Application of cocamidopropyl PG-dimethylammonium chloride as micro-organism-inhibiting agent and application of the cocamidopropyl PG-dimethylammonium chloride as the micro-organism-inhibiting agent in daily chemical products
A kind of technology of dimethyl ammonium chloride and cocamidopropyl, applied in the application of cocamidopropyl PG-dimethyl ammonium chloride as bacteriostatic agent, and the application field of bacteriostatic agent in daily chemical products , can solve the problems such as no data to prove the effect, undisclosed cocamidopropyl PG-dimethyl ammonium chloride bactericidal property, etc., to achieve the effect of good bacteriostatic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A
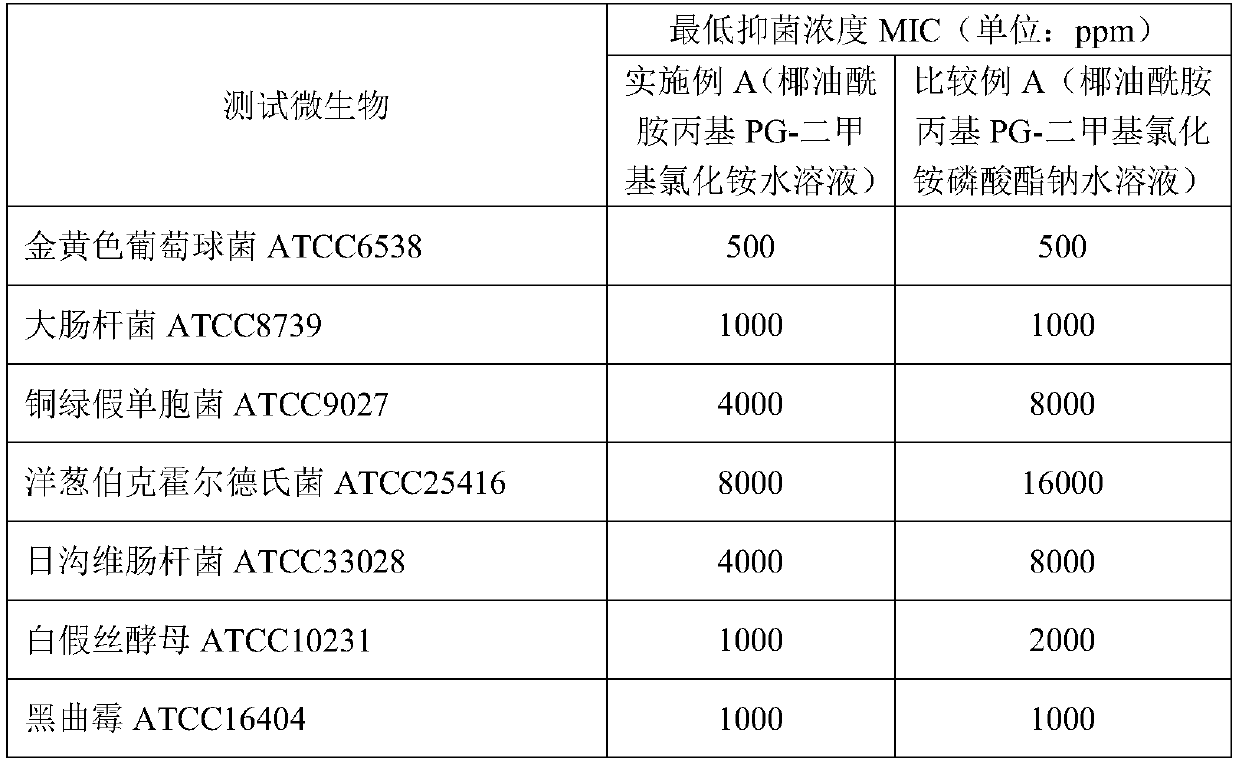
[0022] Measure the minimum inhibitory concentration of Cocamidopropyl PG-dimethylammonium chloride aqueous solution according to "Disinfection Technical Specifications" (2002 Edition) 2.1.8.3 Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Determination Test (Agar Dilution Method), and the test microorganisms are golden yellow Staphylococcus ATCC6538, Escherichia coli ATCC8739, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC9027, Burkholderia cepacia ATCC25416, Enterobacter japonica ATCC33028, Candida albicans ATCC10231, Aspergillus niger ATCC16404.
