Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS composite flexible electrode and solar cell device
A solar cell and flexible electrode technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of low crystallinity of PEDOT, hindering hole transport efficiency and collection efficiency, and low film conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A kind of Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS composite material described in this embodiment, Mxenes is two-dimensional transition metal carbide, nitride or carbonitride, is composed of M n+1 x n T x , where M is an early transition metal, X is carbon, nitrogen or a mixture of both, T x is the surface end group, n = 1, 2 or 3; Mxenes / PEDOT:PSS hybrid colloid solution is prepared by adding PEDOT:PSS solution to Mxenes dispersion to form Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS composite material. Among them, the Mxenes material is: Sc 2 C, Ti 2 C, Zr 2 C,Hf 2 C, Nb 2 C, V 2 C, Cr 2 C, Ta 2 C.Ti 2 N. Mo 2 C.Ti 3 C 2 .
[0046] The preparation of Mxenes (with Ti 3 C 2 T x as an example, but not limited to):
[0047]First, titanium powder, aluminum powder and graphite were mixed in a molar ratio of 3:1.2:2, and then sintered at 1650°C for 2 hours in an argon atmosphere to prepare Ti 3 AlC 2 The MAX phase. Subsequently, at room temperature, by etching Ti in a solution of 12 M LiF / 9 M HC 3 AlC ...
Embodiment 2
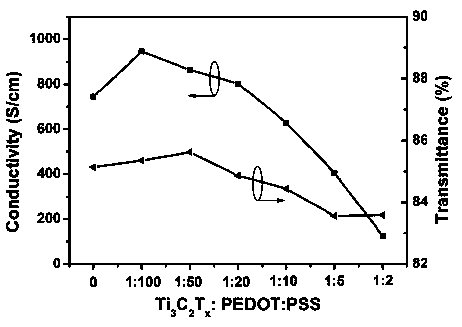
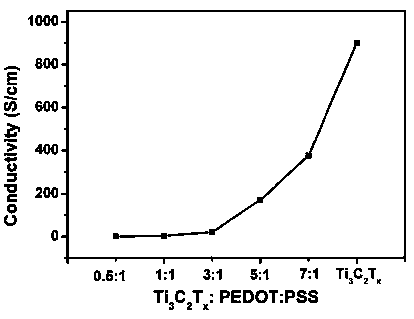
[0051] A Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS composite flexible electrode described in this example is prepared from the Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS composite material by one of solution spin coating, scraping coating, screen printing, inkjet printing, and film transfer printing. Wherein Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS composite material is made by the technical scheme of embodiment 1. to Ti 3 C 2 T x As an example, but not limited to: Ti 3 C 2 T x The preparation of / PEDOT:PSS composite flexible electrodes can be realized by choosing one of various methods such as solution spin coating, doctor blade coating, screen printing, inkjet printing, and film transfer printing according to the device structure. Electrode films with different thicknesses were prepared under different mass mixing ratio conditions to optimize the device performance, so as to determine the Ti 3 C 2 T x / PEDOT:PSS flexible electrode optimal mass ratio and thickness.
Embodiment 3
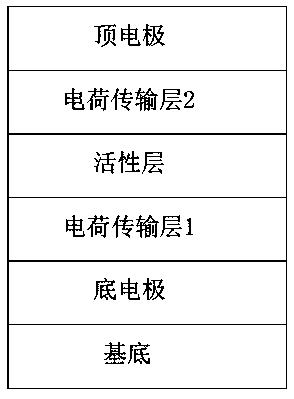
[0053] Such as Figure 4 As shown, a solar cell device described in this embodiment includes a substrate, a bottom electrode, a hole transport layer, an active layer, an electron transport layer, and a top electrode stacked from bottom to top, wherein the bottom electrode adopts Mxenes-PEDOT:PSS Composite flexible electrodes. The substrate is glass or flexible polymer material, including but not limited to PET, PES or PEN, the top electrode can be metal, including but not limited to Ag, Cu, Al, or a non-metallic electrode with a work function of less than 5.0 eV, and the active layer is Inorganic thin film materials or organic small molecules and polymer materials or perovskite materials, the active layer has good light absorption, good charge separation and transport performance, and the main material of the electron transport layer has an electron mobility greater than 10 -5 cm 2 v -1 the s -1 , and an N-type organic or inorganic semiconductor material that matches the e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com