Application of N-methyl phenylethylamine and isotope reagent thereof in carboxyl compound detection
A carboxyl compound, methylphenethylamine technology, applied in the field of organic chemistry and analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of limited application scope, low detection throughput, complicated operation, etc., to achieve the effect of assisting screening and improving sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
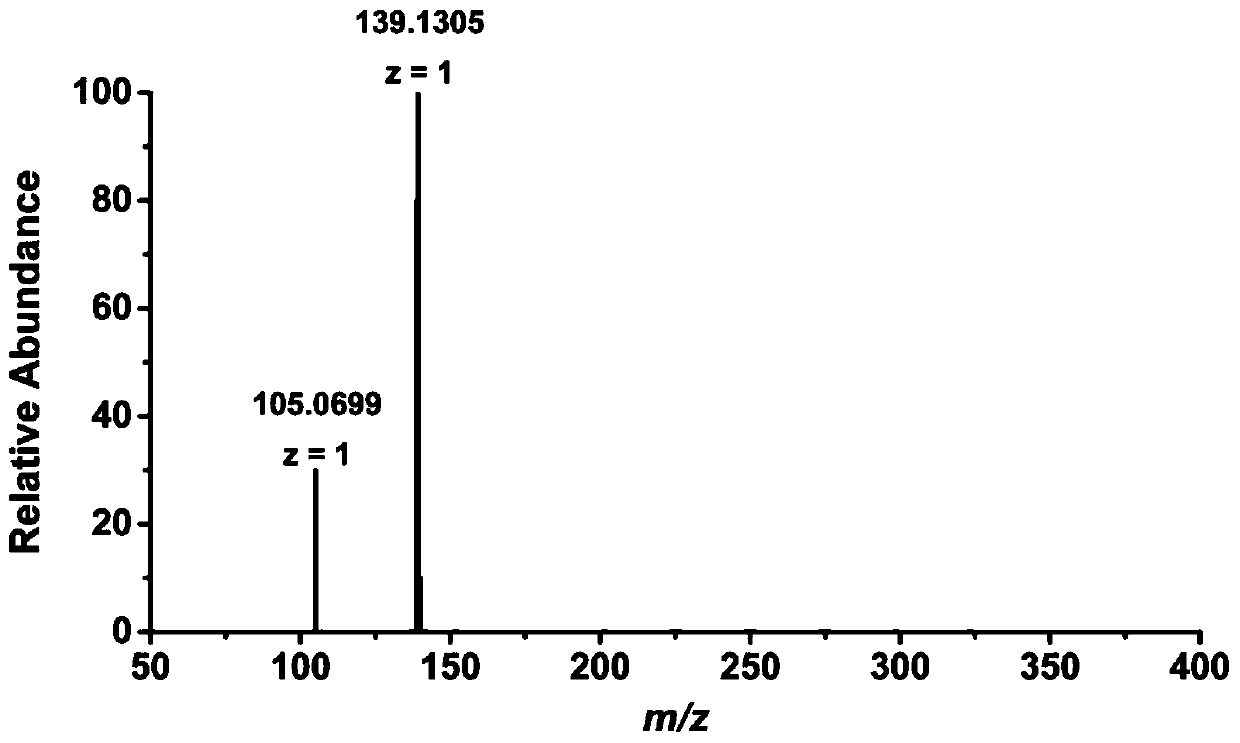
[0029] Example 1: MPEA and d 3 - Application of MPEA in the detection of short-chain carboxylic acids
[0030] d 3 - Synthesis of MPEA:
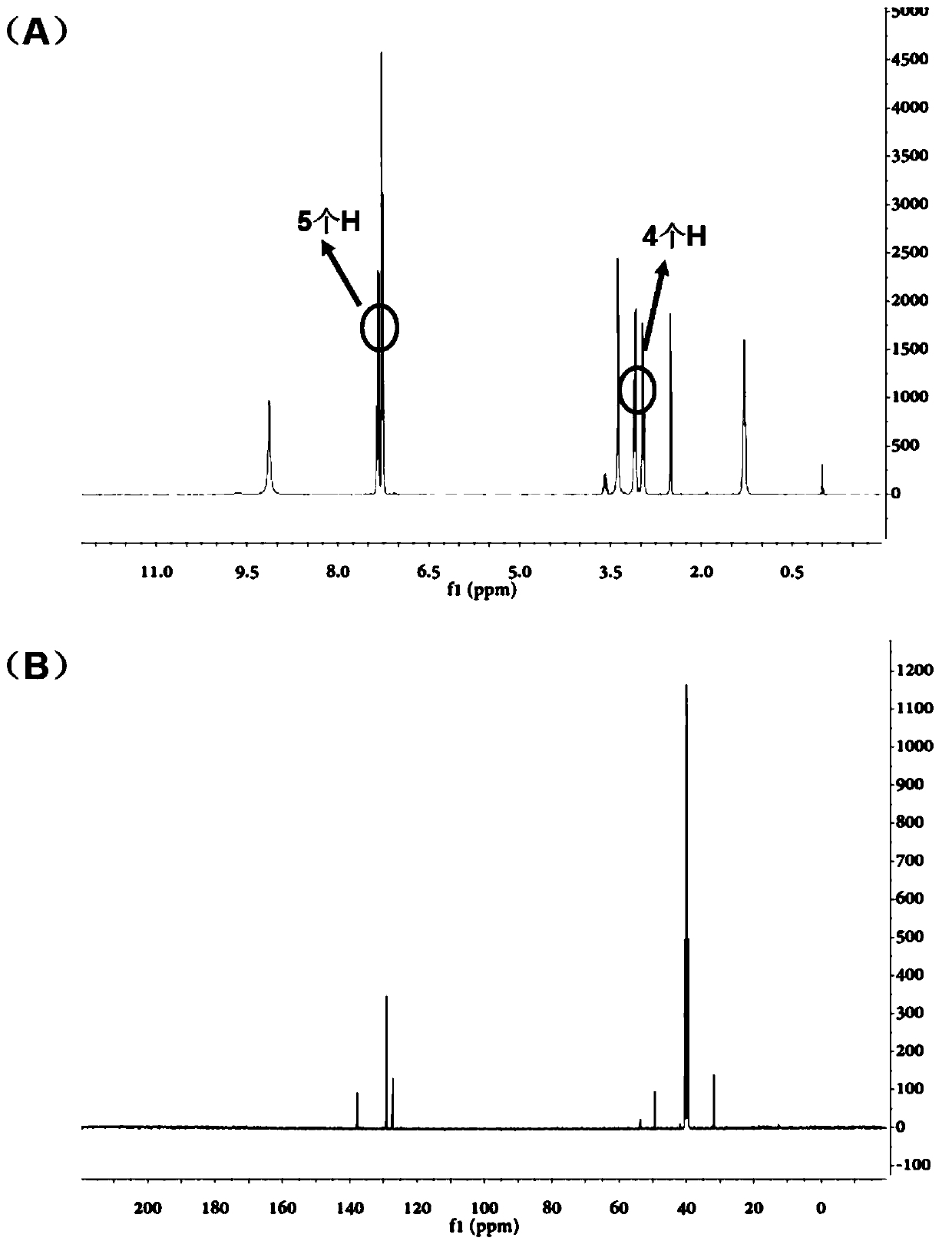
[0031] The first step: under anhydrous and oxygen-free conditions, add 10 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran to a container containing 1.84 mmol of N-(2-phenylethyl) acetamide, stir until dissolved, then add sodium hydride (3.68 mmol) and stir 45min. Add iodomethane-d dropwise 3 (9.19 mmol), reacted overnight. The tetrahydrofuran was spin-dried in vacuo, followed by liquid-liquid extraction with dichloromethane and water. Continuous extraction was performed three times, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, the organic phases were combined and concentrated, and then subjected to column chromatography, the eluent was petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 10:1. Finally, 172.4 mg of oily liquid was obtained.
[0032] Step 2: Dissolve the intermediate obtained above with 3 mL of ethylene glycol, add 0.2 mL of 10% dilute hydrochloric acid, and refl...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Marking Effects
[0034] The instrument used for sample analysis is UPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap MS mass spectrometry. The mass spectrometry system is an LTQ / Orbitrap XL ETD mass spectrometer from ThermoFisher (Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an ESI ion source. Data acquisition and analysis software is Thermo Xcalibur 2.1Software version. The liquid phase system is Dionex Ultimate3000RSLC chromatograph (Thermo Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), equipped with LPG-3400A quaternary gradient pump with built-in online degasser, WPS-3000SL autosampler, and TCC-3000 column thermostat. The type of chromatographic column is Waters ACQUITYUPLC BEH C18 (2.1×100mm, 1.7μm), and the temperature of chromatographic column is 40°C. 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (phase A) and ACN (phase B) were used as the mobile phase for chromatographic analysis, and the chromatographic gradient was: 0-5min 10%B, 5-42min 10%-90%B, 45-58min90%B, 58- 60 min 10% B at a flow rate of 0.4 mL / min.