[0023] The specific steps are as follows: take 5 g of the sample to be tested by aseptic operation, put it into 45 ml of sterilized PBS (0.03 mol / L phosphate buffer saline), fully shake and dissolve, and prepare a 10% uniformly dispersed solution. Then dilute it with PBS to obtain different concentrations of the test solution, and place it in a water bath at 45°C to 50°C for further use. Take 10ml of serially diluted antibacterial solution and add it to the plate....
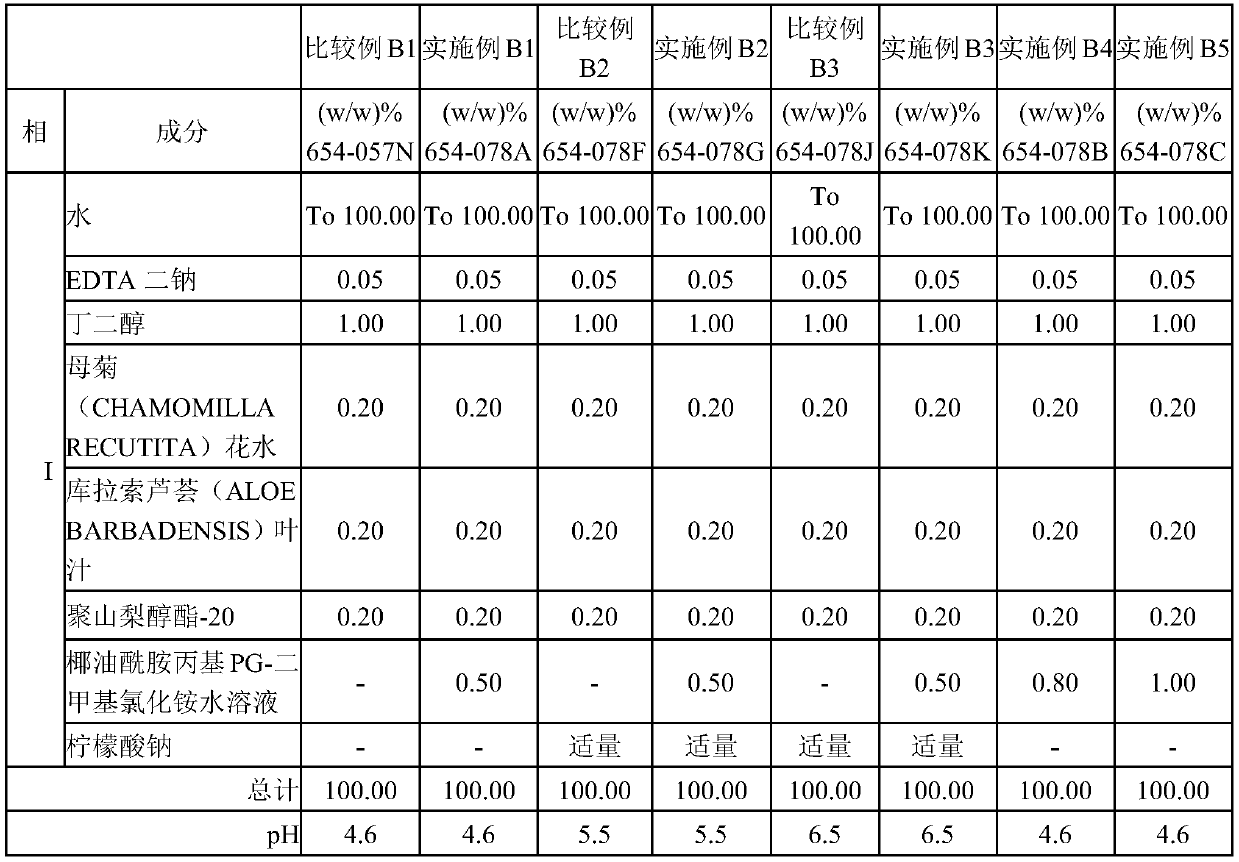
Embodiment B1~B5
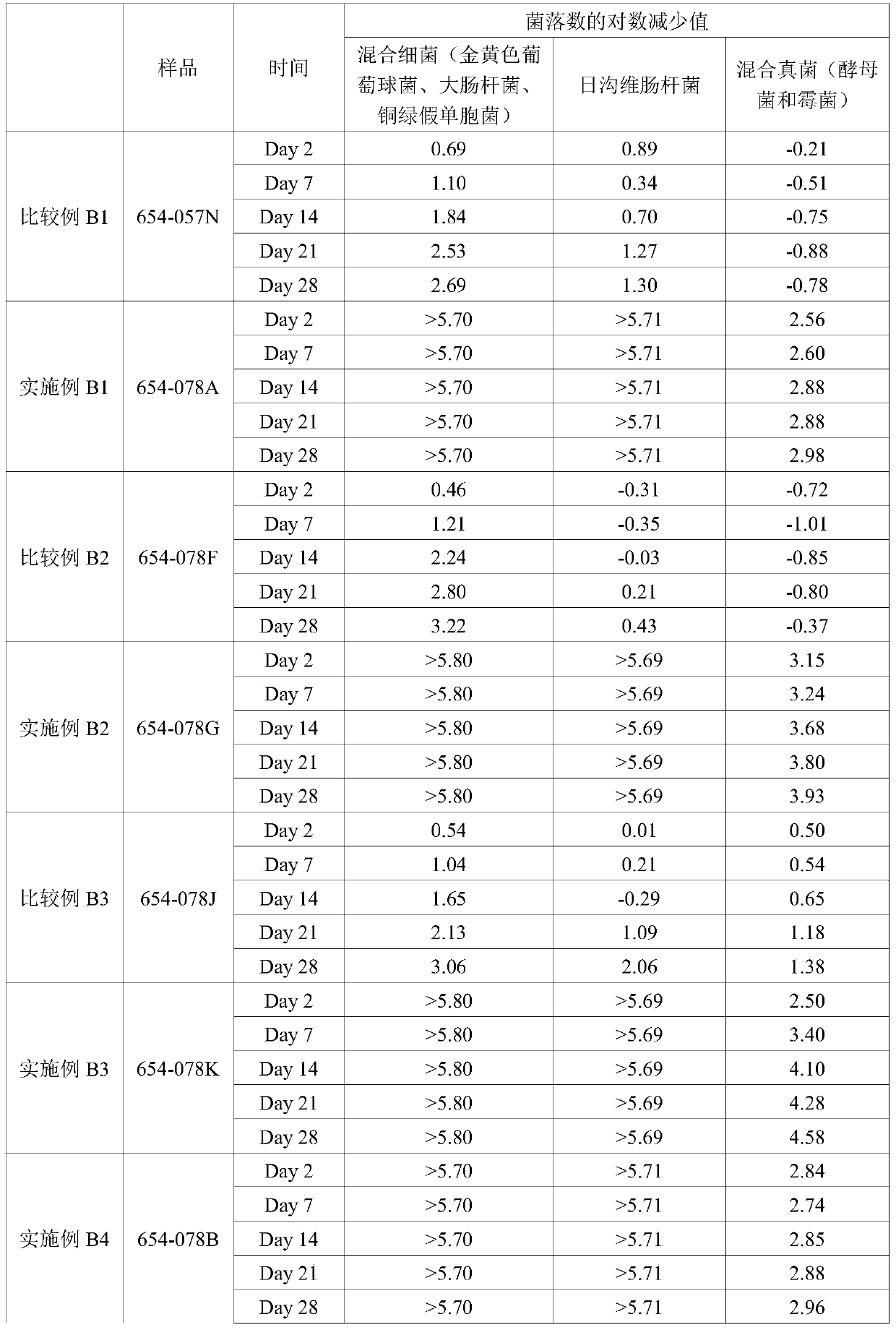
[0028] Add cocamidopropyl PG-dimethylammonium chloride aqueous solution to the wet tissue liquid with pH of 4.6, 5.5, and 6.5 respectively, and use it as a bacteriostatic agent, according to the method of the United States Pharmacopoeia USP32 (51) microbial antiseptic efficacy test Corrosion Challenge Test. The test microorganisms were Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538, Escherichia coli ATCC8739, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC9027, Enterobacter diaspora ATCC33028, Candida albicans ATCC10231, Aspergillus niger ATCC16404. Enterobacter versicolor is a common contaminating bacterium in daily chemical factories in South China, so this experiment deliberately added Enterobacter versicolor for testing. The concentration of the bacterial suspension was adjusted to 10 8 cfu / ml, in which equal amounts of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were mixed to form a mixed bacteria. The concentrations of the mold and yeast suspensions were adjusted to 10 7 cfu / ml, m...
Embodiment C
[0033] Add cocamidopropyl PG-dimethyl ammonium chloride aqueous solution to wet wipes containing non-woven fabrics (wet wipe liquid formula is 654-078Y) as a bacteriostatic agent, according to the United States Pharmacopoeia USP32 (51) microbial antiseptic Methods of Efficacy Testing Conduct a preservative challenge test.
[0034] See Table 4 and Table 5 for the wet wipe formula and test results of Example C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com