensive effect is generated, so that the development of diseases is promoted. The molecular target Gab2 can be applied to prepare medicines for preventing and treating fatty liver and liver cancer, and the molecular target Gab2 can be also used for preparing health care food for preventing and treating fatty liver and liver cancer.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
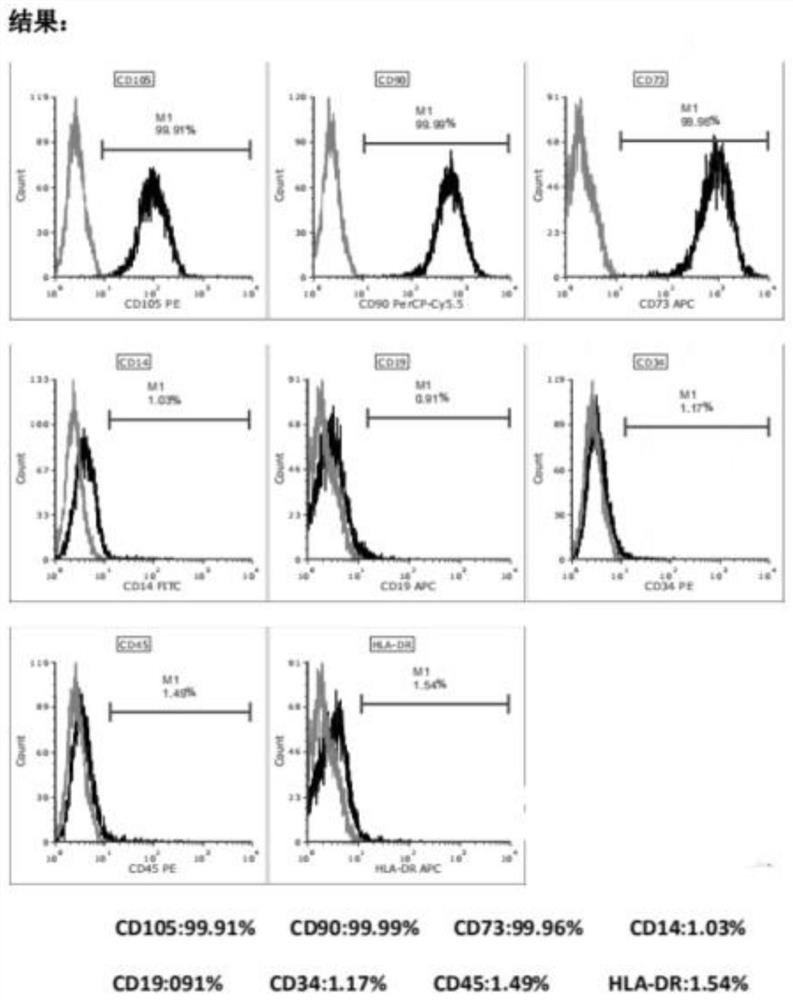
Exosome preparation deriving from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
PendingCN111826345APromote proliferationPromote secretionCell dissociation methodsCulture processUltrafiltrationSodium Chloride Injection
The invention discloses an exosome preparation deriving from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The exosome preparation contains the following raw materials: a Lonza UltraCULTURE serum-freemedium, a PALL UltroserG serum substitute, L-Glutamine and ganoderan. The exosome preparation is prepared by the following steps: dissociating cultured cells, washing the cells by virtue of a sodium chloride injection, and adding the cells into culture supernatant; putting culture supernatant into an ultra-low-temperature refrigerator for refrigeration; taking out the culture supernatant for unfreezing, carrying out high-speed centrifugation, concentrating the supernatant by virtue of an ultrafiltration membrane, and adding sodium hyaluronate, human serum albumin and trehalose, so as to prepare the exosome preparation deriving from the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. By utilizing a serum-free culture system in a preparation method of the exosome preparation deriving from the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, the quality is stable, the batch difference is small, and an exogenous pathogenic factor is not introduced; by adding the ganoderan, proliferation of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can be promoted, and secretion of exosomes by the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can be promoted; a complete culture medium and a condition culture medium are used for acquiring the exosomes, so that the yield is increased; and after the cells are frozen and dissociated, contents are mixed into the culture supernatant, so that the concentration of activesubstances is increased, and the exosome preparation is a face-beautifying anti-aging biological preparation with an excellent effect.
Owner:深圳国科靶点药物有限公司
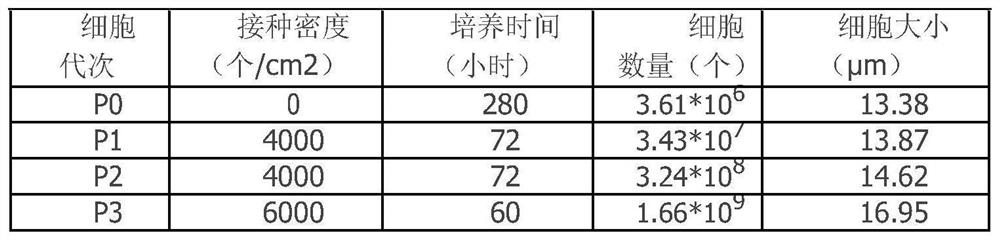
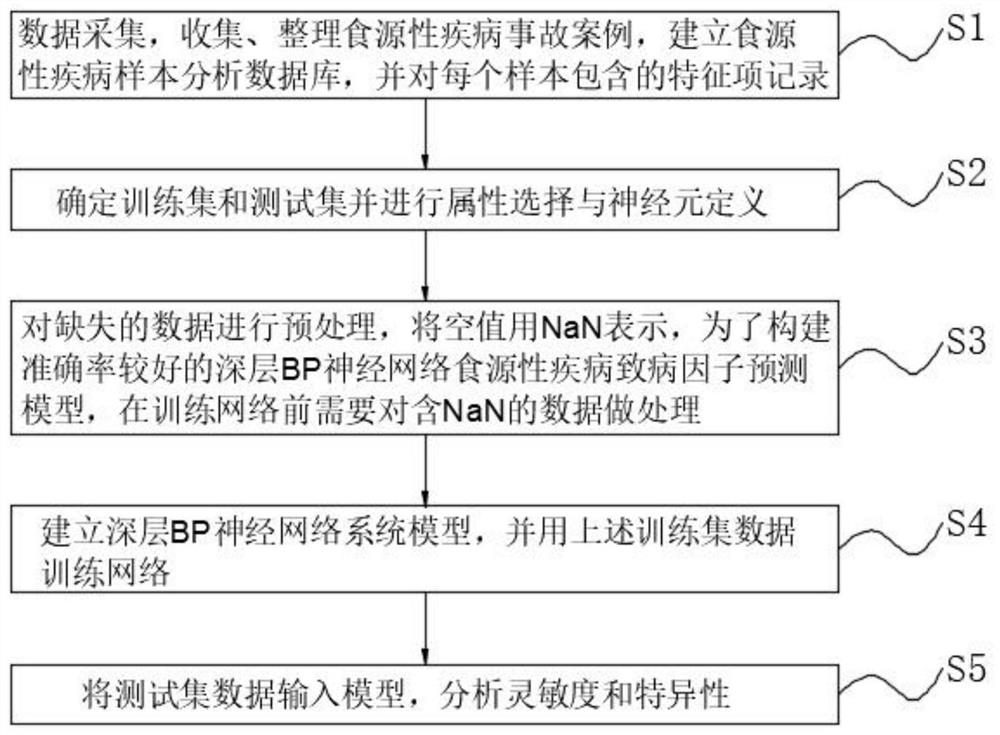
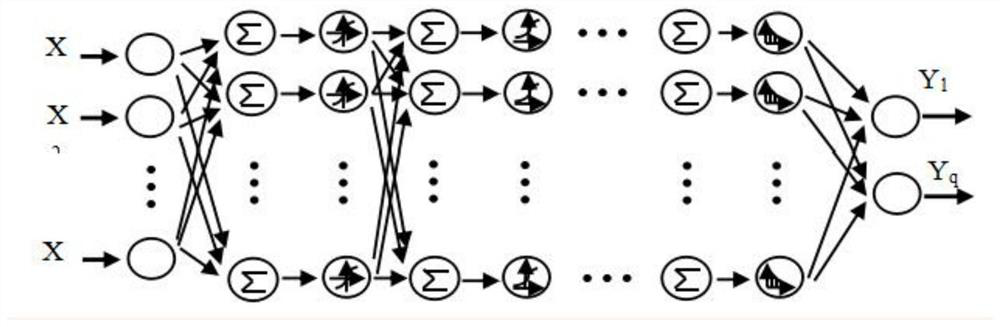
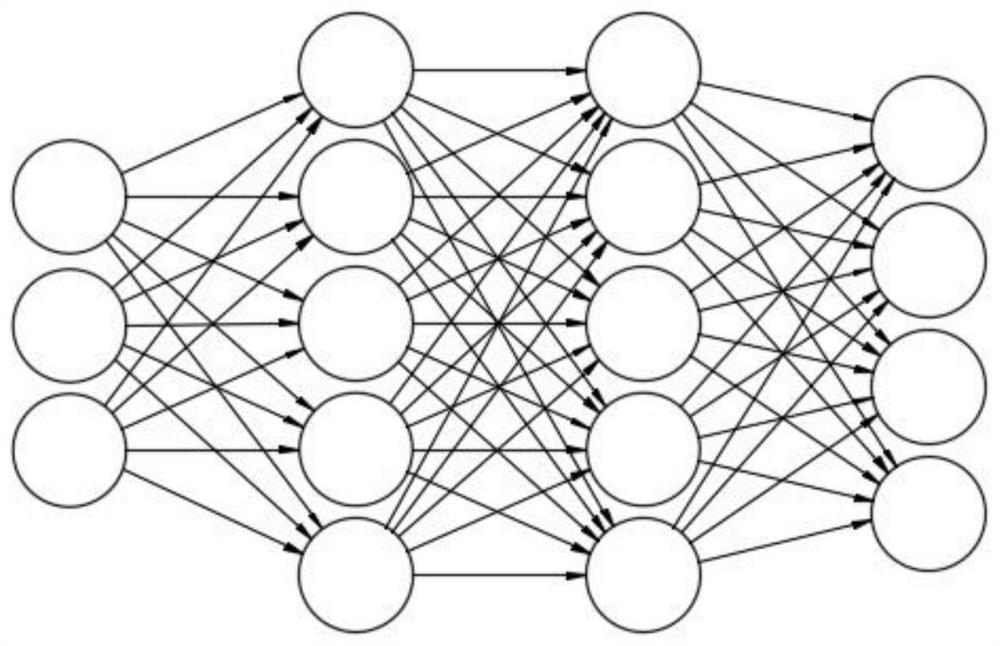
Food-borne disease pathogenic factor prediction method and system based on BP neural network
PendingCN112216399AHigh computational complexityImprove predictabilityMedical data miningEpidemiological alert systemsDiseaseMissing data
The invention discloses a food-borne disease pathogenic factor prediction method based on a BP neural network, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting data, collecting and arranging food-borne disease accident cases, building a food-borne disease sample analysis database, and recording the feature items contained in each sample; and S2, determining a training set and a test set, and performing attribute selection and neuron definition. The method has the beneficial effects that the deep BP neural network model is established, the network structure is improved by increasingthe number of hidden layers of the neural network, the network calculation complexity is optimized, the food-borne disease epidemiological pathogenic factor accurate analysis and prediction network model is established, and real-time updating and overlapping are performed through the dynamic migration network with a self-learning function; the execution efficiency and sensitivity of the discrimination model network for food-borne disease pathogenic factor prediction are improved; and missing data is preprocessed, data containing missing items is reconstructed and analyzed, and the data is made to participate in effective network calculation.
