A kind of genetically engineered polypeptide nano hydrogel loaded with hydrophobic drugs and hydrophilic drugs and its preparation method
A nano-hydrogel, hydrophilic drug technology, applied in the field of genetically engineered polypeptide nano-hydrogel and its preparation, can solve the problems of tumor drug resistance, tissue and organ damage, lack of targeting, etc. Drug properties, long residence time, and the effect of improving loading rate and encapsulation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] PC 10 Preparation of ARGD: Use restriction endonucleases BamHI, NheI and SpeI to cut out the PC containing the target gene fragment 10 A and RGD fragments, and then use T4 DNA ligase to recombine the target gene fragments to obtain PC 10 The ARGD fragment is introduced into Escherichia coli for expression, then denatured and lysed with urea, centrifuged to obtain the protein, purified with a nickel column, dialyzed and freeze-dried to obtain the spongy protein.
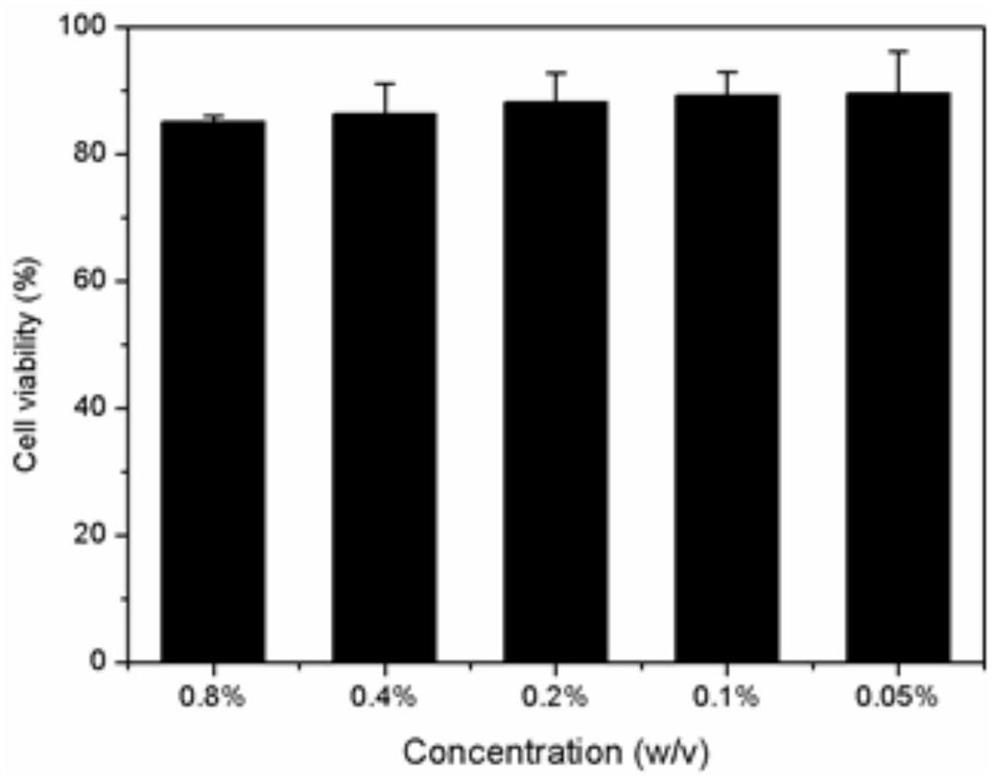
[0031] to PC 10 The biosafety of ARGD is verified: PCs with different weights are weighed separately 10 The ARGD polypeptide is dissolved in 1 milliliter of cell culture medium DMEM, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 7-8 to obtain cell culture fluids containing nano hydrogels with different concentrations. After incubating Hela with the hydrogel at different concentrations for 24 hours, the cell survival rate was examined by MTT method, and the results were as follows: figure 1 As shown: the cells s...
