Poly(amide-imide) copolymer, composition for thin film and thin film
A technology of imide and copolymer, applied in the field of film composition and film and copolymer, can solve the problems of scratches or breakage on the surface of the film, poor optical properties, insufficient film hardness, etc., and achieve good light transmittance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0056]
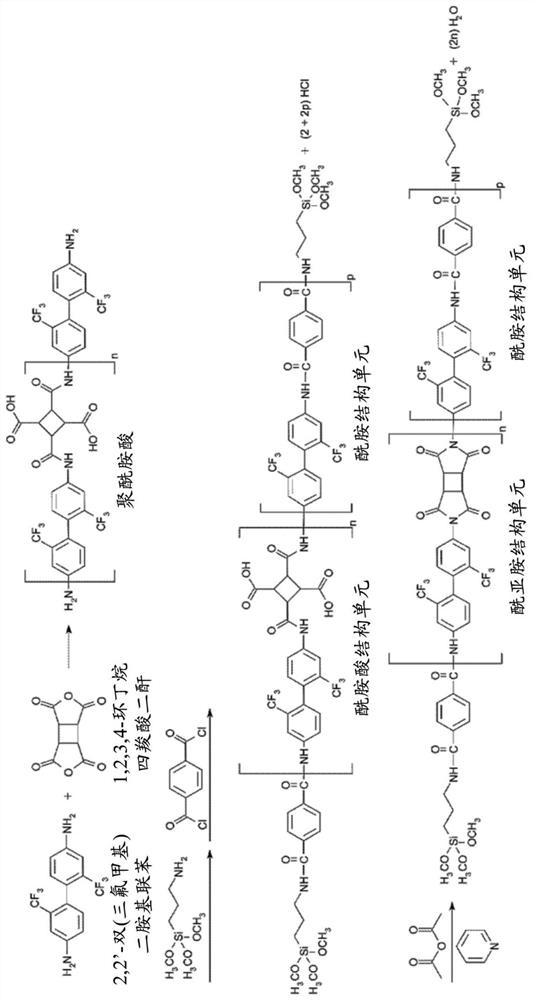
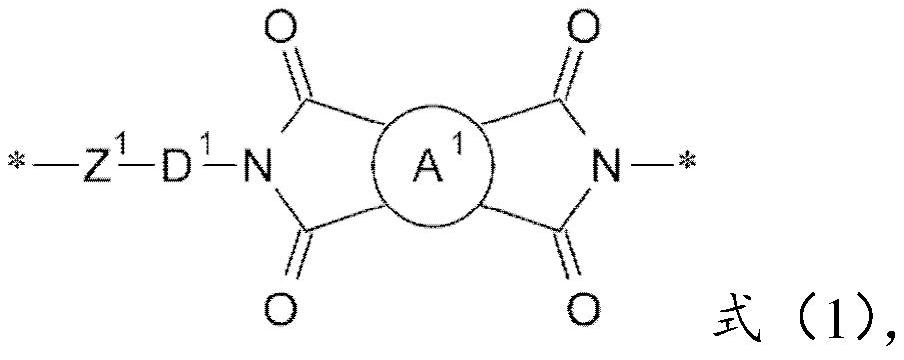
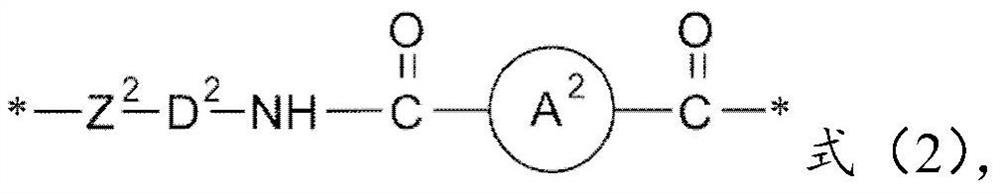
[0057] The aromatic diamine monomer (a1) and the tetracarboxylic dianhydride monomer (a3) can first undergo a polymerization reaction to form a polyamic acid. Then, add alkoxy-containing silane compound (a4) and diacid chloride monomer (a2), and undergo hydrolysis condensation reaction to form poly(amic acid) comprising amic acid structural unit and amide structural unit and having a silane terminal structure -amide) copolymers. Then, the amic acid structural unit in the poly(amic acid-amide) copolymer undergoes a dehydration cyclization reaction to form a poly(amide-imide) comprising an amide structural unit and an imide structural unit and having a silane terminal structure. ) copolymer.
[0058] The polymerization reaction, hydrolysis condensation reaction and dehydration cyclization reaction can be carried out in the presence of a solvent. The solvent is, for example, N-methylpyrrolidone, but the present invention is not limited thereto, and other solvents c...
Synthetic example 1
[0145] When nitrogen is fed into the 1 liter reactor equipped with agitator, nitrogen injection device, dropping funnel, temperature regulator and condenser tube, 669g of N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone (N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone , NMP) into the reactor. Next, after setting the temperature of the reactor to 25° C., 53.49 g (0.167 moles (mol)) of 2,2′-bis(trifluoromethyl)diaminobiphenyl (TFMB) was dissolved in NMP, and The resulting solution was maintained at 25°C. Then, 2.59g (0.009mol) of 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (BPDA), 11.72g (0.026mol) of 4,4'-(hexafluoroisopropene) di Phthalic anhydride (6FDA) and 6.90 g (0.035 mol) of 1,2,3,4-cyclobutanetetracarboxylic dianhydride (CBDA) were stirred for 2 to 4 hours to dissolve and react. Next, the temperature of the solution was maintained at 0-5° C., and then 3.89 g (0.018 mol) of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) was added and stirred evenly. Afterwards, 19.63g (0.097mol) of terephthaloyl chloride (TPC) and 1.78g (0.00...
Synthetic example 2~15
[0148] The preparation methods of Synthesis Examples 2-15 are the same as those of Synthesis Example 1 except for changing the usage amount and type of each component. The composition, usage amount and weight average molecular weight of each synthesis example are listed in Table 1.
[0149]
[0150] In Table 1, the abbreviations are as follows:
[0151] PAI: poly(amide-imide) copolymer
[0152] PA: polyamide
[0153] PI: polyimide
[0154] TFMB: 2,2’-bis(trifluoromethyl)diaminobiphenyl
[0155] ODA: 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether (4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether)
[0156] FDA: 9,9-bis(4-aminophenyl)fluorene (9,9-bis(4-aminophenyl)fluorene)
[0157] APTES: 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane
[0158] APTMS: 3-Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane
[0159] Alink25: 3-isocyanatopropyltriethoxysilane
[0160] CBDA: 1,2,3,4-cyclobutanetetracarboxylic dianhydride
[0161] 6FDA: 4,4'-(hexafluoroisopropylene) diphthalic anhydride
[0162] BPDA: 3,3’,4,4’-Biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride
[016...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yellowness index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com