Metal selective melting forming method based on laser spot patterning output
A technology of laser spot and selective melting, which is applied in the field of metal laser processing, can solve the problems of production efficiency, workpiece layer quality, isotropy, and workpiece defects, etc., to avoid anisotropy on the metal workpiece layer, and to avoid Anisotropy, the effect of improving molding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
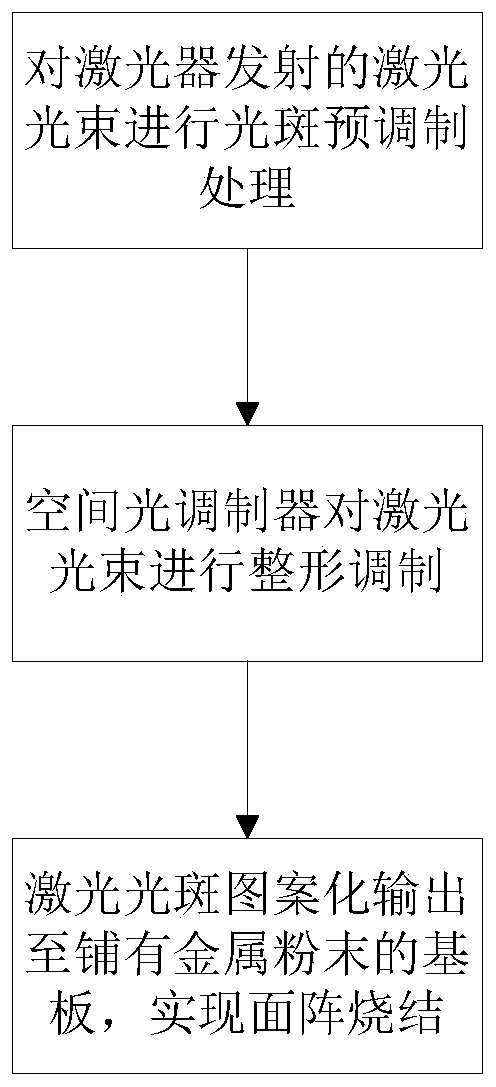
[0039] This embodiment proposes a metal selective melting forming method based on the patterned output of the laser spot, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1: Perform spot pre-modulation on the laser beam to obtain the initial seed light and enter it into the spatial light modulator for processing.
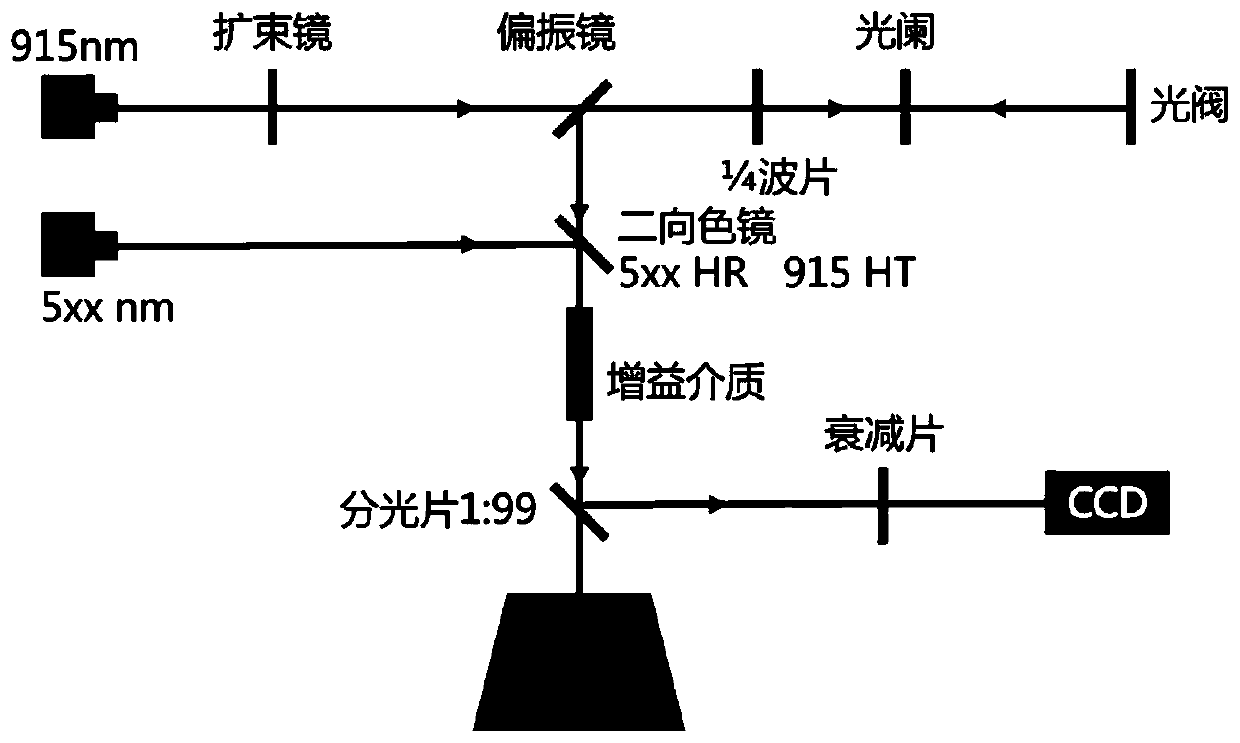
[0041] In this embodiment: First, build as figure 2 The laser light path and equipment platform are shown, and then the terminal light path output is directed to the substrate covered with metal powder, and the beam direction is perpendicular to the substrate. The laser light path and equipment platform in this embodiment specifically include: a laser, a beam expander, a polarizer, a quarter wave plate, an aperture, and a spatial light modulator (the spatial light modulator in this embodiment adopts but is not limited to Light valve); It also includes a substrate covered with metal powder, as well as attenuators and CCDs for measuring op...