Embodiment 2
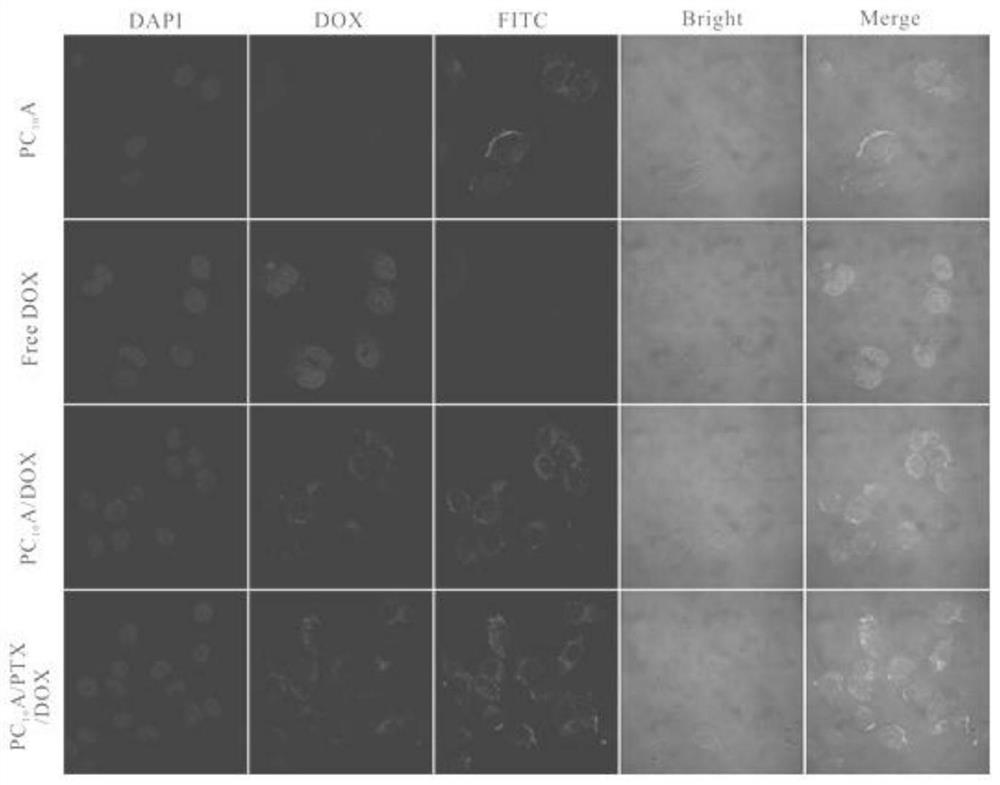
[0034] PC 10 Application of ARGD / PTX / DOX·HCL nanohydrogels: PC 10 ARGD polypeptide, DOX, PC 10 ARGD polypeptide / DOX, PC 10 ARGD polypeptide / PTX / DOX·HCL was dissolved in DMMEM cell culture medium and co-incubated with Hela cells for 4 hours, the results were as follows figure 2 Shown: It can be seen under the confocal microscope that individual DOX enters the cytoplasm and nucleus through molecular diffusion, while PC 10 ARGD polypeptide / DOX·HCL nano hydrogel and PC 10 ARGD polypeptide / PTX / DOX·HCL nanohydrogels only entered the cytoplasm, indicating that PC 10 ARGD polypeptide / DOX·HCL nano hydrogel and PC 10 ARGD polypeptide / PTX / DOX·HCL nano hydrogel entered Hela cells through phagocytosis.
Embodiment 3
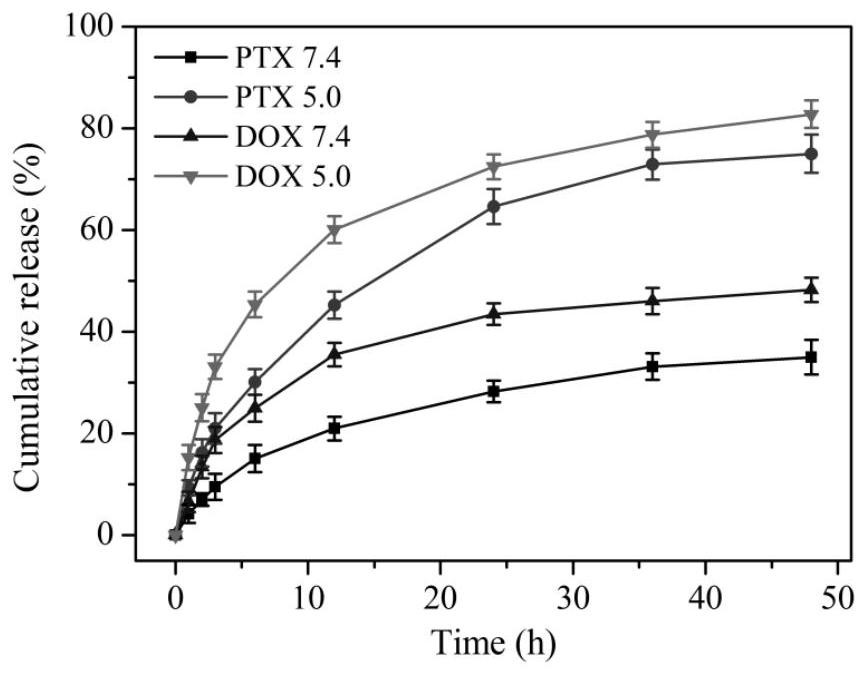
[0036] PC 10 Slow drug release from ARGD / PTX / DOX·HCL nanohydrogels: mixing PC 10ARGD / PTX / DOX·HCL nanohydrogels were respectively placed in buffers of different pH (pH 7.4 PBS phosphate buffer, pH 5.0 acetate buffer). The release behaviors of DOX·HCL and PTX in different pH buffers were detected by UV absorption and HPLC analysis. It can be seen from the experimental results that the release of DOX·HCL and PTX in the acetate buffer at pH 5.0 is faster than in the neutral pH 7.4 PBS phosphate buffer, and the tumor environment is also acidic, which is conducive to the release of DOX·HCL and PTX in acidic tumors. The release in the environment, and the drug release time lasts for more than 48 hours, achieving an obvious slow release effect.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| encapsulation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| encapsulation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com