Owner:黑龙江省疾病预防控制中心
Rna-based therapeutic methods to protect animals against pathogenic bacteria and / or promote beneficial effects of symbiotic and commensal bacteria
PendingUS20210310001A1Widespread potentialEfficient expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a method to inhibit gene expression in bacteria, which is referred to here as Antibacterial Gene Silencing (AGS). In particular embodiments, the method is used to protect plants and animals against pathogenic bacteria by targeting pathogenicity factors and / or essential genes in a sequence-specific manner via small non-coding RNAs. The method can also be used to enhance beneficial effects and / or growth of symbiotic or commensal bacteria. The invention involves the exogenous delivery of small RNA entities onto bacteria, either in the form of RNA extracts or embedded into plant extracellular vesicles (EVs), so as to reduce bacterial growth, survival and / or pathogenicity. The invention also describes a method to identify in a rapid, reliable and cost-effective manner, small RNAs that possess antibacterial activity and that have the potential to be further developed as anti-infective agents. In addition, the latter method is instrumental to rapidly characterize any gene from any bacterial species.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Novel polypeptide and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20100286368A1No risk of pathogenic infection and side effectImprove securityCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesSide effectPathogenicity Factors
The present invention provides a novel polypeptide or polypeptide derivative which has no risk of infection with a pathogen or propagation of a pathogenic factor and of an undesirable side effect, and which is useful as a carrier of various biologically-active substances or apatite, as well as a process for producing the same. More particularly, the present invention provides a polypeptide comprising a peptide unit having an amino acid sequence represented by the formula: -Pro-X-Gly- (wherein X represents Pro or Hyp) and a peptide unit having an amino acid sequence represented by the formula: -Pro-Hyp(O—Y—Z)-Gly- (wherein Y represents a carbonyl group, a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon group with or without a carbonyl group, or a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon group with or without a carbonyl group, including an aromatic group, and Z represents a carboxyl group), as well as a process for producing the same.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
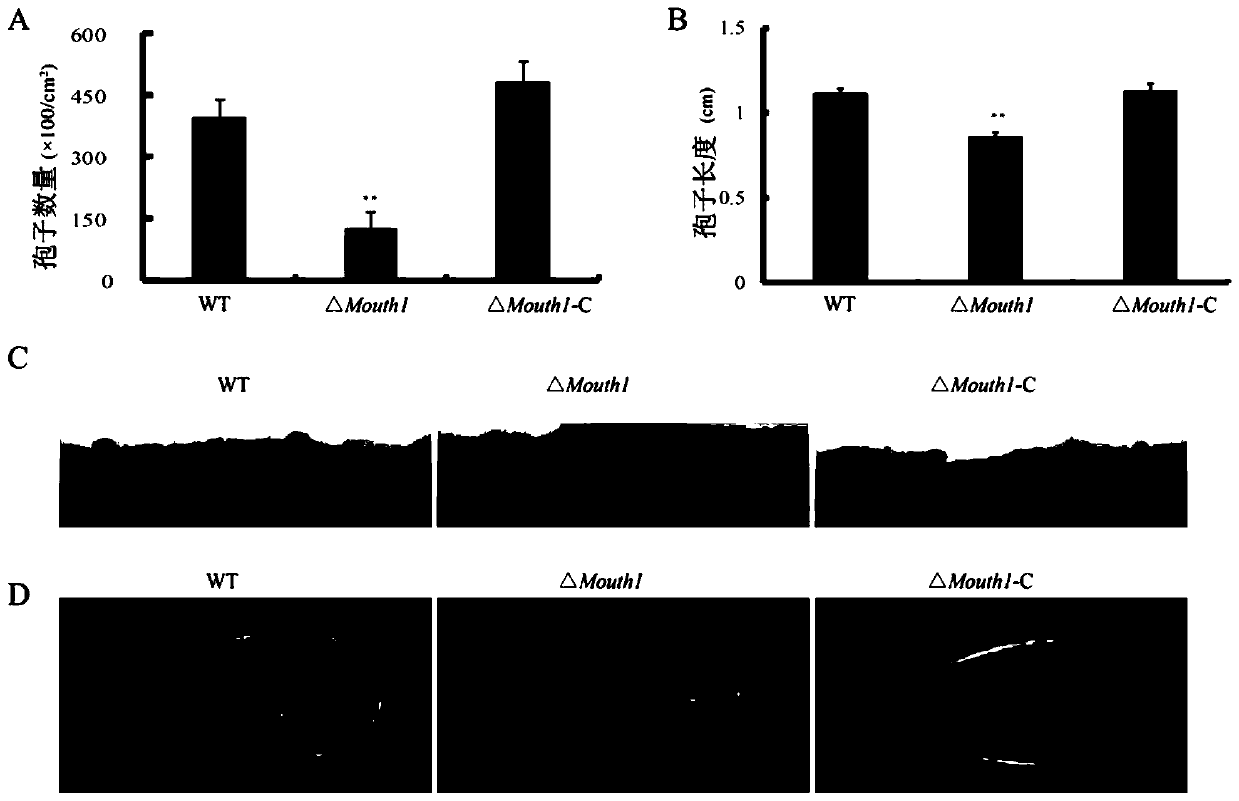
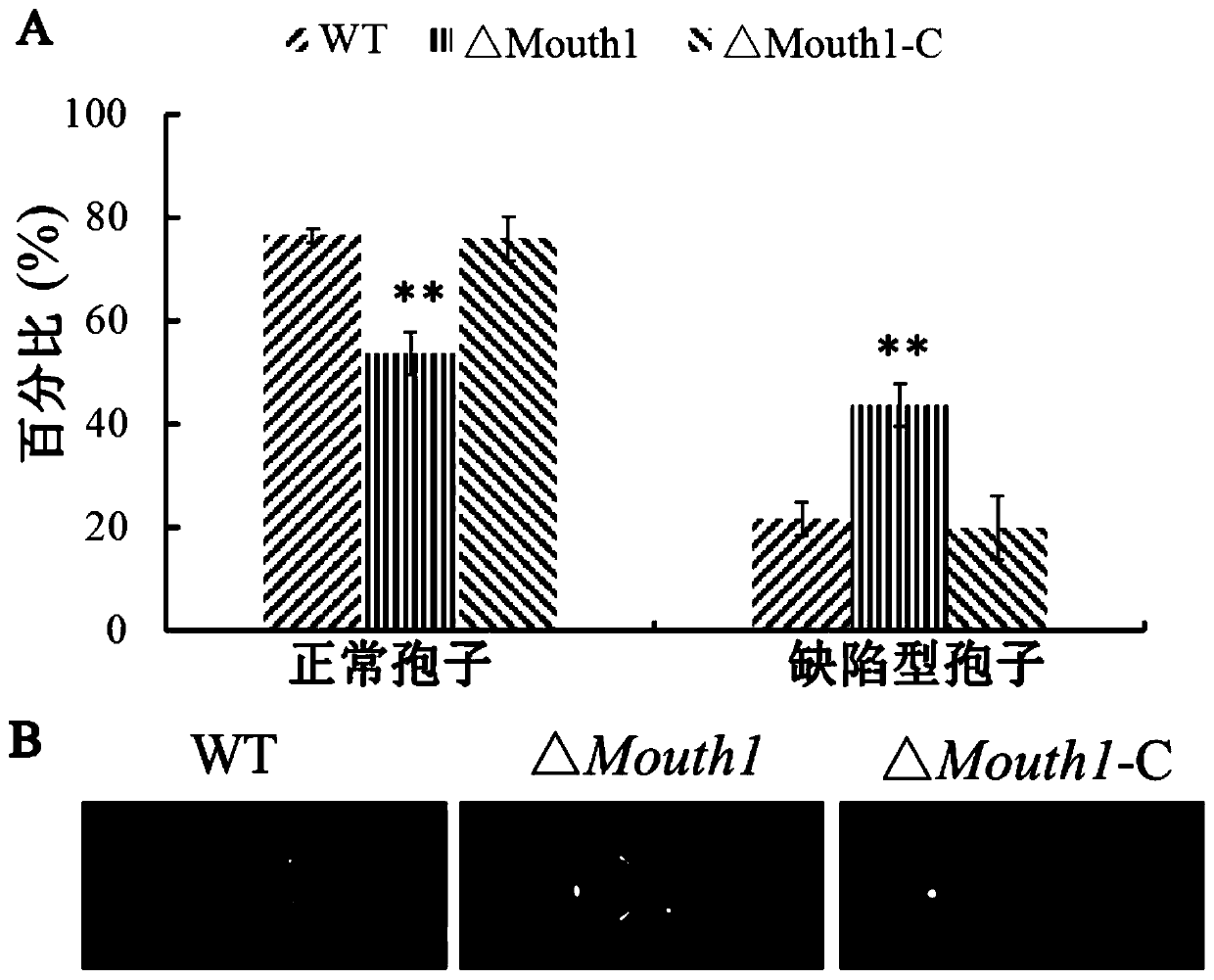
Pyricularia grisea mitophagy related pathogenic factor, gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110669115ALow sporulationReduce pathogenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesBiotechnologyAntifungal drug
