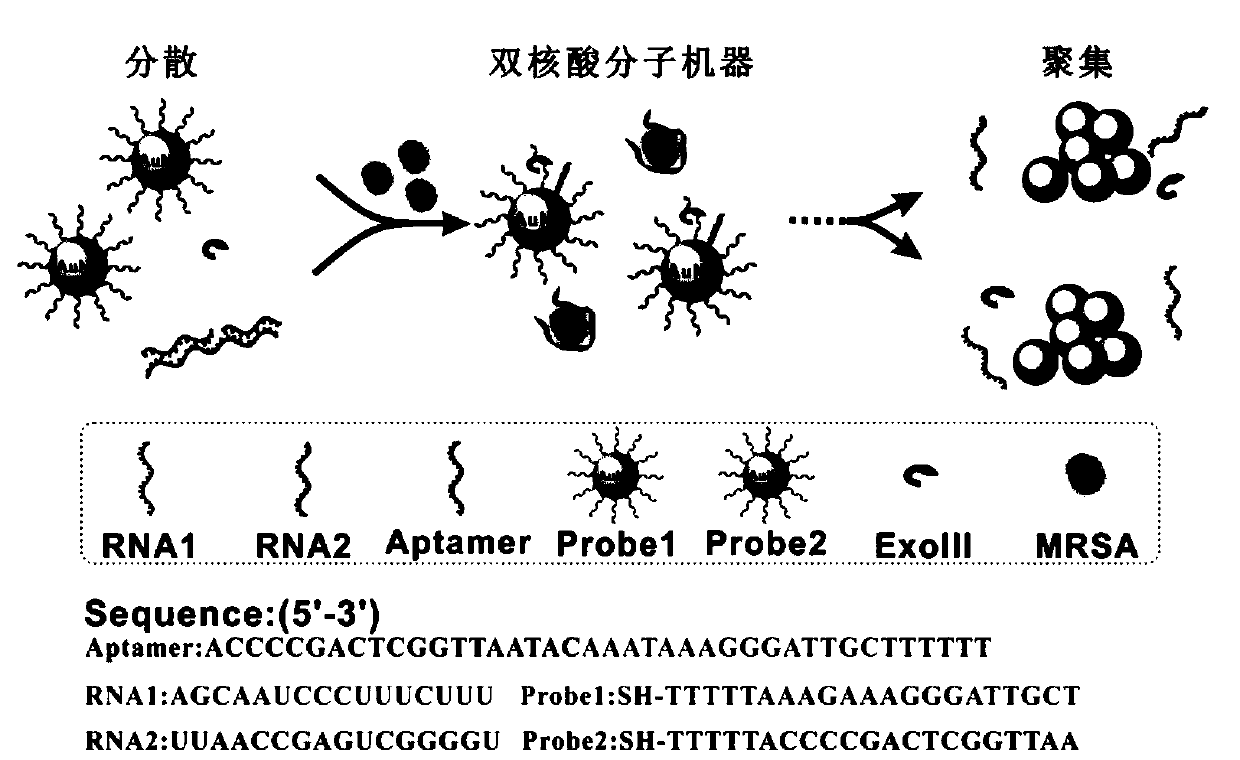
Drug-resistant bacterium detection method based on nucleic acid molecule machine colorimetry
A detection method and technology of nucleic acid molecules, applied in the detection field, can solve problems such as time-consuming, cumbersome detection process, and inability to quantitatively detect, and achieve the effects of high binding efficiency, large false positive signals, and short time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] The preparation of embodiment 1 double probe
[0123] The traditional method uses sulfhydryl-modified DNA to connect to the surface of the gold ball and uses the salt aging method, which often takes one to two days, which is time-consuming and laborious. The present invention adopts a new double-probe preparation method: a certain concentration of citrate is directly added to the double-probe that responds specifically to bacteria, and the pH in the solution is controlled to be 3, thereby weakening the static electricity between AuNPs and SH-DNA Repulsion, enhance the binding probability of SH-DNA and AuNPs.
[0124] In this example, 4 μl of sulfhydryl-modified probe chains was mixed with 40 μl of AuNPs (60 nM) at a volume ratio of 1:1, 4.88 μl of citrate (100 mM, pH=3) was added and vortexed rapidly for 2 min. And make the final concentration of citrate 10mM. After standing in the dark for 15 minutes, centrifuge at 10,000 r for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, an...
