Engineering bacteria genetically modified by neomycin biosynthetic gene cluster, and applications thereof
A technology of biosynthesis and genetic engineering, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, microbial-based methods, etc., can solve the problems of negative mutation, time-consuming and labor-intensive, and efficiency reduction of mutagenesis breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
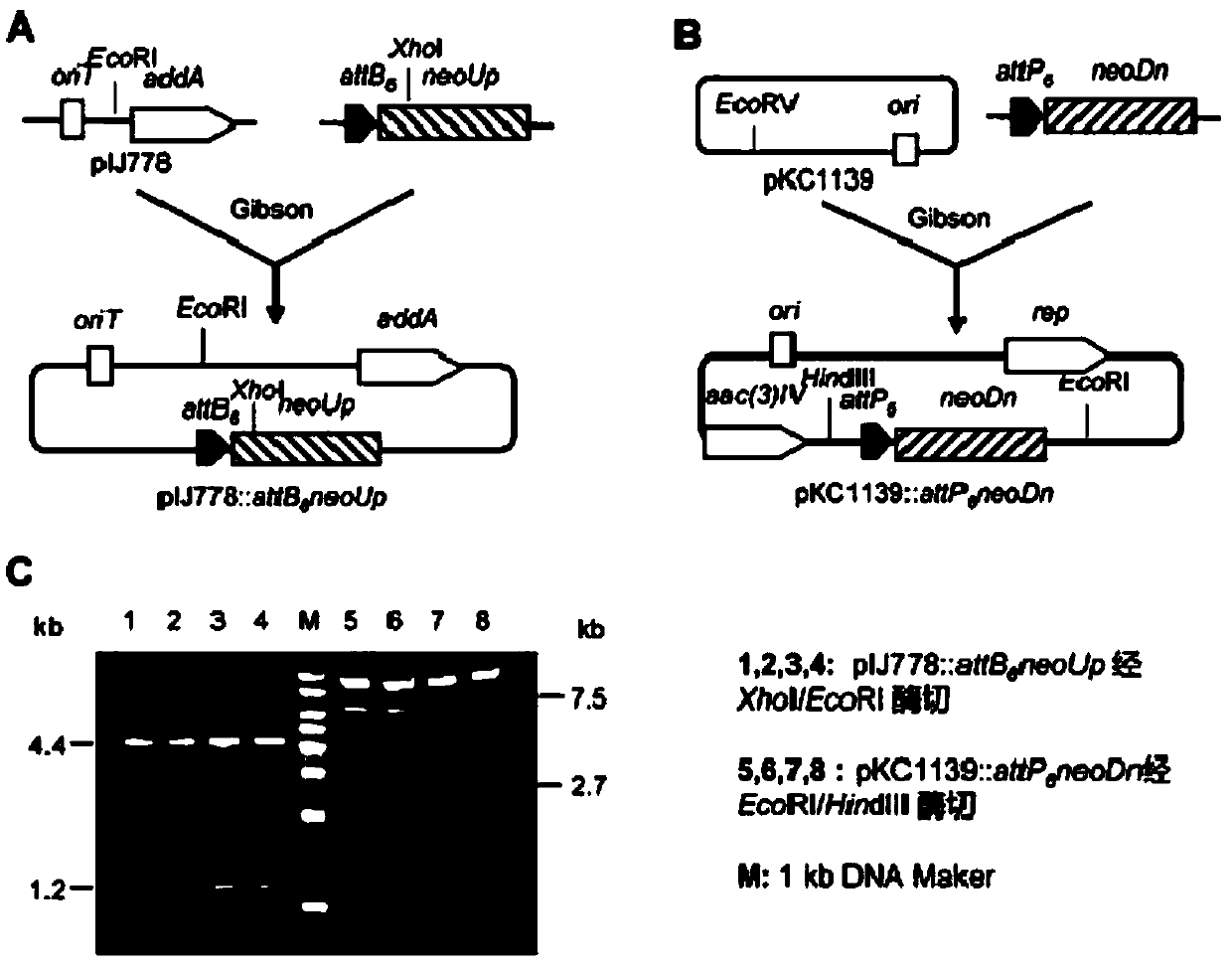
[0039] Example 1: Cloning of the Neomycin Biosynthesis Gene Cluster
[0040]The cloning strategy of neomycin biosynthesis gene cluster adopts φBT1 attP-attB-int integration system (Zhang, L., et al. (2008). Highly efficient in vitro site-specific recombination system based on Streptomyces phage φBT1 integrase. Journal of Bacteriology, 190(19), 6392; Du, D., et al. (2015). Genome engineering and direct cloning of antibioticgene clusters via phageφBT1 integrated-mediated site-specific recombination in Streptomyces. Scientific Reports, 5, 8740.), first need to pass Two homologous single exchanges will attB 6 and attP 6 The sequence and temperature-sensitive plasmid pKC1139 was introduced into both ends of the target gene cluster through the homology arm sequences on both sides of the cluster, so two plasmids for homologous integration were constructed: pIJ778::attB 6 neoUp and pKC1139::attP 6 neoDn.