The invention discloses a pyricularia grisea mitophagy related pathogenic factor, a gene and an application thereof. The gene deletion mutation caused by homologous recombination causes slow growth ofpyricularia grisea, reduction of sporulation quantity, reduction of formation of infected hyphae and great reduction of pathogenicity on susceptible rice varieties. Therefore, the most important purpose of the pathogenic factor is to design and screen a compound capable of destroying the expression and shearing of the gene and the expression of the encoded protein, or design and screen a compoundcapable of modifying an amino acid sequence of the protein by applying the achievements, thereby developing a new antifungal drug. Meanwhile, the gene family where the gene is located does not have ahomologous gene in a plant, so that an antifungal drug developed by taking the gene as a target has relatively small influence on a host plant.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
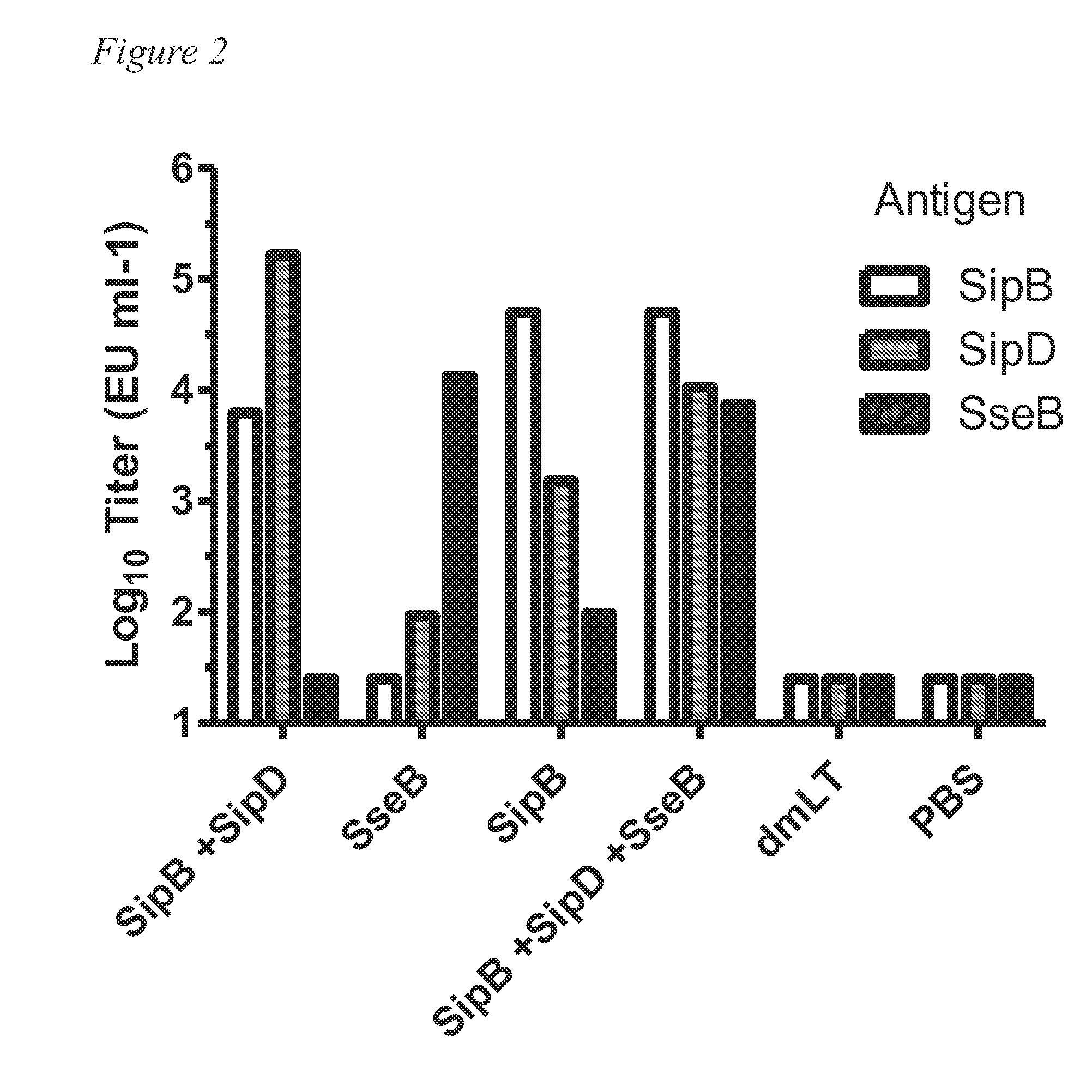
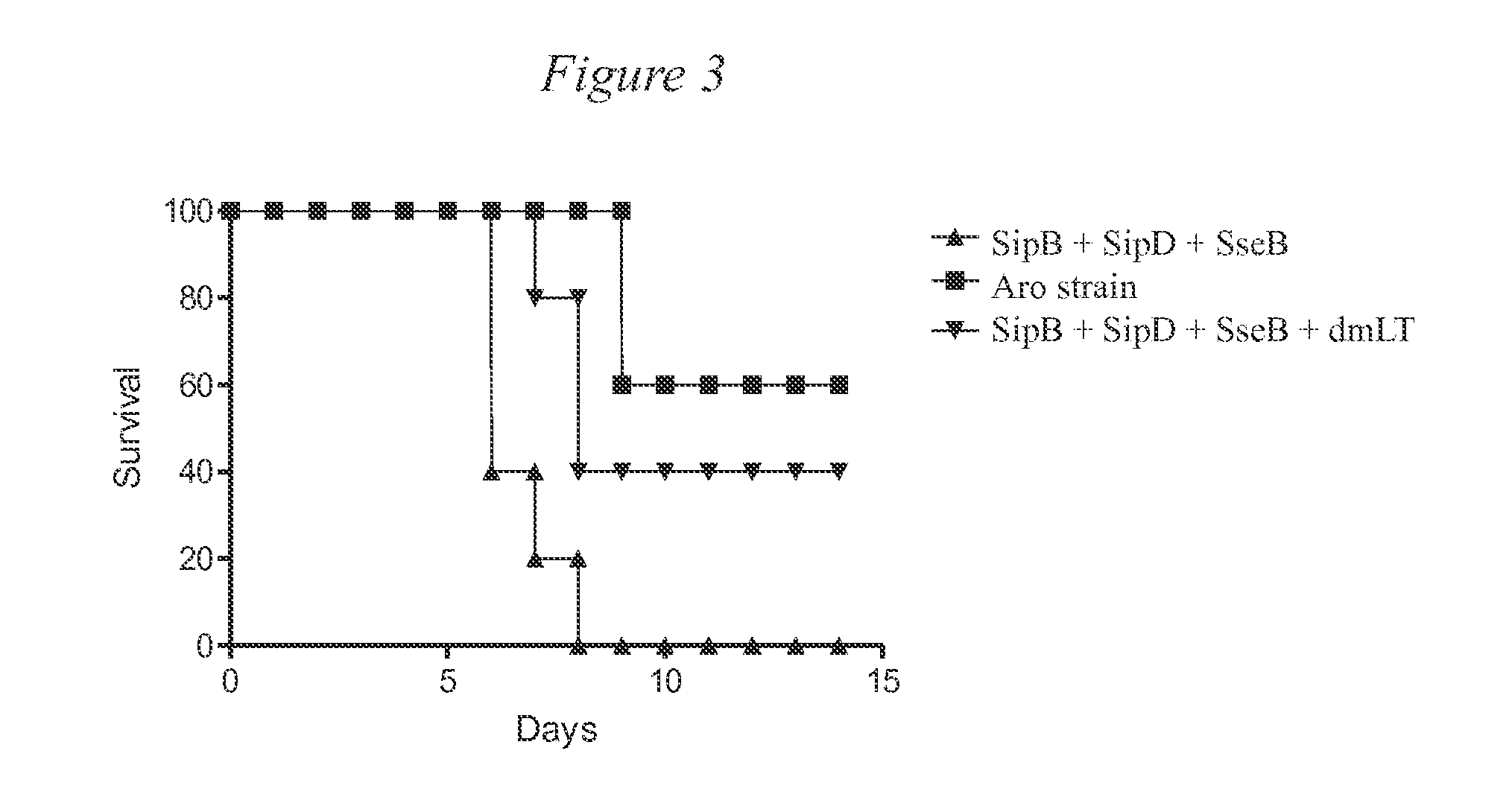
Use of the salmonella spp type iii secretion proteins as a protective vaccination
InactiveUS20150238590A1Broad protectionReduce severityBacterial antigen ingredientsVeterinary vaccineBacteroidesProtective antigen
Salmonella enteric serotype Typhimurium is a causative agent for gastroenteritis. It is the leading cause of hospitalization and death caused by a food-borne pathogen in the US. As is the case with many gram- negative pathogens, Salmonella spp. use type III secretion systems (T3SS) to deliver proteins to host cells to induce infections. The T3SS uses a molecular syringe and needle, the type III secretion apparatus (T3SA), as a conduit for the transport of the T3SS proteins from the bacteria to the host. Because proteins associated with the tip of the T3SA are extracellular, they are potential protective subunit vaccine candidates against Salmonella. These pathogens also have a T3SS that is involved with intracellular escape from the vacuole with an associated T3SA. Within this invention, we begin to show proof of concept that these proteins are protective.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Biochemical detection liquid for urine protein
InactiveCN1570633ARapid Biochemical Detection SolutionFit closelyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingPercent sodium chlorideSalicylic acid
This is a biochemistry detection liquid of urine protein comprising 9.4-10.5w / v percents sulphur salicylic acid (sulfosalicylic acid) 0.5-2w / v percents sodium chloride, adding waterless glacial acetic acid to1-3 percents, and 95 percents carbinol to 50 percents and distilled water. This invention offers biochemistry detection liquid of urine protein which the essential component is albumin and self-checking method of urine protein for the mass scoutting and checking dynamically Through the recording curve diagram in accordance with series detecting color result one can self-judge something: 1,warning signal of health and pathogenic factor; 2, forepart detectable rate acute and chronic nephrosis; 3, the synchronous tracking monitoring of curative effect acute and chronic nephrosis during the treating course. The above liquid offer the likelihood of carrying out all this function.