Embodiment 2
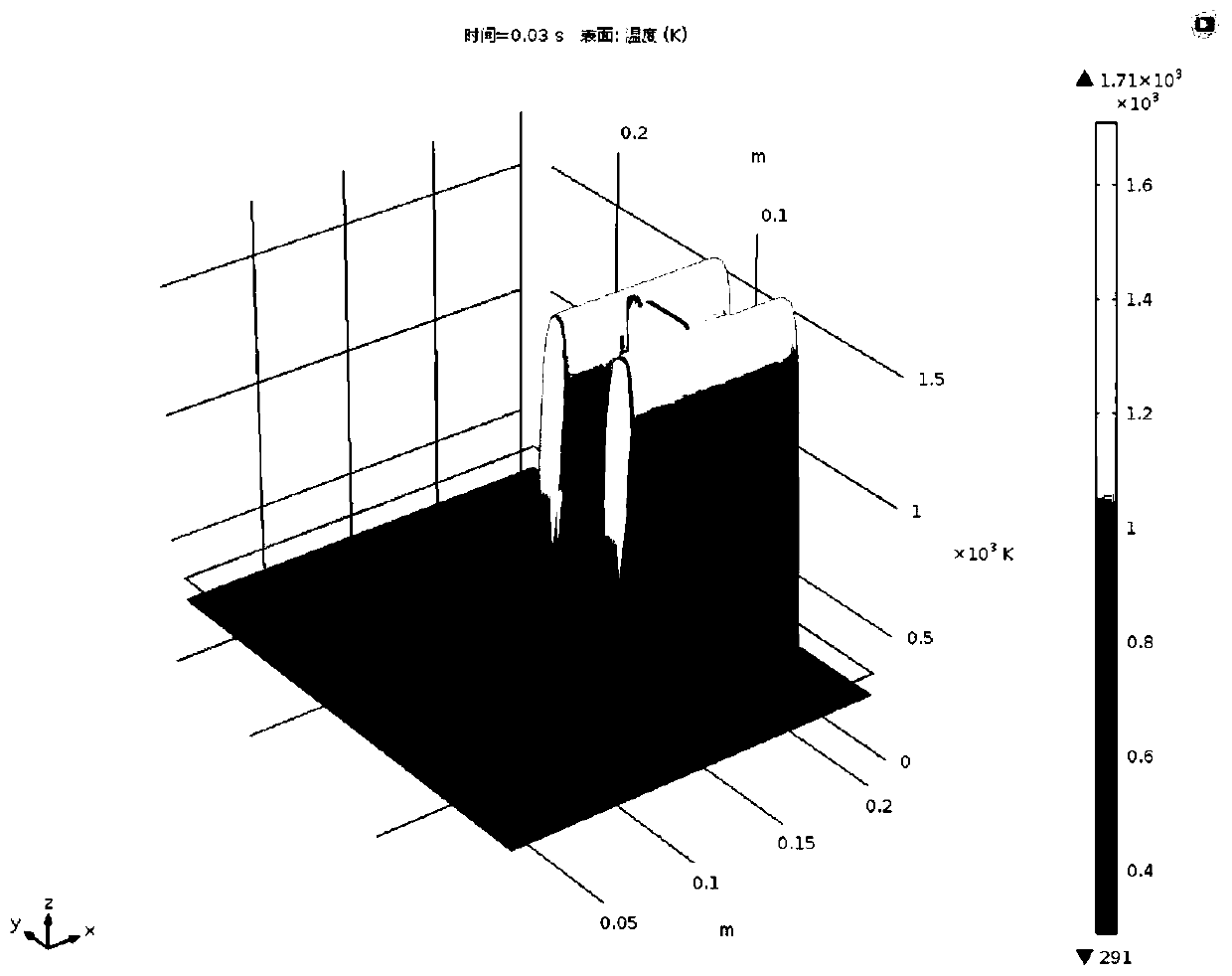
[0057] In this embodiment, the method proposed in the above embodiment 1 is used to simulate the forming temperature field of 6061 material, and obtain the following image 3 The simulation renderings shown are by image 3 It can be seen that when the laser spot is a planar patterned spot, the exposure and sintering of the area to be processed is completed instantaneously. The instantaneous time in the figure is 0.03 seconds, and the highest temperature in the exposed area can reach within 0.03s of exposure time. At 1700K, the highest uniform and stable temperature area is about 1200K. This temperature has reached the melting point of aluminum alloy and can be sintered. The sintering effect (such as under-burning, over-burning, moderate) is determined by the exposure time and exposure power. The effect diagram shows that the temperature field generated by surface exposure is more uniform, avoiding the multiple molten pools generated by point scanning exposure and sintering and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com