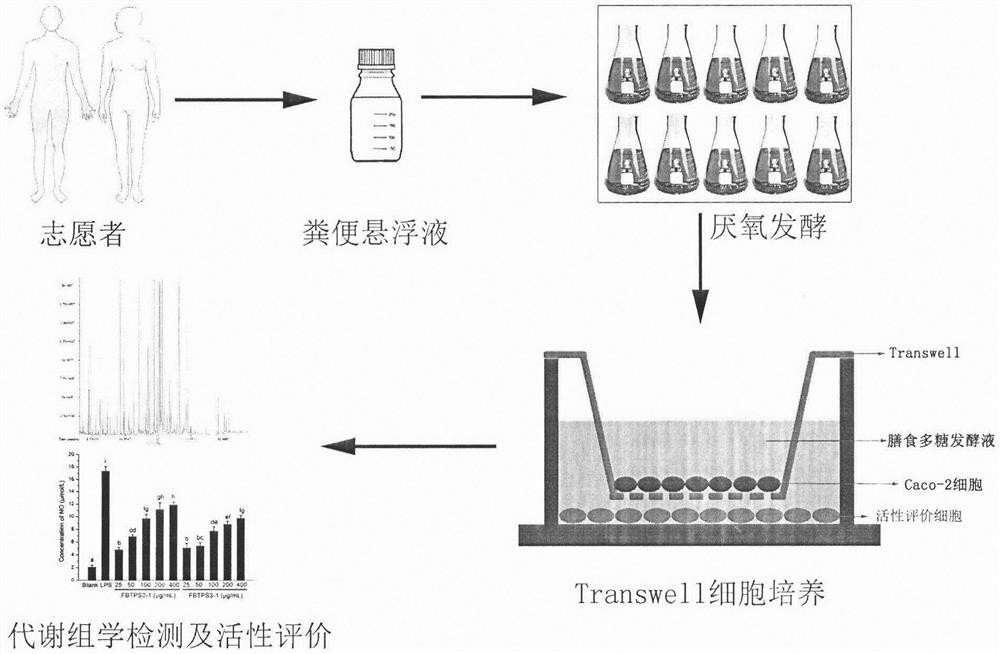
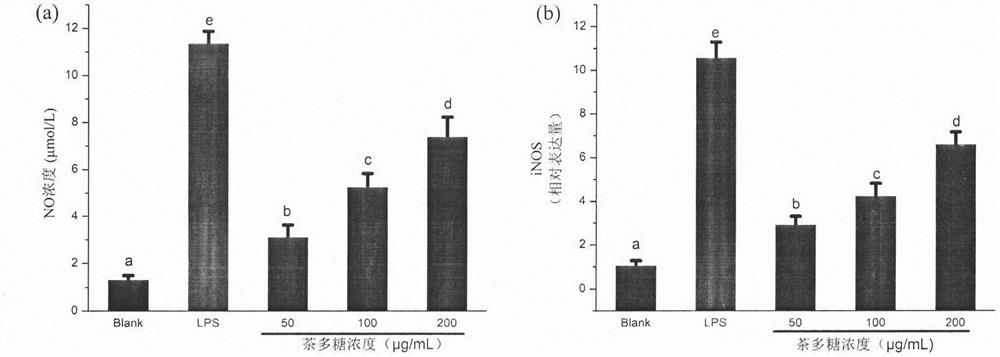
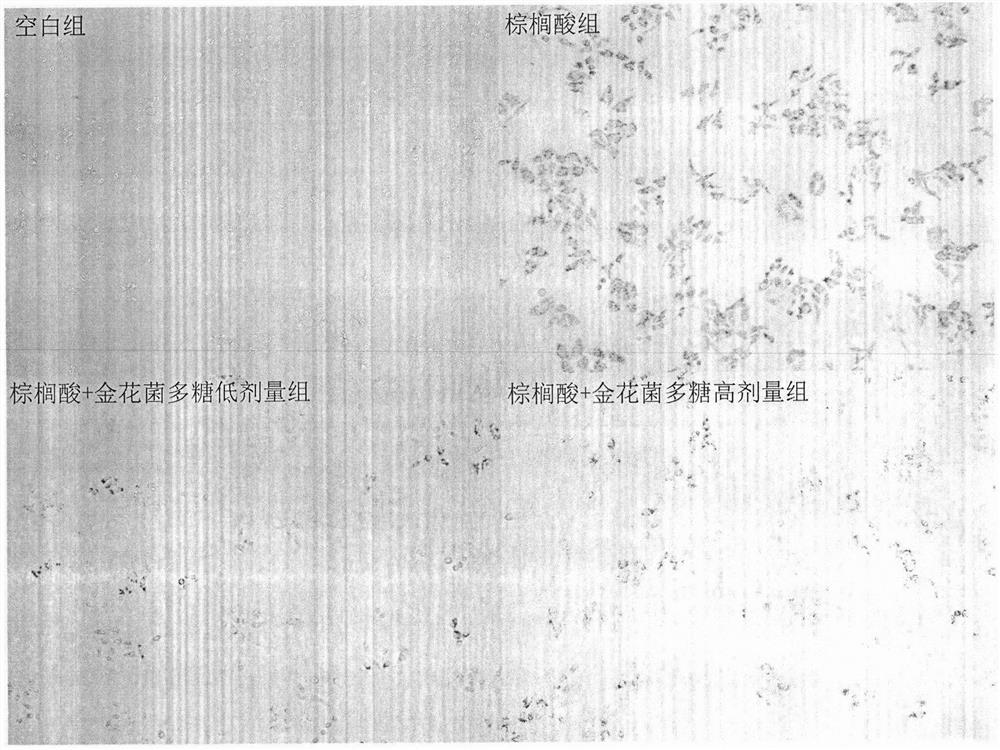
Method for evaluating activity of dietary polysaccharide
A polysaccharide and diet technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that the biological activity of dietary polysaccharides cannot be accurately reflected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] (1) Replace the carbon source glucose in the microbial basal medium with tea polysaccharide, that is, the medium contains: tea polysaccharide 10g / L, peptone 2.0g / L, yeast extract 2.0g / L, sodium chloride 0.1g / L, phosphoric acid Dipotassium hydrogen 0.04g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.04g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.01g / L, calcium chloride 0.01g / L, sodium bicarbonate 2.0g / L, hemin 0.02g / L, semi Cystine hydrochloride 0.5g / L, bile salt 0.5g / L, resazurin 1.0g / L, Tween 80 2.0mL / L and vitamin K1 10μL / L;
[0020] (2) Fermented stool samples in vitro were provided by 4 healthy volunteers (2 males and 2 females, aged 22 to 28 years old). The volunteers had not taken antibiotics or probiotics within 3 months and had no gastrointestinal diseases. Immediately after each volunteer collected 5g of fresh feces, mixed with 45g of normal saline (NaCl 8.5g / L, cysteine hydrochloride 0.5g / L), stirred evenly, and centrifuged (250rmp) to obtain a 10% feces suspension;
[0021] (3) Take 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Replace the carbon source glucose in the microbial basal medium with mycopolysaccharide, that is, the medium contains: 10g / L of mycopolysaccharide, 2.0g / L of peptone, 2.0g / L of yeast extract, and 0.1g of sodium chloride / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.04g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.04g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.01g / L, calcium chloride 0.01g / L, sodium bicarbonate 2.0g / L, hemin 0.02g / L, cysteine hydrochloride 0.5g / L, bile salt 0.5g / L, resazurin 1.0g / L, Tween 80 2.0mL / L and vitamin K1 10μL / L;
[0027] (2) Fermented stool samples in vitro were provided by 4 healthy volunteers (2 males and 2 females, aged 22 to 28 years old). The volunteers had not taken antibiotics or probiotics within 3 months and had no gastrointestinal diseases. Immediately after each volunteer collected 5g of fresh feces, mixed with 45g of normal saline (NaCl 8.5g / L, cysteine hydrochloride 0.5g / L), stirred evenly, and centrifuged (250rmp) to obtain a 10% feces suspension;
[0028] (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com