Owner:赵青华
Novel plasma purification system and application thereof
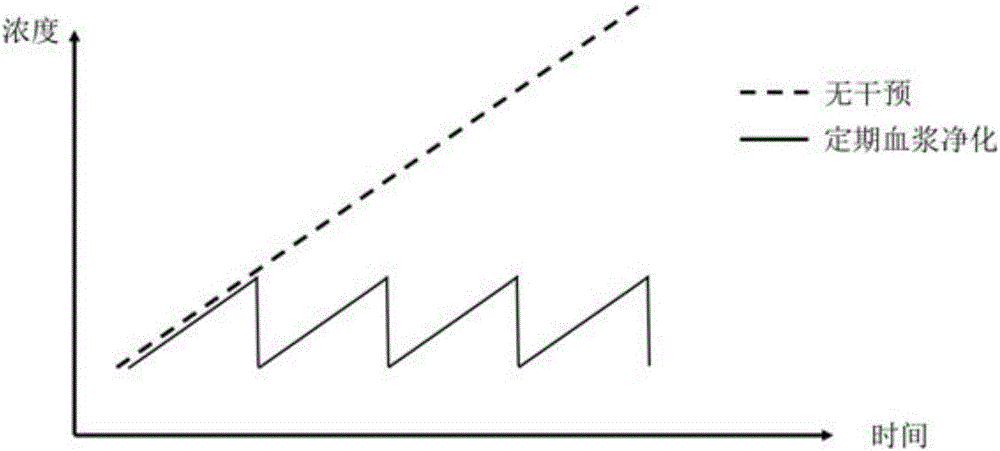
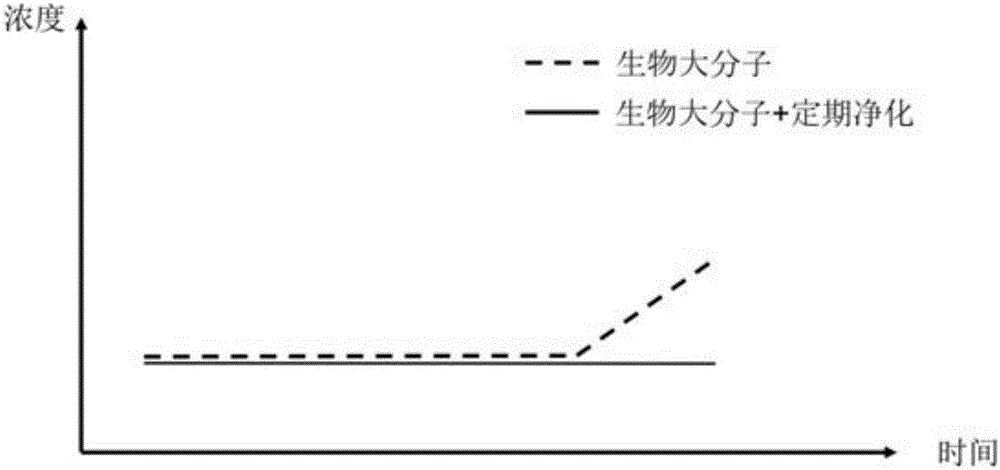
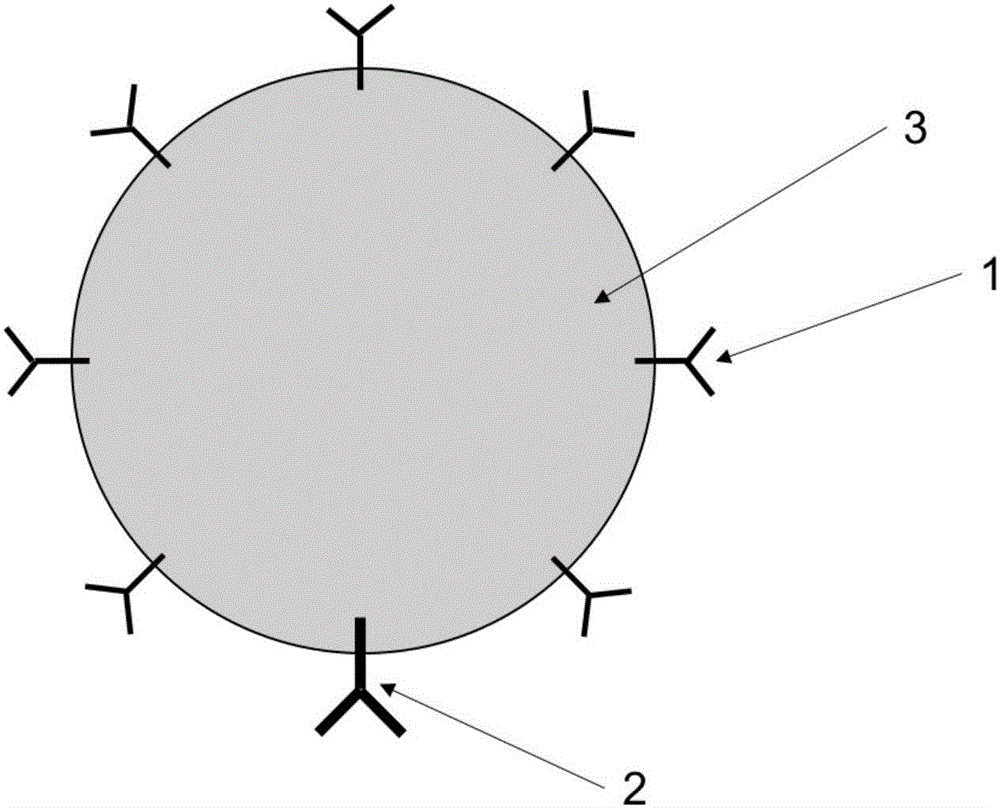
InactiveCN106166311AReduce concentrationReduce the number of purificationsOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsImmunosorbentsFree state
The invention relates to a novel plasma purification system. The novel plasma purification system comprises a specific ligand-1 (immunoadsorbent) (1), a tissue compatibility carrier (3), a ligand-2 (2) and a plasma purification device. The specific ligand-1 still keeps the immunological activity, part of the ligand-1 is embedded into the surface of the carrier, the ligand-1 can be specifically combined with specific pathogenic factors (antibodies) in blood, therefore, a large quantity of the pathogenic factors keep a combined state, and only a few of pathogenic substances are dispersed in plasma in a free state. Carrier protein and the pathogenic factors are together removed regularly by specifically combining the plasma purification device with the ligand-2. According to the novel plasma purification system, the pathogenic factors in the blood can be specifically combined to enable the pathogenic factors to be in the combined state, therefore, the free-state pathogenic factors keep a low-concentration state for a long term, the tissue involvement degree is decreased, an 'immune storm' in a body is interrupted, the plasma purification frequency of a patient is decreased, and the complication incidence rate is decreased.
Owner:张小曦
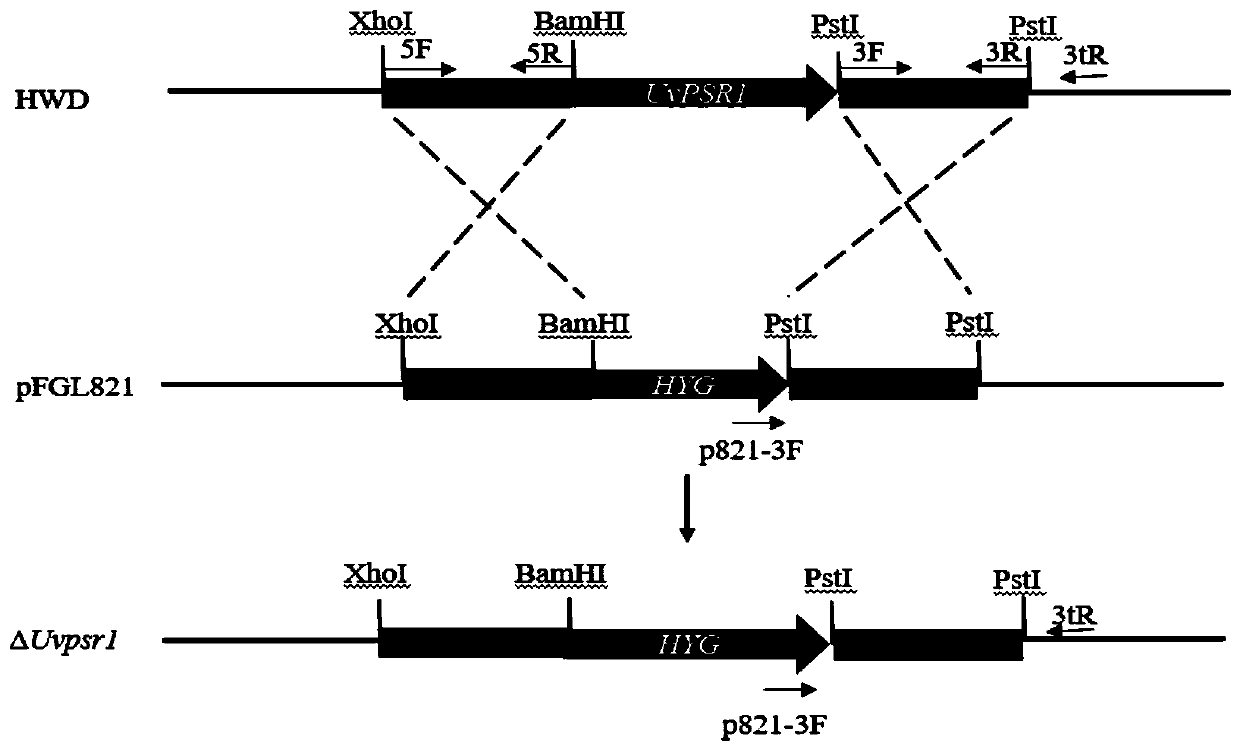
Pathogenic factor for negatively regulating ustilaginoidea virens spore production, gene and application thereof
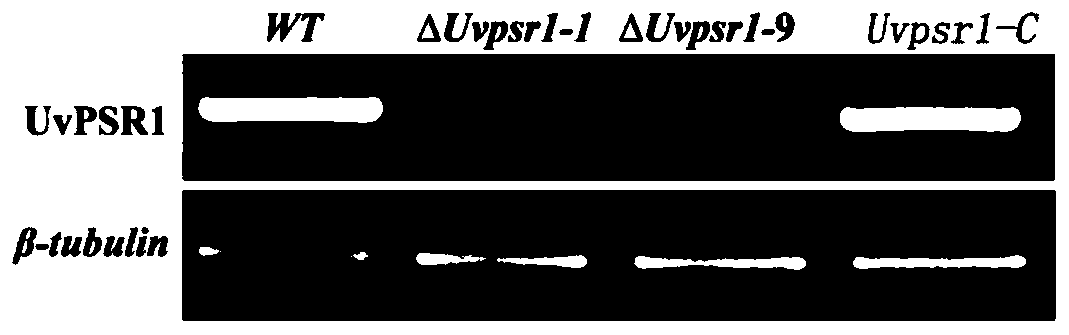
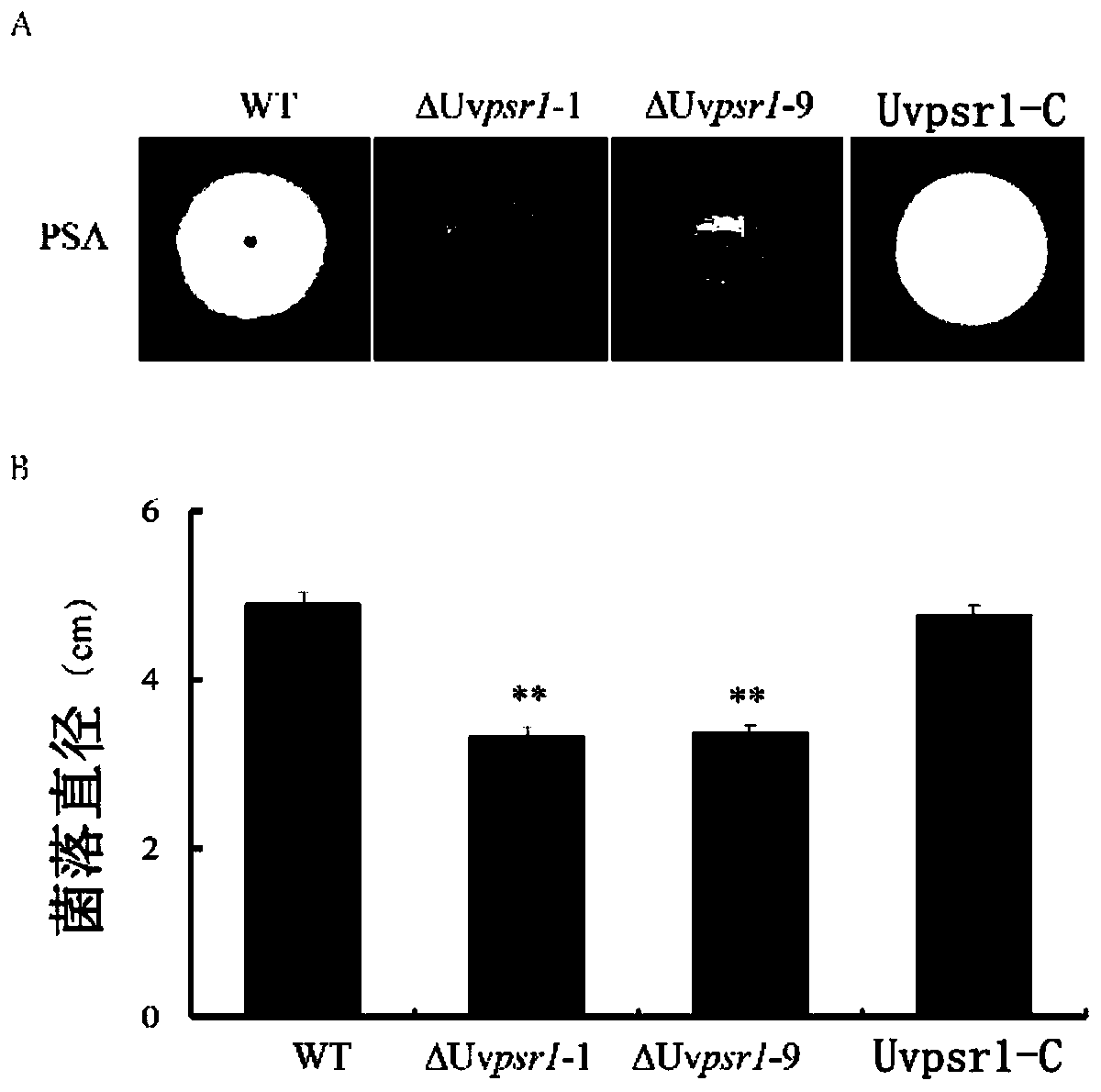
The invention discloses a pathogenic factor for negatively regulating ustilaginoidea virens spore production, a gene and an application thereof. An amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the gene sequence is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. The researches find that the fungus pathogenic gene ustilaginoidea virens UvPSR1 derived from ustilaginoidea virens plays an important role in fungus vegetative growth, spore yield, infected hypha formation and pathopoiesis process, and the gene or protein encoded by the gene can be used as a target for designing and screening antifungal drugs.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Identification of granins as the pathogenic factor of alzheimer's disease and compositions and methods for inhibiting granin aggregation and treating alzheimer's disease
ActiveUS20190314375A1Reducing and inhibiting cell toxicityInhibit aggregationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHuntingtons choreaPrevention of dementia