Embodiment 2
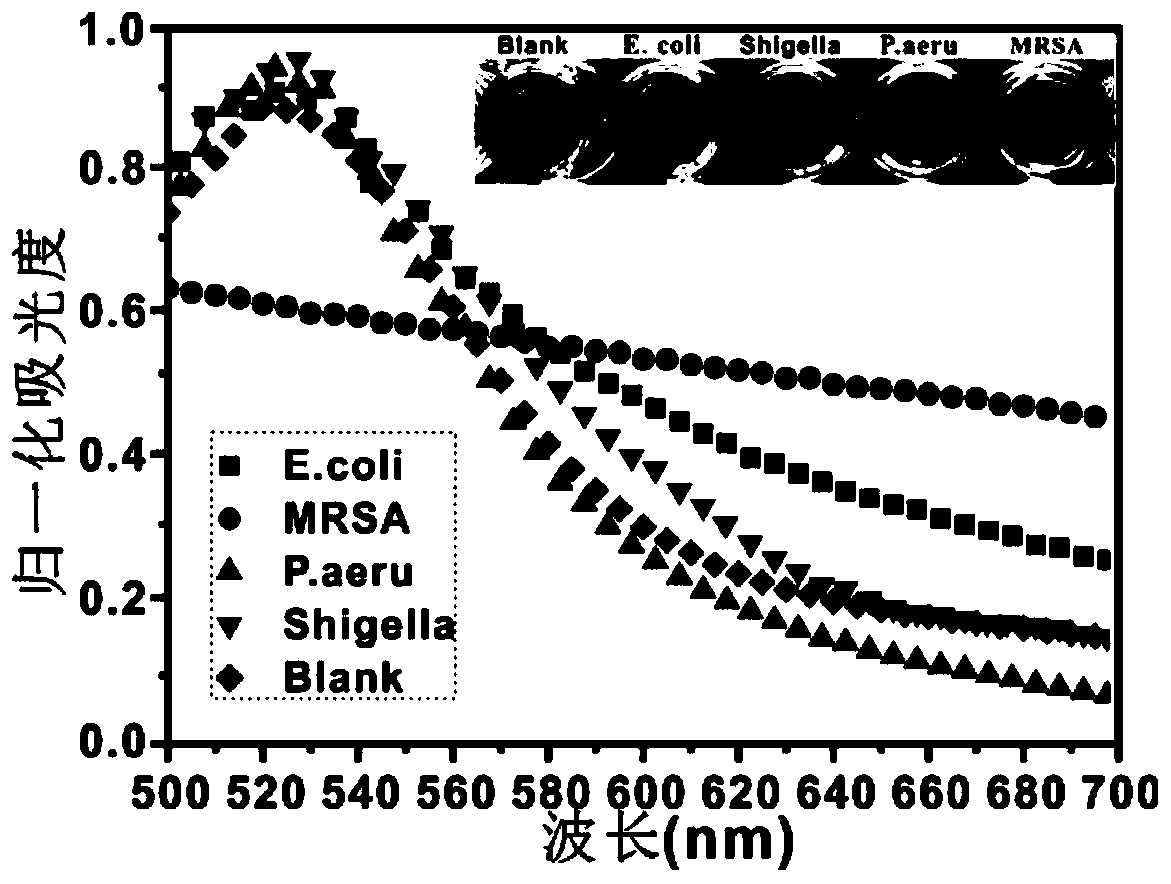
[0127] Embodiment 2 specificity experiment
[0128] MRSA was used as the experimental group, and PBS, Escherichia coli (E.coli), Shigella funeri (Shigella) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Paeru) were used as the control group. Take 5 reaction mixtures, each reaction mixture includes: 100μl dual probe (30nM), 30μl double-stranded core (RNA1-RNA2-Aptamer), 2μl EXOIII and 20μl 10×buffer, and then add to the 5 reaction mixtures respectively 50 μl of different types of the above bacterial suspension (MRSA, Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and 50 μl of PBS were prepared as samples. The bacterial concentration in all samples was controlled at 10 8 CFU / ml (except PBS group). After measuring the initial absorbance of the reaction mixture solution with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, the reaction mixture solution was incubated in a 37° C. incubator for 2 h, and the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer.
[0129...
