Astragalus sinicus LHY gene and application thereof
A milk vetch and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering and plant genetic breeding, can solve the problems of unclear functions of flowering-related genes and achieve good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Unless otherwise specified, the examples are all in accordance with conventional experimental conditions, such as Sambrook et al. Molecular Cloning Experiment Manual (Sambrook J & Russell DW, Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2001), or in accordance with the conditions suggested by the manufacturer's instructions. Example 1 Cloning and sequence analysis of milk vetch LHY gene
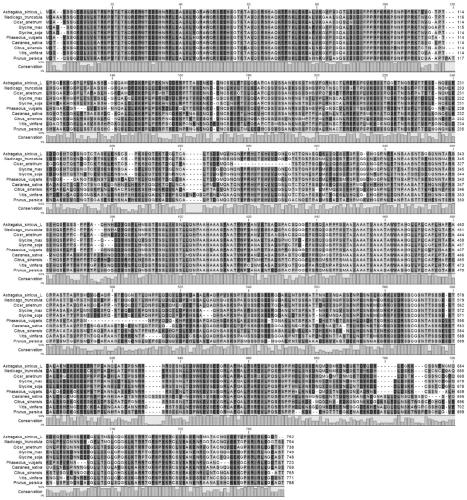
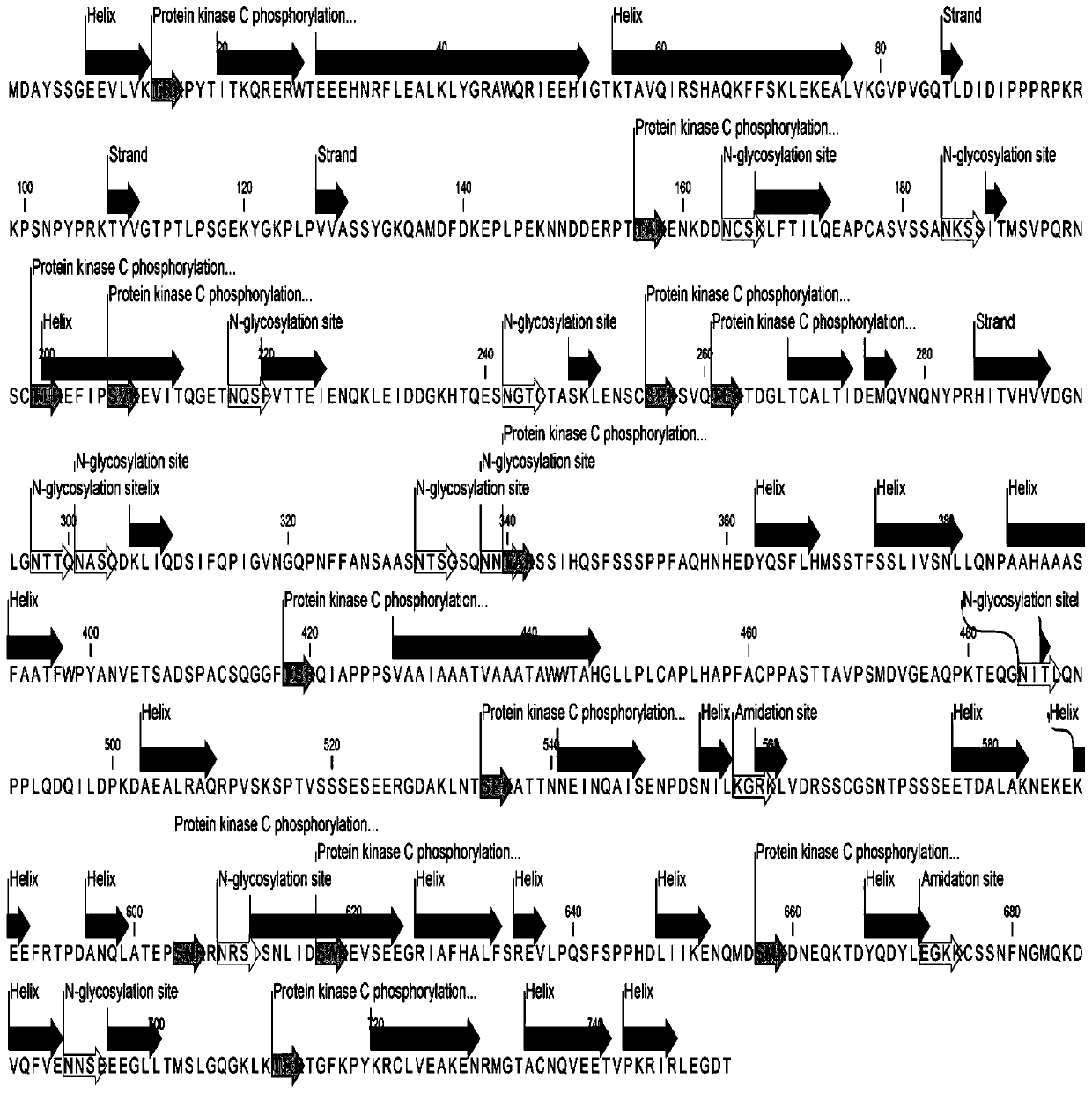
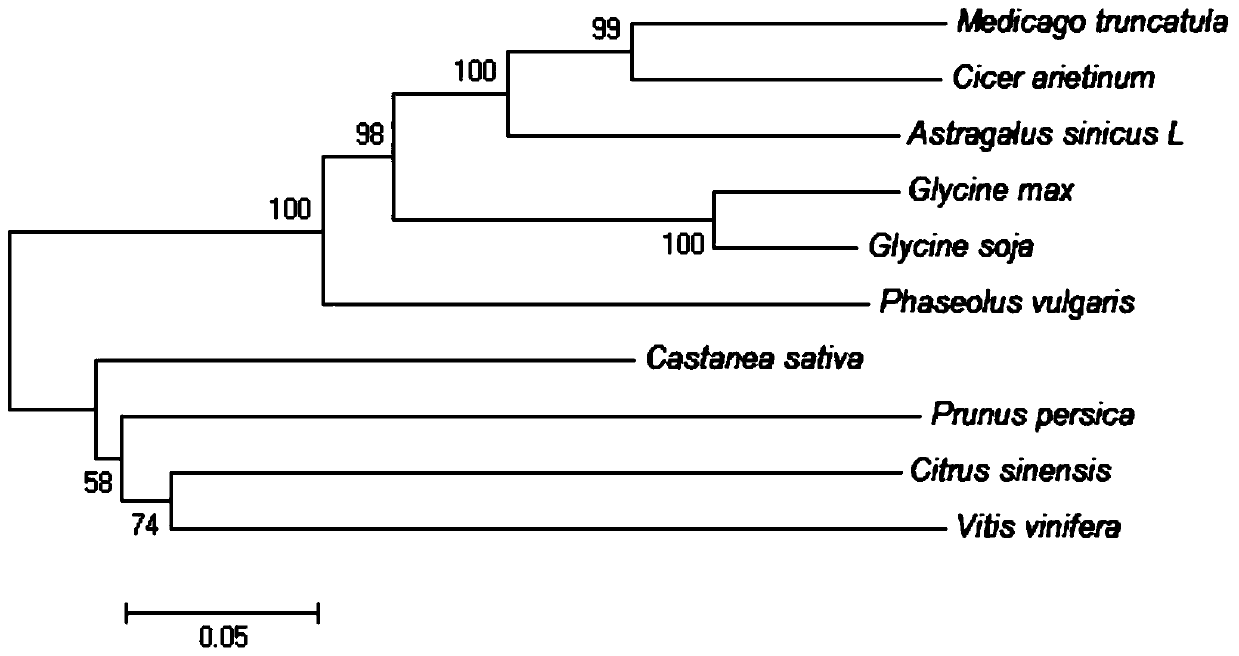
[0035] The present invention uses RACE technology to obtain the full-length cDNA sequence of the LHY gene from milk vetch, which is 2865bp (SEQ ID NO: 1), contains an open reading frame of 2259bp, and the lengths of the 5' and 3' non-coding regions are 407bp and 3' respectively. 199bp. The PolyA tail signal peptide region is located at 2854-2859bp. The amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The specific method is as follows: ...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2 Detection of relative expression levels of LHY gene in various tissues of milk vetch
[0102] 1. Total RNA extraction
[0103] Milk vetch is a plant material grown in a greenhouse, and it is a fresh milk vetch tissue sample cultivated by collecting seeds from common milk vetch plant materials.
[0104] 2. Design and synthesis of fluorescent quantitative PCR primers