Compositions for inhibiting the aggregation of a granin from a non-toxic low molecular weight form to a toxic high molecular weight aggregated form and / or dissociating a high molecular weight aggregated form to a low molecular weight form are provided. Such a composition typically includes one or more active compounds or agents, which may also be referred to herein as disaggregation compounds. Using the compounds and compositions described herein, methods of i) modulating, inhibiting or preventing the interaction of granins with metal ions, ii) modulating, inhibiting, preventing the aggregation of granins or dissociating aggregated granins, iii) reducing or inhibiting cell toxicity, iv) treating or preventing dementia or Alzheimer's disease, and v) preventing or treating Parkinson's and / or Huntington's diseases are also provided.
Owner:YOO SEUNG HYUN
Rna-based biocontrol methods to protect plants against pathogenic bacteria and / or promote beneficial effects of symbiotic and commensal bacteria
PendingUS20210324394A1Reduce usageSignificant environmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologySymbiotic bacteria
The present invention pertains to the field of agriculture. The invention relates to a method to inhibit gene expression in bacteria, which is referred to here as Antibacterial Gene Silencing (AGS). In particular embodiments, the method is used to protect plants against pathogenic bacteria by targeting pathogenicity factors and / or essential genes in a sequence-specific manner via small non-coding RNAs. The method can also be used to enhance beneficial effects and / or growth of plant-associated symbiotic or commensal bacteria. The invention involves either the generation of stable transgenic plants that constitutively express antibacterial small RNAs or, alternatively, the exogenous delivery of these small RNA entities onto plants, either in the form of RNA extracts or embedded into plant extracellular vesicles (EVs), which were found to be effective in reducing bacterial pathogenicity. The invention also describes a method to identify in a rapid, reliable and cost-effective manner, small RNAs that possess antibacterial activity and that can be further exploited for RNA-based biocontrol applications to confer plant protection against pathogenic bacteria. In addition, the latter approach is instrumental to rapidly characterize any genes from any bacterial species.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
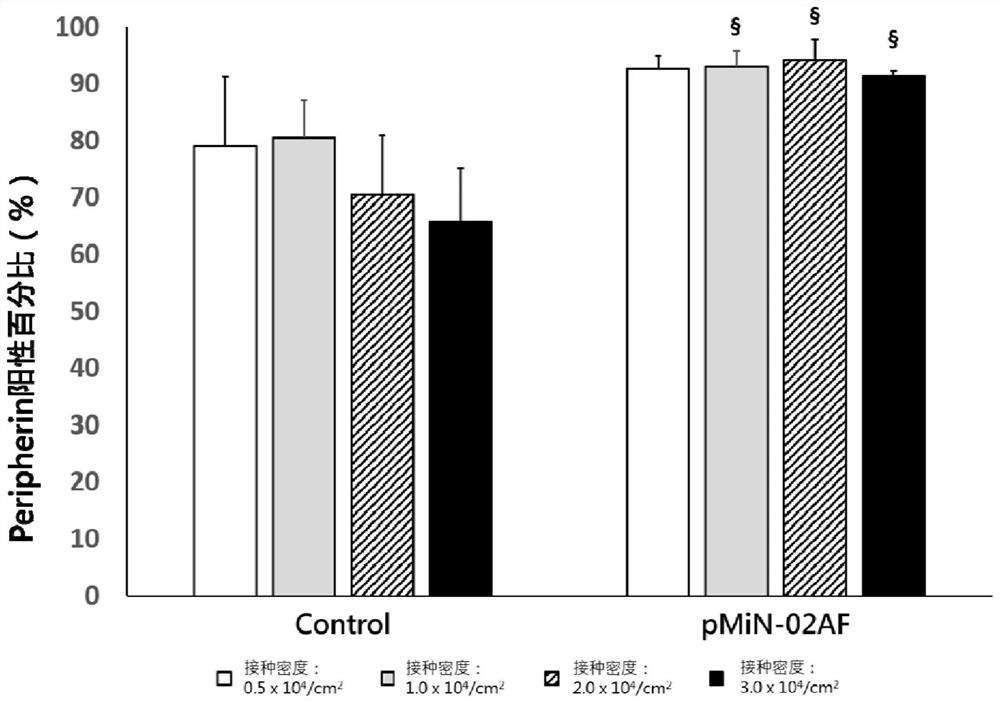
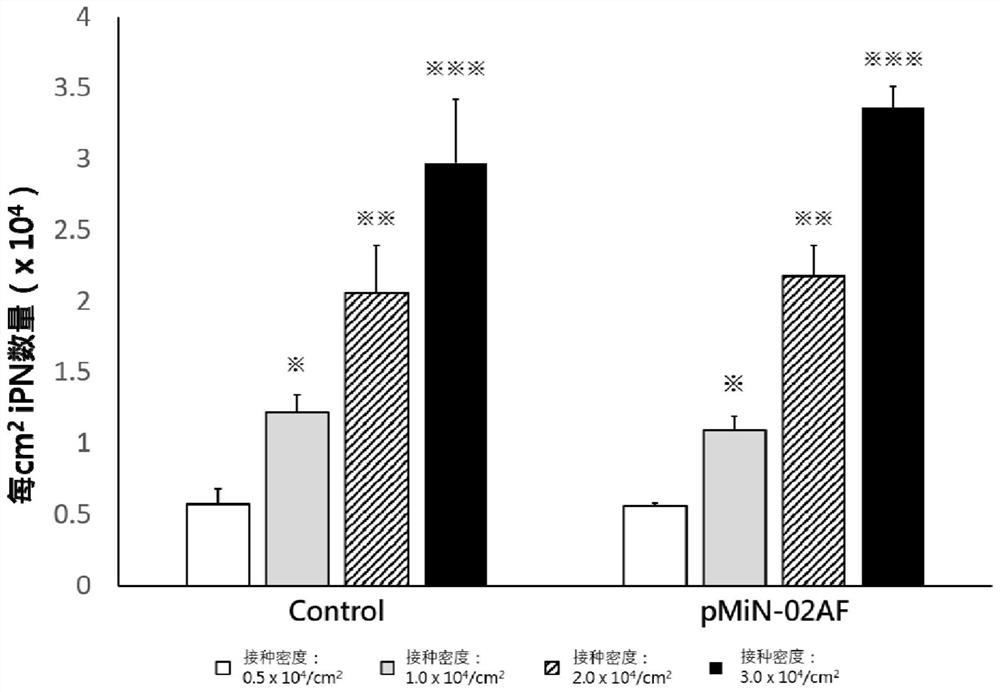
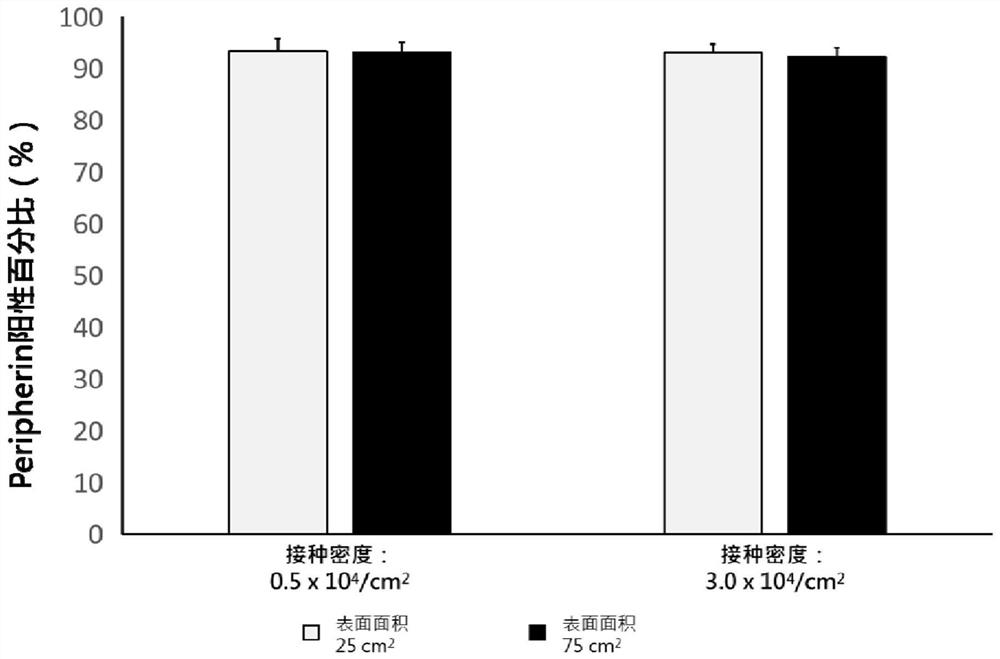
Method, culture medium and system for promoting iPSC to differentiate into peripheral neuronal cells
PendingCN113416709AReduce quality fluctuationsSimple preparation processGenetically modified cellsCulture processPeripheral neuronPeripheral nerve
