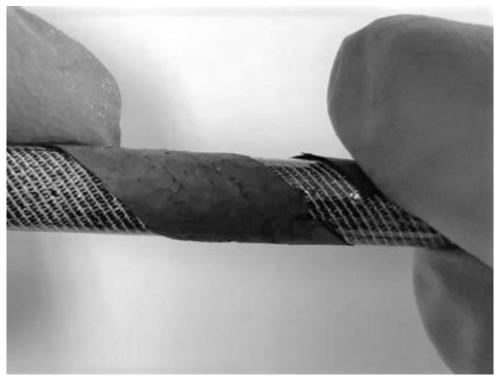
Flexible self-supporting MoO2@C nanofiber thin film material, preparation method and applications thereof
A technology of nanofiber and film materials, applied in the field of preparation of self-supporting flexible films, can solve the problems of not meeting the requirements of flexibility and weakening electron transmission, etc., and achieve excellent cycle stability, simple and easy-to-control preparation method, and low energy consumption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] (1) Take 0.45 g of (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 Dissolve O in a mixture of deionized water and 10 mL of ethylene glycol at a volume ratio of 2:1, heat and stir at 80°C and 600 r / min to completely dissolve to obtain solution A;
[0041] (2) Take 1.3 g of PVP with an average molecular weight of 1,300,000 and add it to solution A, stir it under a magnetic stirrer to dissolve it completely, and stir for 12 hours to obtain solution B;
[0042](3) The solution B was electrospun with a positive voltage of 15 kV, a negative voltage of -5 kV, a receiving distance of 15 cm, and a spinning temperature of 40 °C. , get MoO 2 @C fiber precursor;
[0043] (4) Dry the obtained molybdenum dioxide@carbon fiber precursor in an oven at 60 °C for 24 h;
[0044] (5) The dried precursor was pre-oxidized in a muffle furnace. The pre-oxidation temperature was 240 °C, the heating rate was 1 °C / min, and the pre-oxidation time was 3 h. get MoO 2 @C nanofiber film precursor;
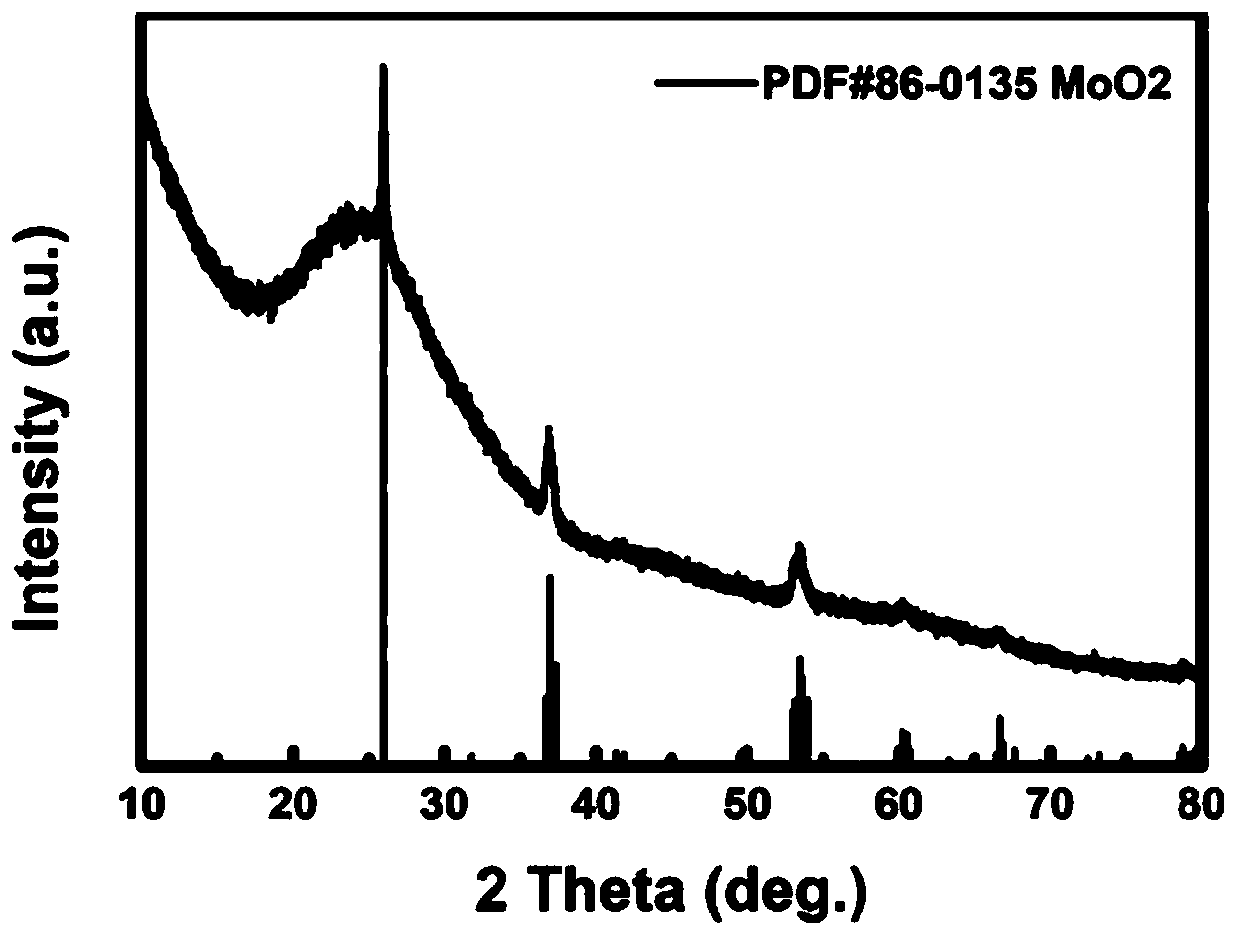
[0045] (6) MoO ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] (1) Take 0.4 g of (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 Dissolve O in a 10mL mixture of deionized water and ethylene glycol at a volume ratio of 1:1, heat and stir at 80°C and 600 r / min to completely dissolve to obtain solution A;