...
Embodiment 3
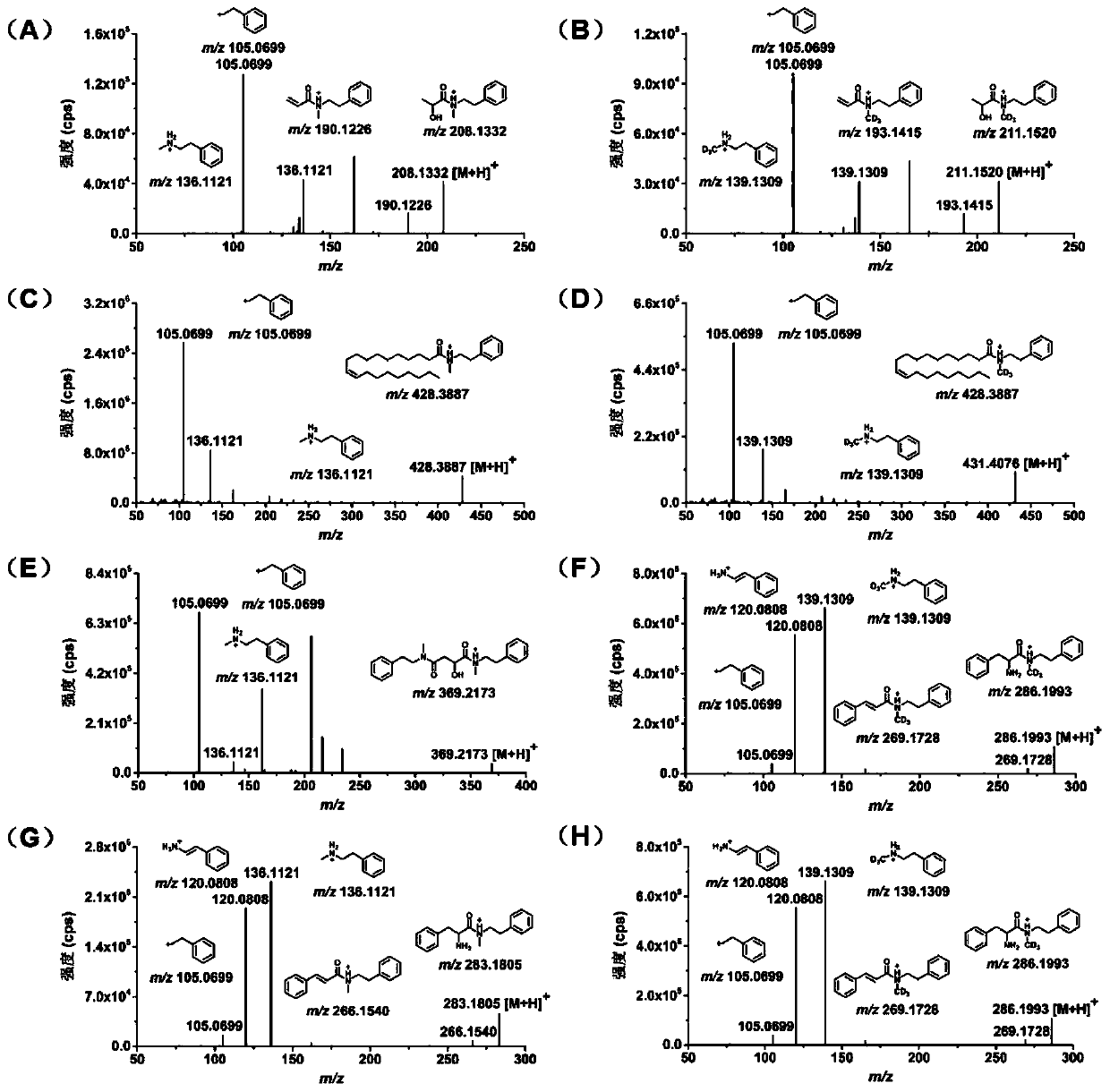
[0042] Example 3: Comparison with reported labeling effects of reagents
[0043] In order to further evaluate the labeling effect of MPEA, we selected two other derivatization reagents with higher sensitivity reported in the literature for comparison, namely: N, N-dimethylethylenediamine (DMED) and N-4-formazan Aminobenzylaniline (4-AMBA). The experimental results are presented in the form of a heatmap as Figure 4 As shown, the darker the color, the stronger the mass spectrometry signal, and the better the effect of the labeled reagent. The results showed that the labeling effect of MPEA on various carboxyl compounds was significantly better than that of DMED and 4-AMBA.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com