[0041] Based on a section of pIJ778 containing the resistance gene and oriT...
Embodiment 2
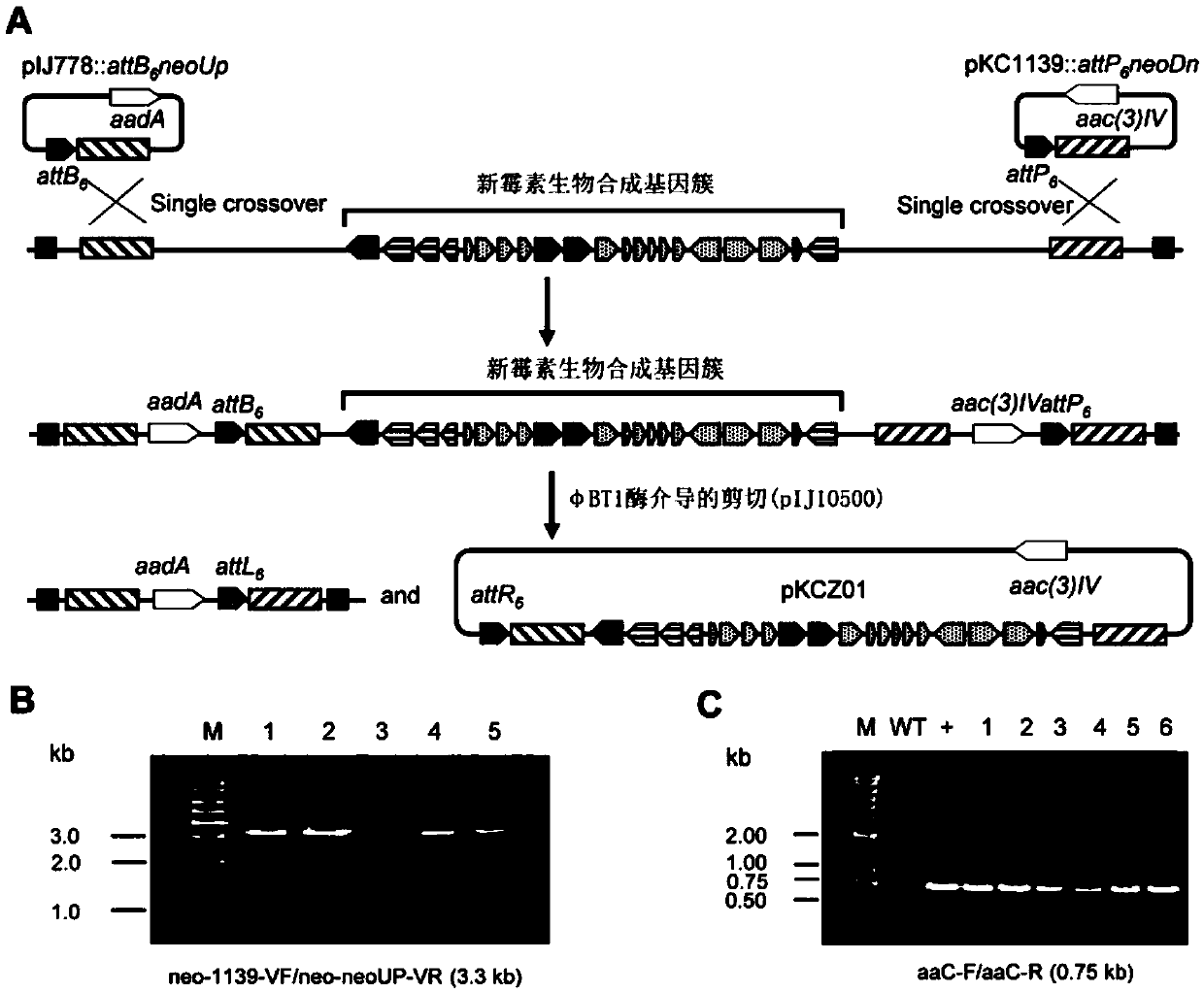
[0045] Embodiment 2 Transformation of Neomycin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
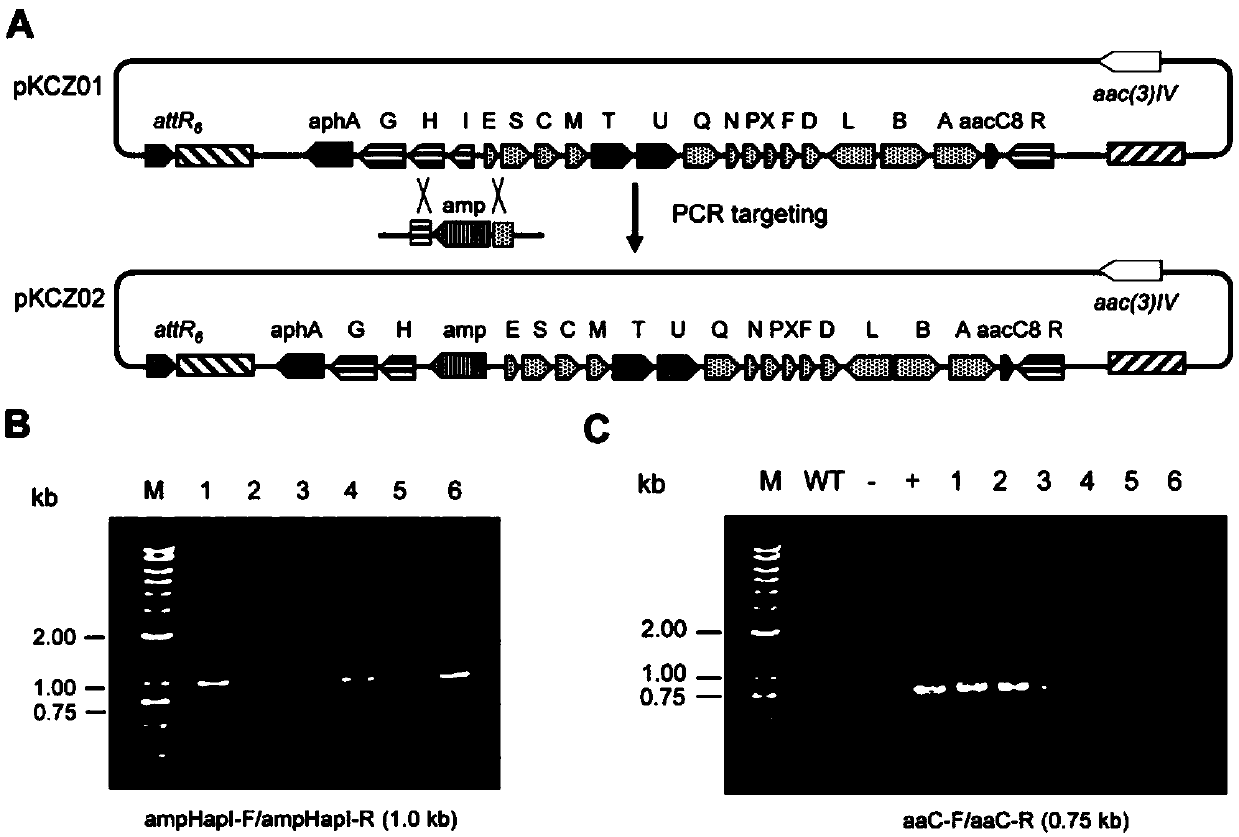
[0046] The negative regulatory gene neoI (SEQ ID NO.8) in the cloned neomycin biosynthesis gene cluster was blocked by PCR targeting large fragment editing method. First, pNIK-DNI (Zhuo, J., et al.( 2017). Reconstruction of a hybrid nucleoside antibiotic gene cluster based onscarless modification of large DNA fragments. Science China Life Sciences, 60(9), 1-12.) as a template, using neoItoamp-F / neoItoamp-R as primers for PCR amplification A basic element HapI-bla-HapI was obtained. The two ends of neoItoampF / neoItoampR primers respectively have 39bp homologous sequences with the upstream and downstream of neoI gene so as to facilitate λRED recombination. The above recovered product HapI-bla-HapI was introduced into Escherichia coli E. coli BW25113 / pIJ790 / pKCZ01 strain by electrotransformation (BW25113 / pIJ790 strain was used for gene editing by PCR targeting method. The pIJ790 plasmid contains λ-RED rec...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The construction of embodiment 3 neomycin high-yielding engineering strains
[0049] The specific operation process of joint transfer is as follows:
[0050] Firstly, the plasmids constructed above (pKCZ01, pKCZ02, pKCZ03) were transformed into E.coli ET12567 / pUZ8002 (see Paget, M.S., Chamberlin, L., Atrih, A., Foster, S.J. and Buttner, M.J. (1999). Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor sigma E is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2).JBacteriol 181,204–211.), pick the clone containing the recombinant plasmid and put it in liquid LB medium (tryptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, chloride Sodium 10g / L, pH 7.0) to OD 600 = 0.4 to 0.6 (100 µg / mL kanamycin, 100 µg / mL apramycin and 25 µg / mL chloramphenicol were added during culture). The collected bacteria were washed twice with fresh LB medium without antibiotics, and resuspended in 2×YT medium (tryptone 16g / L, yeast powder 10g / L, NaCl 5g / L, pH 7.0) in equal volume for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com