Micro-fluidic chip and whole blood separation method based on micro-fluidic chip
A microfluidic chip and bifurcation technology, applied in the field of microfluidics, can solve the problems of high viscosity, difficult to separate and miniaturize the device, and achieve the effect of huge application potential.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
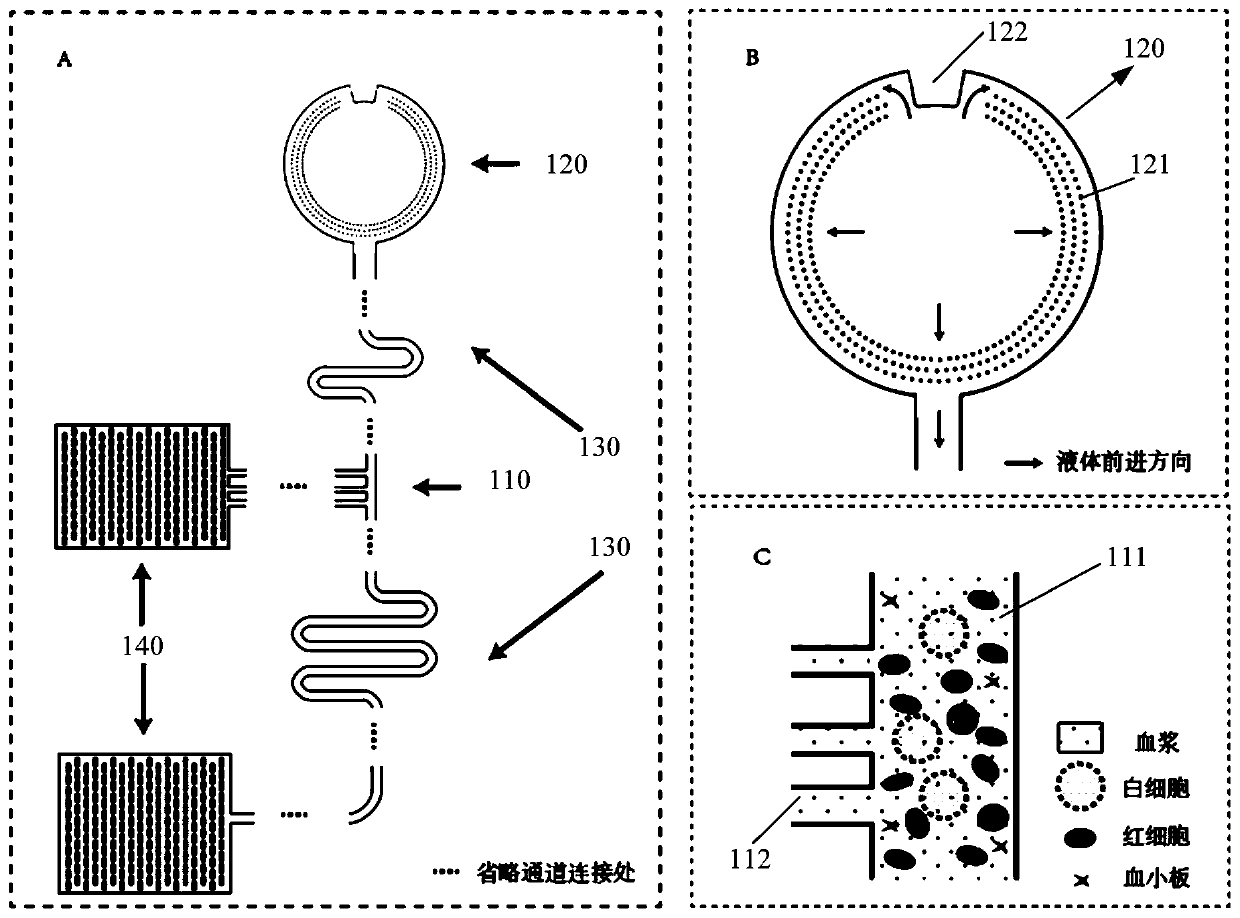
[0032] see figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of a microfluidic chip provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, including: at least one bifurcated branch unit 110, any one of the bifurcated branch units 110 includes a main channel 111 and is extended from the main channel 111 When the whole blood flows through the bifurcated branch channel 112, the blood cells are subjected to asymmetric shear force on both sides, and will choose the main channel 111 with high flow rate and small flow resistance. The channel continues to move forward, and part of the blood plasma enters the bifurcated branch channel 112 .