[0105] Primer Premier 6.0 and Beacon designer 7.8 software were used for quantitative PCR primer design, and then synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The internal reference gene used was 18S rDNA (GenBank: AF359603.1).
[0106] 3. Real-Time PCR (Q-PCR) statistical analysis of gene expression differences
[0107] Each sample was repeated three times, and the relative expression levels of each gene were compared with 2 (Ct内参基因-Ct目的基因) conduct statistical analysis. The results of LHY gene Q-PCR expression analysis are shown in Table 17.
[0108] Table 17 LHY gene Q-PCR exp...
Embodiment 3
[0112]Embodiment 3 The cultivation of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana and its phenotype analysis
[0113] 1. Construction of a recombinant plasmid containing the milk vetch LHY gene (SEQ ID NO: 1) of the present invention.
[0114] 2. Transform Agrobacterium Competent
[0115] Transform the recombinant plasmids with correct sequencing into competent Agrobacterium. Colony PCR identification showed that the vector plasmid had been successfully transferred into Agrobacterium.
[0116] 3. Arabidopsis transformation process (inflorescence dipping method)
[0117] (1) Planting: Choose the rock with good water absorption and soft soil with nutrient soil (1:1 / 2) as the planting soil for Arabidopsis. For flower pots with a diameter of 9 cm, 100-150 seeds are sown in each pot. After sowing, cover the flowerpot with a film to provide a moist environment for the growth of the plant.
[0118] (2) Transplanting: 10-15 days after sowing, the Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings grow to the fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com