The invention discloses a method, a culture medium and a system for promoting induced pluripotent stem cells to differentiate into peripheral neuronal cells, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, culturing the induced pluripotent stem cells: treating cell culture vessels with vitronectin; S2, inducing the pluripotent stem cells to differentiate into peripheral neural stem cells, using a cell culture vessel treated by recombinant laminin, and using a non-animal-origin peripheral nerve induction culture medium 01 at the same time; and S3, further differentiating the peripheral neural stem cells into peripheral neuronal cells, and culturing by using the cell culture vessel treated by recombinant laminin and a non-animal-origin peripheral nerve induction culture medium 02. Compared with an existing method, the technology is integrally optimized, high-purity peripheral neuronal cells can be prepared through two culture media, chemical components of the culture media are clear, the technology has obvious advantages in quality control of the culture media and quality control of final products, the whole technology can be free of animal origin, the pollution risk of animal-origin pathogenic factors is avoided, the method is suitable for the cell culture vessel with a large surface area, increases the yield of peripheral neuronal cells in each batch, and is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:HONG KONG REGEN MEDTECH LTD
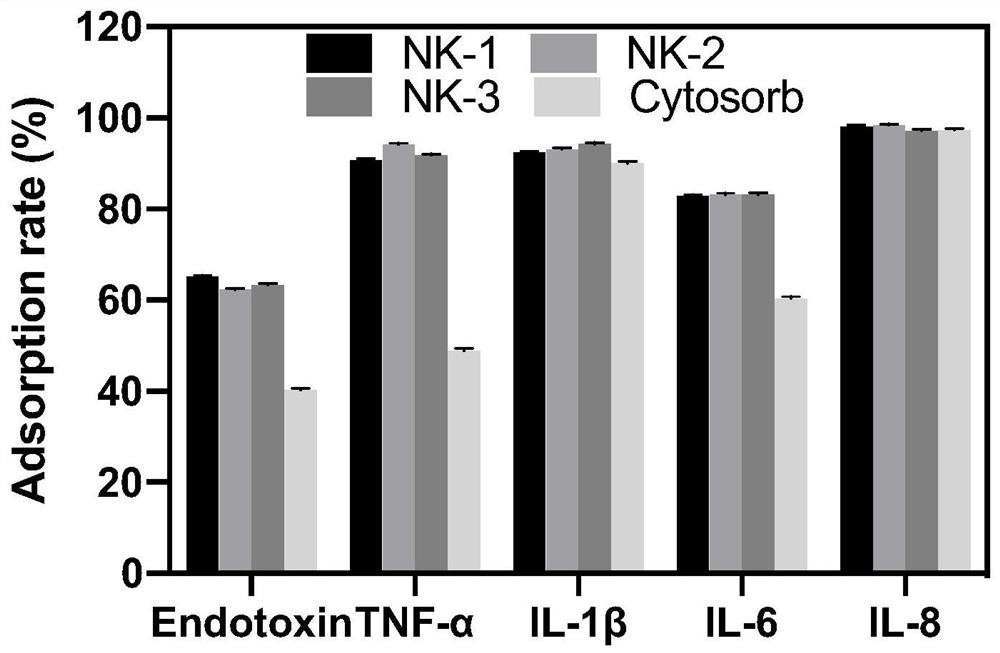
Adsorbent capable of being used for removing endotoxin and inflammatory factors in blood of sepsis patient and preparation method of adsorbent
ActiveCN113509919AImprove adsorption capacityRich in mesoporesOther chemical processesOther blood circulation devicesInflammatory factorsBenzoyl peroxide
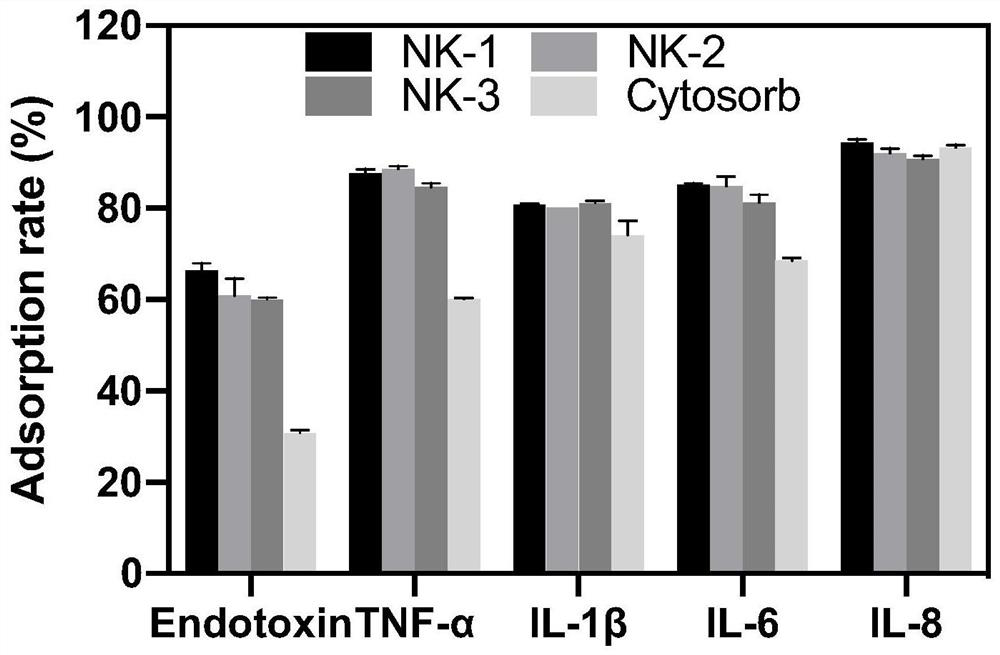
The invention discloses an adsorbent capable of being used for removing endotoxin and inflammatory factors in the blood of a sepsis patient and a preparation method of the adsorbent. The adsorbent is prepared on the basis of a carrier which is prepared on the basis of a carrier through surface activation and grafting of ligands such as polyamino amino acid or polypeptide and the like, wherein the carrier is prepared by taking nanometer calcium carbonate-styrene-divinylbenzene as a basic framework, a mixture of methylbenzene, gasoline (or liquid wax), multi-carbon alcohol and the like as a pore-foaming agent and benzoyl peroxide as an initiator. The adsorbent has a developed mesoporous structure and a high specific surface area, the synergistic effect of a nanometer material and active ligands greatly improves the removal efficiency of the adsorbent on pathogenic factors in the blood or the plasma, and animal test results show that the survival rate of a sepsis mouse can be effectively improved. The adsorbent is simple to prepare, has an efficient removal effect on endotoxin, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8 and other pathogenic factors, and is suitable for removing excessive endotoxin and pathogenic inflammatory factors in the body of a patient through blood or plasma perfusion.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Detection of anthrax pathogenicity factors