[0033] The specific structure of each component and the way of connecting with each other will be described in detail below.
[0034] see figure 1 Middle C and figure 2 A schematic structural view and a partially enlarged view of any one of the bifurcated branch units 110 provided in this embodiment.
[0035] In this embodiment, the bifurcated branch ...
Embodiment 2
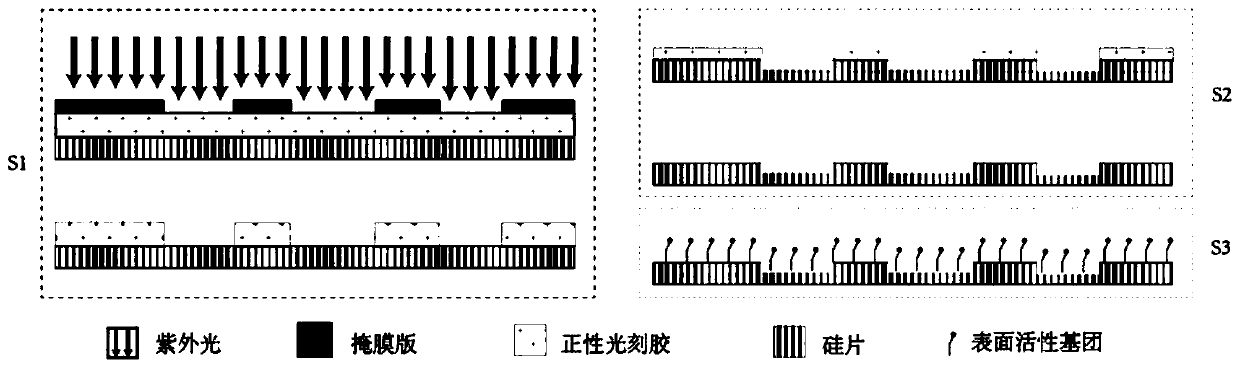
[0054] In this embodiment, the microfluidic chip provided by the present invention can be a material that can be manufactured by micro-nano processing methods, such as silicon-based materials such as single crystal silicon, silicon oxide, and silicon nitride, or glass materials such as quartz. Or it can be polymer materials such as polydimethylsiloxane (Polydimethylsiloxane, PDMS), polymethyl methacrylate (Polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA). For different materials and different sizes of channels in the chip, the preparation methods include but are not limited to laser etching, 3D printing, photolithography, plasma etching and other micro-nano processing methods.
[0055] see image 3 , is a process schematic diagram of the microfluidic chip provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0056] S1: Hang coat a layer of photoresist on the substrate, use the corresponding microchannel mask plate to form a microchannel etching window by...
Embodiment 3
[0067] see Figure 4 , the present invention also provides a whole blood separation method based on the microfluidic chip, comprising the following steps:
[0068] Step S110: adding a blood sample into the sample inlet unit 120 of the microfluidic chip;
[0069] It can be understood that the blood samples used for the whole blood separation realized by the microfluidic chip can be untreated blood, anticoagulated blood, diluted blood, etc.
[0070] Step S120: under the action of the flow resistance adjustment unit 130 provided at the front end and the rear end of the bifurcated branch channel 112, respectively perform flow resistance adjustment on the front end and the rear end of the bifurcated branch channel 112;
[0071] Step S130: when the blood flows through the bifurcated branch channel 112, due to the asymmetrical shear force on both sides, the blood cells will be oriented to enter the main channel 111, and the plasma will enter the bifurcated branch channel 112;
[00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com