Multifunctional specific biological bonding hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
A specific and multi-functional technology, applied in bandages, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of dressings that cannot be removed, poor mechanical properties of viscous hydrogels, and biological safety issues, so as to achieve good biocompatibility and promote wound healing , to avoid cytotoxic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] Based on the multifunctional specific bioadhesive hydrogel of the above embodiments, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a preparation method of a multifunctional specific bioadhesive hydrogel, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0034] Step 1: Prepare an aqueous solution of acrylic acid A, an aqueous solution of acryloyl glycinamide B and an aqueous solution of polyphenolic compounds C;
[0035] Step 2: Stir and mix the acrylic acid aqueous solution A and the acryloylglycylamide aqueous solution B at room temperature, remove oxygen, add an initiator and a catalyst, and polymerize under nitrogen protection to obtain an acrylic acid-acryloylglycylamide copolymer pregel; and
[0036] Step 3: adding the polyphenolic compound aqueous solution C into the acrylic acid-acrylglycylglycylamide copolymer pregel, shearing and stirring to obtain the multifunctional specific bioadhesive hydrogel.
[0037] In the above step 1, the preparation of the acrylic acid aqu...
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Preparation method of bioadhesive hydrogel
[0044] (1) Dissolve 0.6 gram, 0.7 gram and 0.8 gram of acrylic acid (AA) in 5 milliliters of water respectively to obtain solution A with a concentration of 12wt.% 1 , 14wt.% solution A 2 , 16wt.% solution A 3 . 0.4 g, 0.3 g, and 0.2 g of acryloyl glycinamide (NAGA) were dissolved in 5 ml of water respectively to obtain a solution B with a concentration of 8 wt.%. 1 , 6wt.% solution B 2 , 4wt.% solution B 3 .
[0045] (2) the solution A 1 and solution B 1 , solution A 2 and solution B 2 , solution A3 and solution B 3 After stirring and mixing at room temperature, nitrogen was bubbled for 30 minutes to remove oxygen, 0.02 g of ammonium persulfate (APS) and 0.01 g of tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) were added, and polymerized at 60 ° C for 2 hours under nitrogen protection to obtain acrylic acid and acryloyl Pregelatin PAA6-NAGA4, PAA7-NAGA3, PAA8-NAGA2 with glycinamide monomer ratios of 6:4, 7:3 and 8:...
Embodiment 2
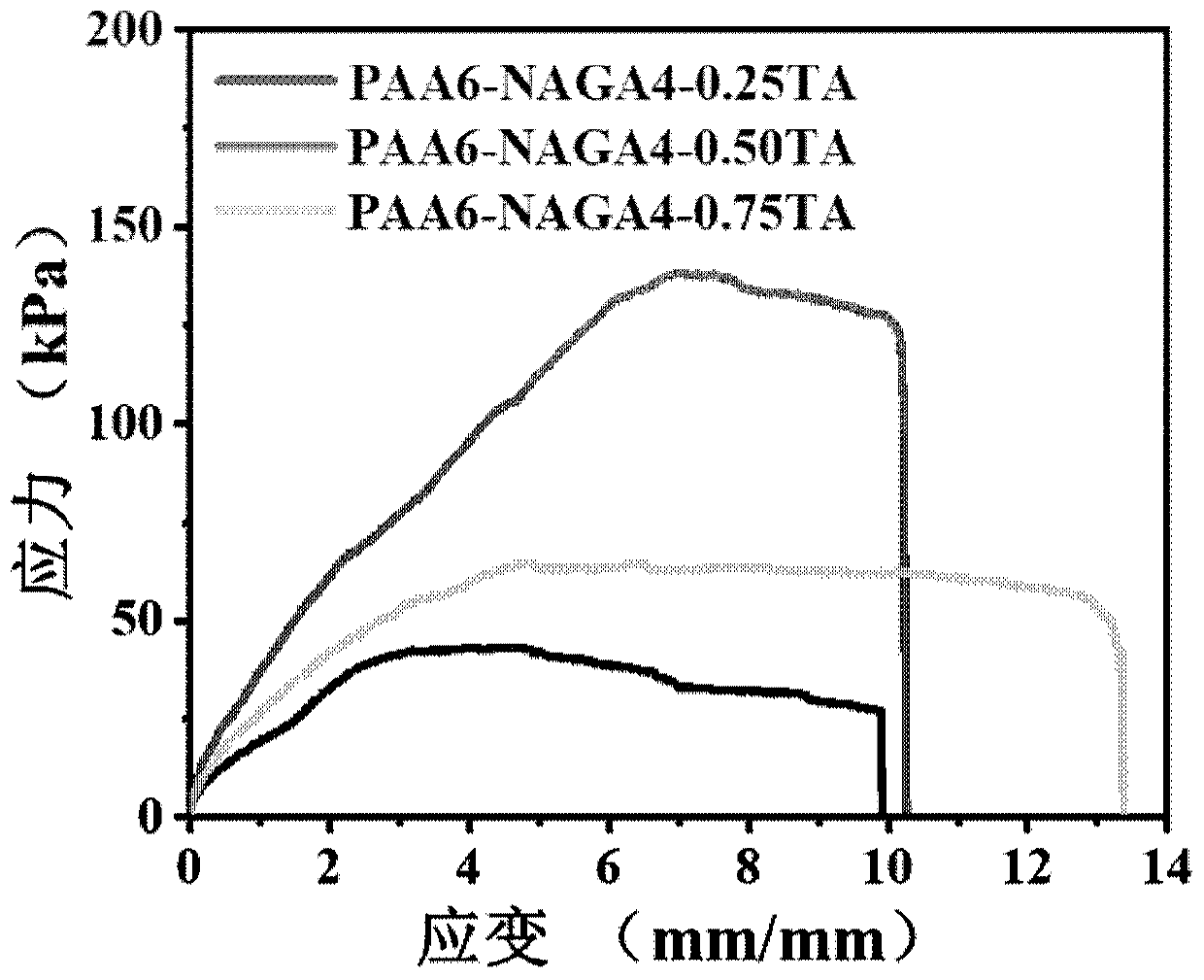
[0047] Example 2: Preparation method of multifunctional specific bioadhesive hydrogel and testing of tensile strength and adhesive strength using the hydrogel
[0048] (1) Dissolve 0.6 g of acrylic acid (AA) in 5 ml of water to obtain solution A; dissolve 0.4 g of acryloyl glycinamide (NAGA) in 5 ml of water to obtain solution B. 0.25 g, 0.5 g, and 0.75 g of tannic acid were respectively dissolved in 1 ml of water to obtain solution C.
[0049] (2) After stirring and mixing solution A and solution B at room temperature, nitrogen gas was bubbled for 30 minutes to remove oxygen, and 0.02 g of ammonium persulfate (APS) and 0.01 g of tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) were added. Polymerize for 2 hours to obtain pregel PAA6-NAGA4 with a monomer ratio of acrylic acid to acrylglycylglycylamide of 6:4.
[0050] (3) Add solution C to the PAA6-NAGA4 pre-gel prepared in step (2), shear and stir for 10 minutes to obtain PAA6-NAGA4-0.25TA, PAA6 with tannic acid content of 0.25 grams, 0.5...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com