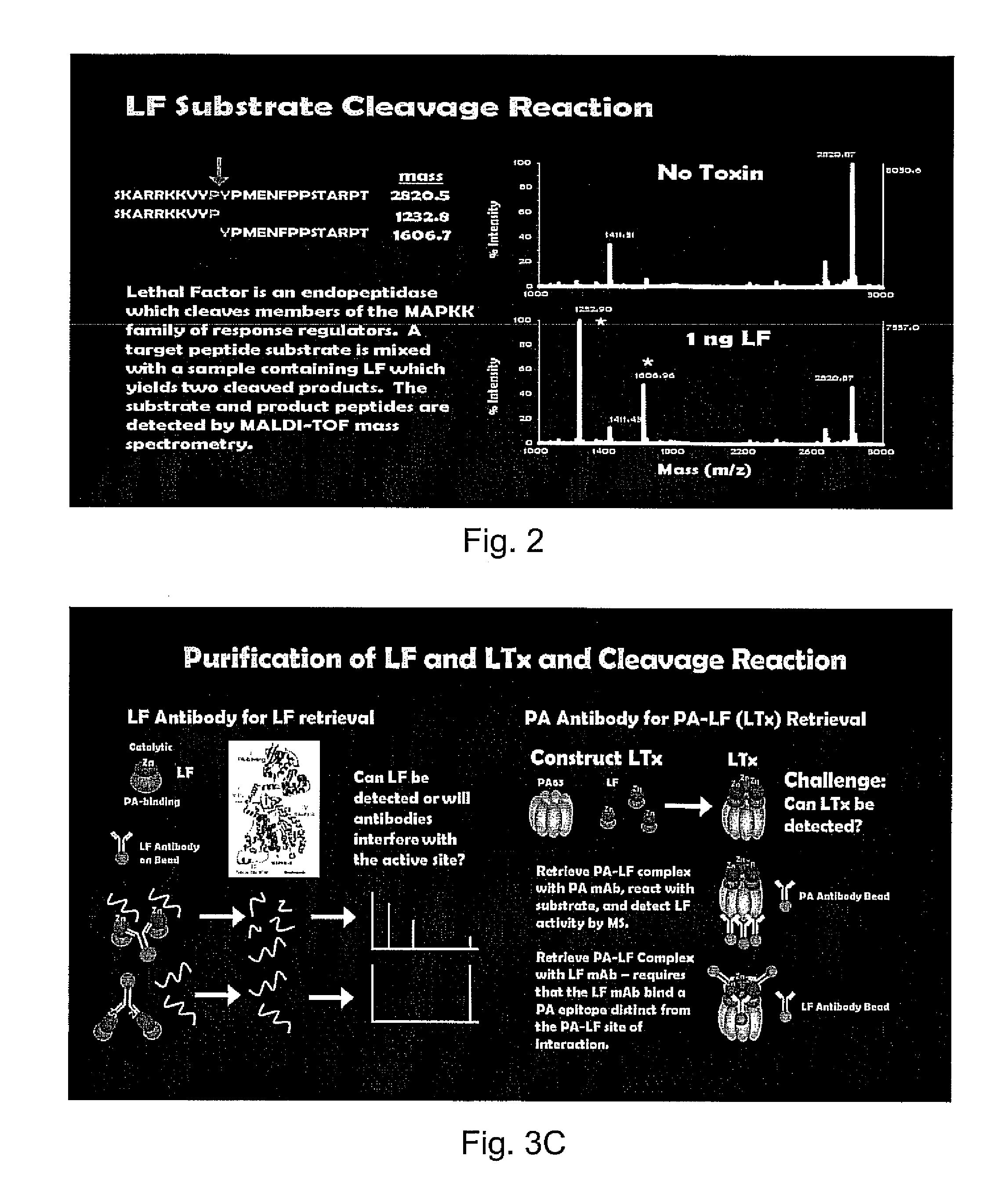
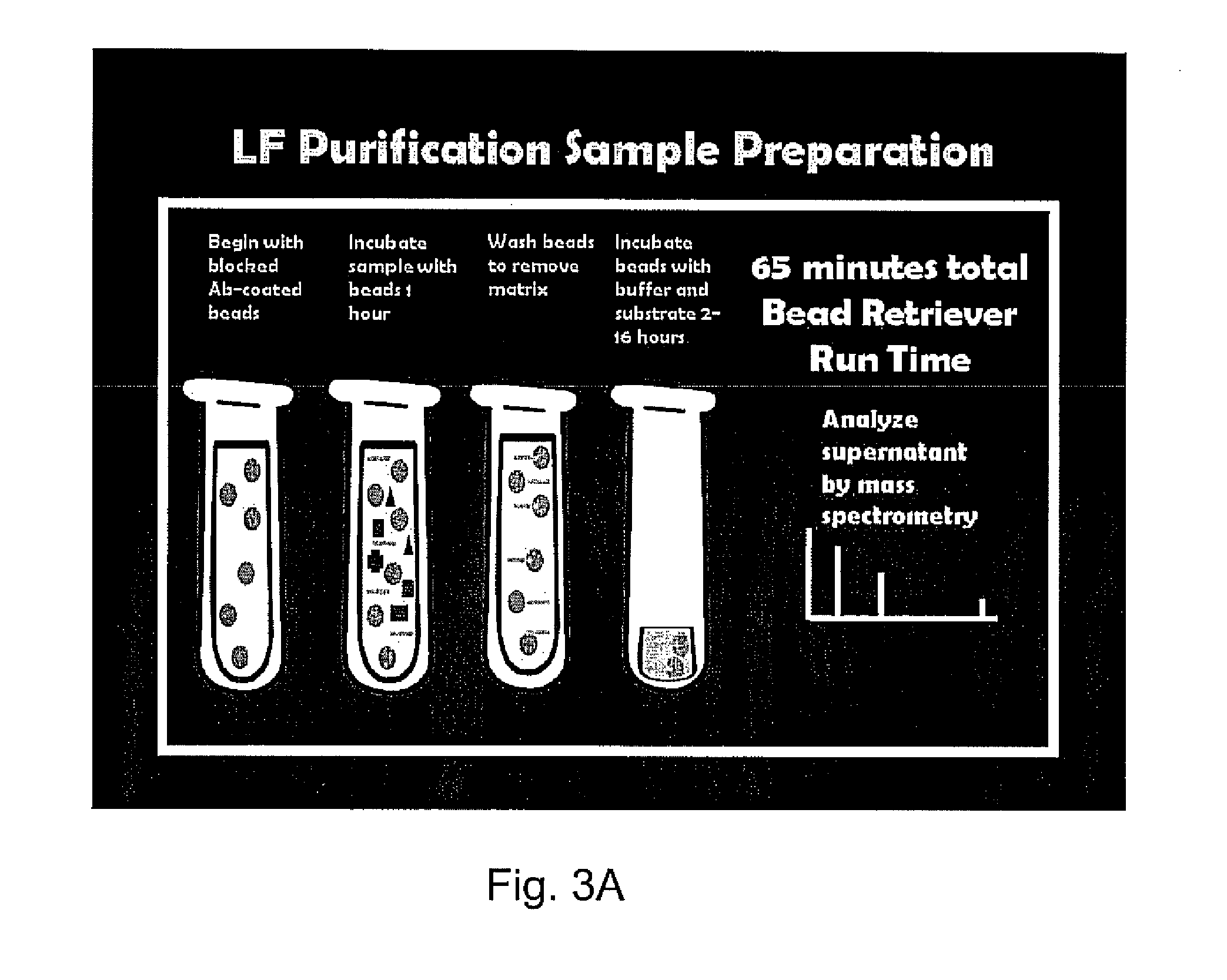
ActiveUS8663926B2Gentle and rapid separationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProper treatmentRapid identification
One major problem in diagnosis methods presently available for anthrax is that these methods require several days to produce a result. The only existing treatment for anthrax requires administration soon after infection at a time when patients are exhibiting only mild flu-like symptoms. Thus, a patient may be days beyond the time when treatment would be effective by the time a diagnosis is made. The present invention reduces diagnosis time to as little as four hours providing same day identification of anthrax radically increasing the odds of delivering proper treatment and patient recovery. The rapid identification of anthrax lethal factor activity exhibited by the instant invention is also amenable to in vivo screening protocols for the discovery and development of anthrax vaccines and lethal factor inhibitors. The instant invention isolates and concentrates lethal factor and lethal toxin from nearly any biological sample. By capitalizing on the endopeptidase activity of lethal factor the present invention amplifies output signals producing reliable detection of picomolar concentrations of lethal factor. The instant invention involves novel purification and detection techniques and substrates for rapid, reproducible, and quantitative measurements of anthrax lethal factor in biological samples.
Owner:CDC THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES CENTS FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Blood purification adsorbent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111686704AHigh mechanical strengthImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesOther blood circulation devicesPorous tantalumPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological materials, and particularly relates to a blood purification adsorbent and a preparation method and application thereof. The blood purification adsorbent comprises an inner core with mesopores and macropores, a first outer modification layer distributed in the mesopores of the inner core, and a second outer modification layer distributed inthe macropores of the inner core, wherein the inner core comprises a porous carbon-based material and a porous titanium-based material, the first outer modification layer comprises polyvinyl alcohol,porous zinc oxide and porous tantalum oxide, the second outer modification layer comprises polyethylene glycol and medical macromolecules containing hydroxyl groups, and the ratio of the number of the hydroxyl groups to the number of carbon atoms in the medical macromolecules is not less than 1: 5. The blood purification adsorbent has good mechanical strength, adsorption performance and biocompatibility, and can adsorb pathogenic factors in blood or plasma.