[0048] (2) Take 1.3 g of PVP with an average molecular weight of 1,300,000 and add it to solution A, stir it under a magnetic stirrer to dissolve it completely, and stir for 12 hours to obtain solution B;
[0049] (3) The solution B was electrospun with a positive voltage of 15 kV, a negative voltage of -5 kV, a receiving distance of 15 cm, and a spinning temperature of 40 °C. , get MoO 2 @C fiber precursor;
[0050] (4) will get MoO 2 The @C fiber precursor was dried in an oven at 60 °C for 24 h;
[0051] (5) The dried precursor was pre-oxidized in a muffle furnace. The pre-oxidation temperature was 250 °C, the heating rate was 1 °C / min, and the pre-oxidation time was 4 h. get MoO 2 @C nanofiber film precursor;
[0052] (6) MoO obtained in st...
Embodiment 3
[0054] (1) Take 0.45 g of Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 Dissolve O in a mixture of deionized water and 10 mL of ethylene glycol at a volume ratio of 2:1, heat and stir at 80°C and 600 r / min to completely dissolve to obtain solution A;
[0055] (2) Take 1.3 g of PVP with an average molecular weight of 1,300,000 and add it to solution A, stir it under a magnetic stirrer to dissolve it completely, and stir for 12 hours to obtain solution B;
[0056] (3) The solution B was electrospun with a positive voltage of 15 kV, a negative voltage of -5 kV, a receiving distance of 15 cm, and a spinning temperature of 40 °C. , get MoO 2 @C fiber precursor;
[0057] (4) will get MoO 2 Dry the @C fiber precursor in an oven at 60°C for 24 hours;
[0058] (5) The dried precursor was pre-oxidized in a muffle furnace. The pre-oxidation temperature was 240 °C, the heating rate was 1 °C / min, and the pre-oxidation time was 3 h. get MoO 2 @C nanofiber film precursor;
[0059] (6) MoO obtained in step (5) 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com