Embodiment 3
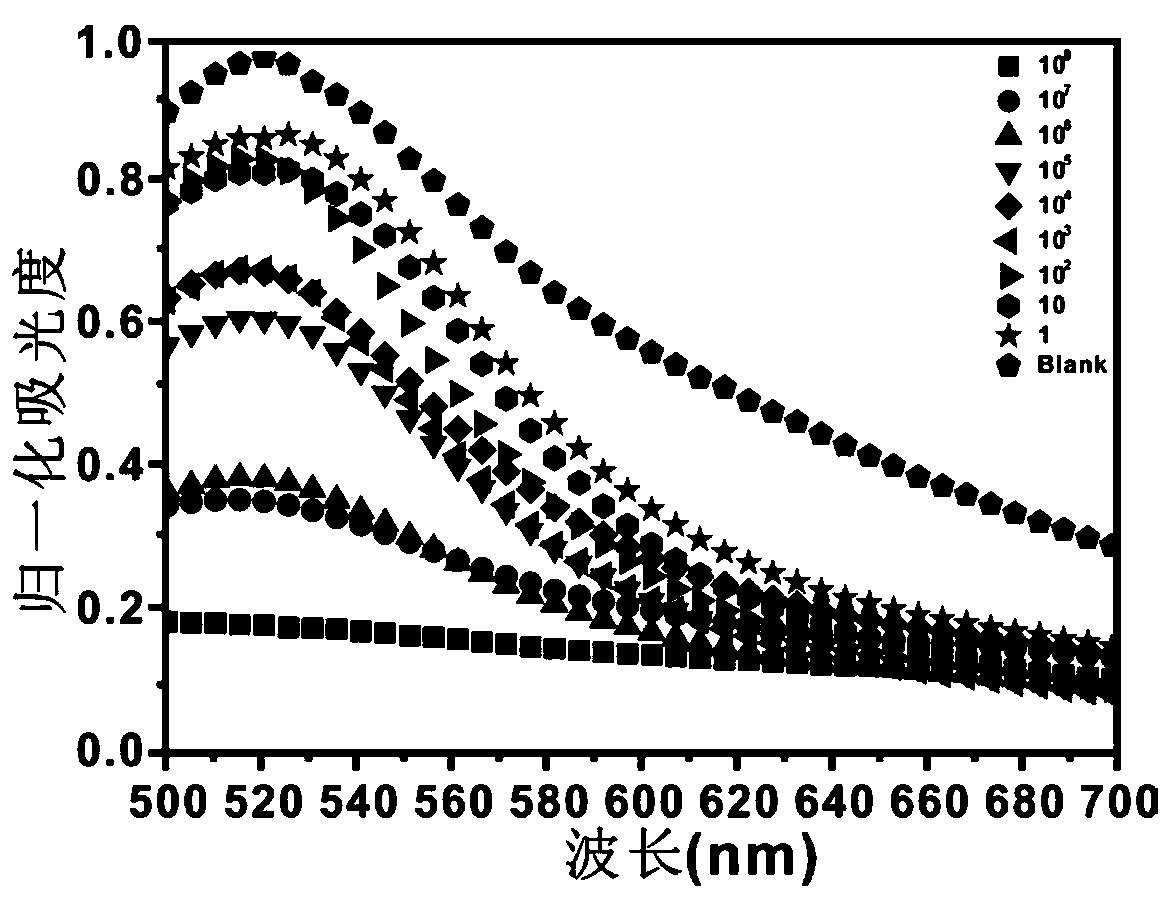
[0131] The detection of embodiment 3 MRSA
[0132] The high-concentration MRSA cultured in liquid medium was centrifuged and washed three times, redispersed with PBS, and bacterial suspensions of various dilutions were obtained after gradient dilution. Take nine copies of 100 μl double-probe (30nM), add 50 μl bacterial suspension with different concentration gradients, 30 μl double-stranded nucleic acid (RNA1-RNA2-Aptamer), 2 μl EXOIII, and 20 μl 10× buffer to the control reaction system The final concentration of EXOIII was 15U / L and the final concentrations of the serially diluted bacterial solution were 0, 1, 10, 10 2 , 10 3 , 10 4 , 10 5 , 10 6 , 10 7 , and 10 8 CFU / ml to obtain a reaction mixture solution.
[0133] After measuring the initial absorbance of the reaction mixture solution with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, the above reaction mixture solution was incubated in a 37° C. incubator for 2 hours, and the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com