Owner:苏州仝康医疗科技有限公司
Targeted treating medicine for cardiac microangiopathy caused by Coxsackie B3 virus infection
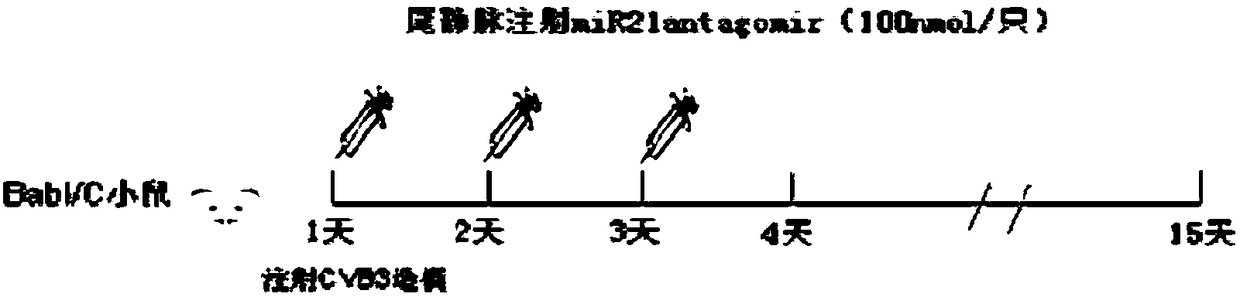
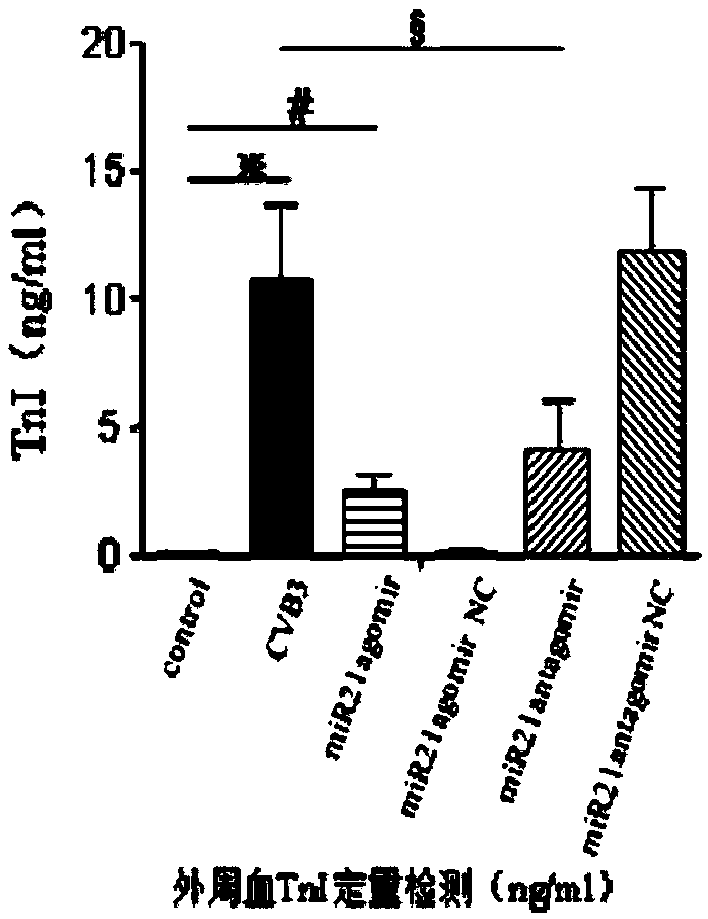
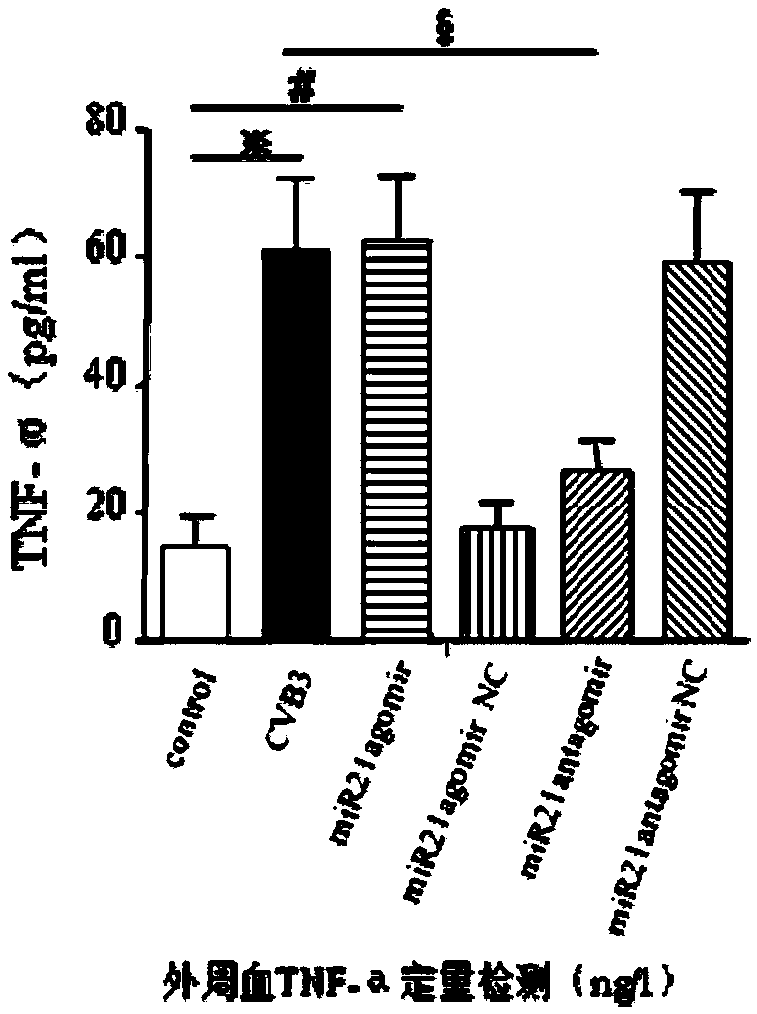
InactiveCN109498642AAlleviate myocardial tissue lesionsReduce lesionsOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPhysiological functionMyocardial tissue
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedicines, and particularly discloses a targeted treating medicine for cardiac microangiopathy caused by Coxsackie B3 virus infection. The targeted treating medicine is miRNA21antagomir, and the nucleotide sequence is 5'-UCAACAUCAGUCUGAUAAGCUA-3'. The targeted treating medicine is an inhibitor specifically targeting highly-expressed miRNA21 in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells, specifically targets highly-expressed miRNA21 molecules, weakens the gene silencing effect of endogenous miRNA21, and inhibits apoptosis of the vascular endothelial cells to maintain the normal physiological functions of microvessels by increasing the expression quantity of target gene protein and regulating related signaling pathways. The targeted treating medicine can be used for treating the cardiac microangiopathy caused by the Coxsackie B3 virus infection, blocks migration of pathogenic factors to a target organ, alleviates myocardial tissue lesions,and is a novel treating medicine for viral myocarditis intervention.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
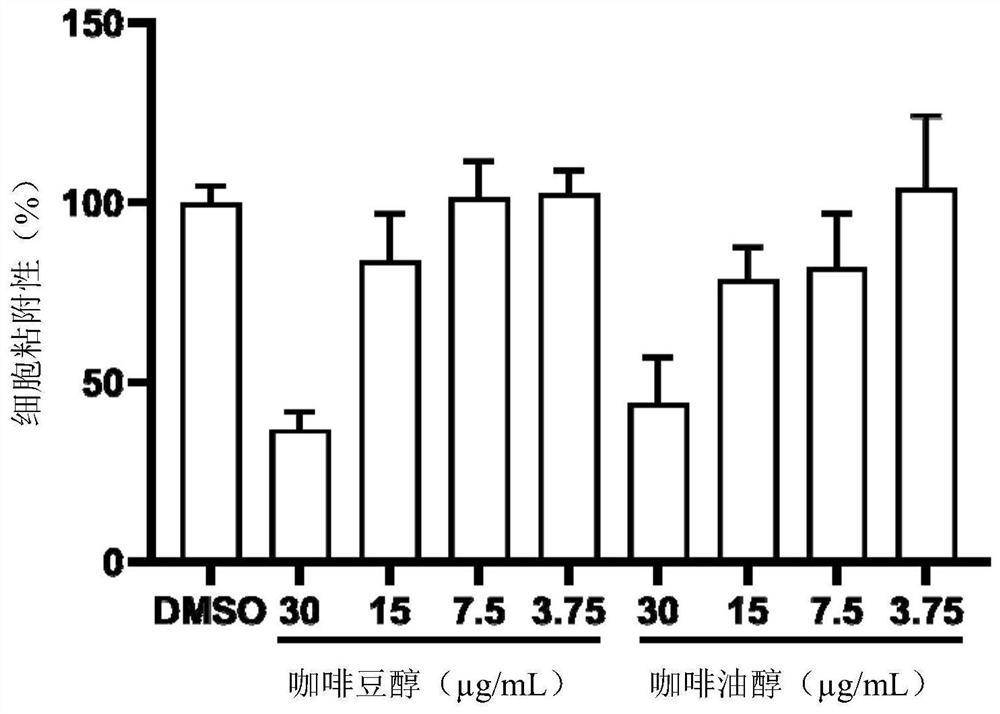
Application of caffeol or caffeol derivative in preparation of anti-candida albicans drugs or anti-candida albicans daily necessities
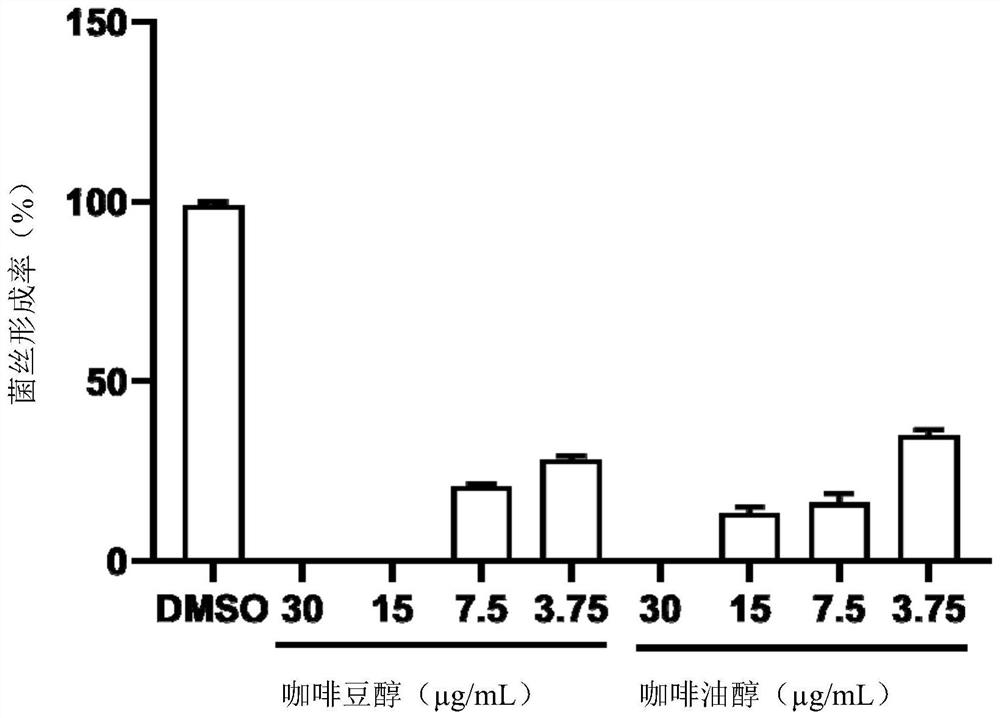
ActiveCN113648303ALower resistanceSlight inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsBiotechnologyCafestol
The invention discloses application of caffeol or a caffeol derivative in preparation of anti-candida albicans drugs or anti-candida albicans daily necessities. Candida albicans is taken as a test object, a compound which is efficient, low in toxicity and not prone to generating drug resistance is screened, and it is found that the caffeol or the caffeol derivative has a good inhibition effect on adhesion, hypha formation, biofilm formation and pathogenicity of the Candida albicans. The bean alcohol has a good inhibition effect on mouse oral cavity infection of a candida albicans strain SC5314, and the compound is non-toxic to human cells; the low-concentration kahweol and the low-concentration cafestol have no inhibition effect on cell growth of the candida albicans, which indicates that the effect of the caffeol or the caffeol derivative on the candida albicans does not depend on killing candida albicans cells, but inhibits the expression of pathogenic factors of the candida albicans, so that the caffeol or the caffeol derivative is not easy to generate drug resistance. The caffeol or the caffeol derivative has a good application prospect in the development of novel antifungal drugs, especially in the development of anti-candida albicans drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A method, device and application of medical examination data completion based on side information
The invention discloses a physical examination data supplementing method based on edge information. The method comprises the steps of (1), constructing and supplementing a physical examination-diseasematrix, a pathogenic factor-disease matrix, a pathogenic factor-physical examination matrix according to the edge information; (2), establishing coding-decoding networks D2F Net, D2C Net and F2C Netbetween two random matrixes; (3), performed combined training on the D2F Net, D2C Net and F2C Net, wherein after training is finished, the pathogenic factor-physical examination matrix is supplemented; and (4), inputting the to-be-supplemented physical examination-disease matrix into the D2F Net, D2C Net, and by means of the supplemented pathogenic factor-disease matrix, the pathogenic factor-physical examination matrix and the F2C Net, supplementing the physical examination-disease matrix through calculation. The invention further discloses a physical examination data supplementing device based on the edge information, wherein the physical examination data and the disease result can be supplemented according to existing information.
Owner:SHANDONG IND TECH RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com