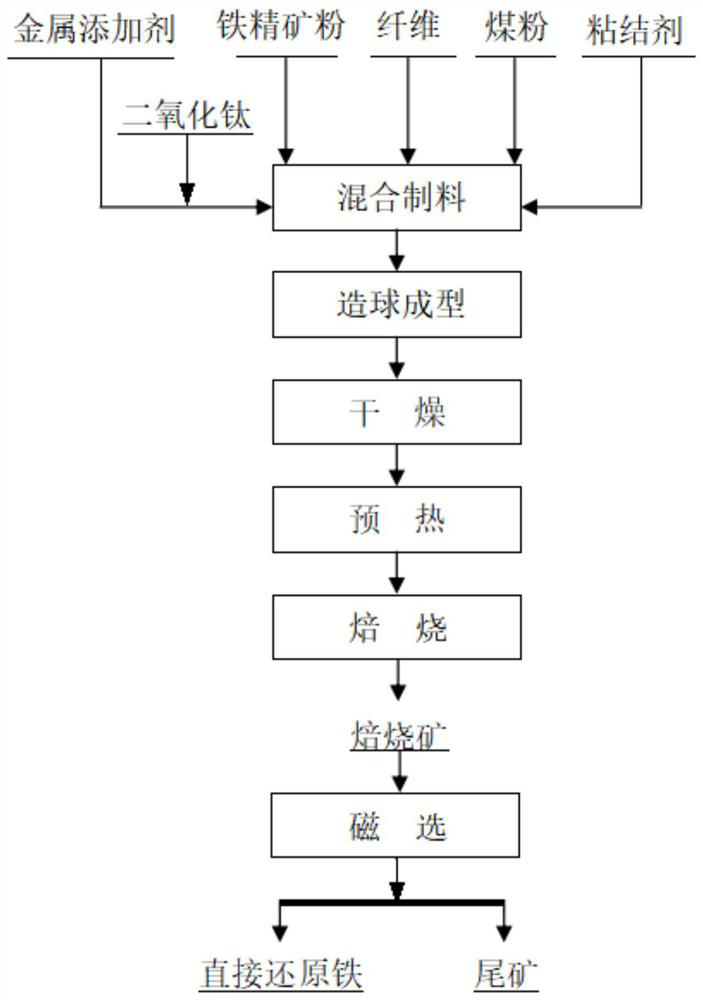
A direct reduction metallurgy method of iron ore based on 3D printing
A 3D printing, direct technology, applied in 3D printing to prepare direct reduced iron, based on 3D printing in the field of iron ore direct reduction metallurgy, can solve the problems of easy powder generation, high reaction temperature, long time, etc., to achieve sufficient gas-solid contact, Reducing the reaction temperature and time, and the effect of increasing the specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] 1) Take 120 parts of hematite ore powder in Brazil, 3 parts of bentonite in India, 0.12 parts of nano-sized titanium dioxide, 0.12 parts of micron-sized vanadium pentoxide, 0.08 parts of micron-sized cerium dioxide, and 24 parts of coal powder in proportion. Stir and mix evenly, and add 0.6 parts of high elastic modulus polyethylene fiber in batches 3 times during the stirring process to obtain the final 3D printing mixture.
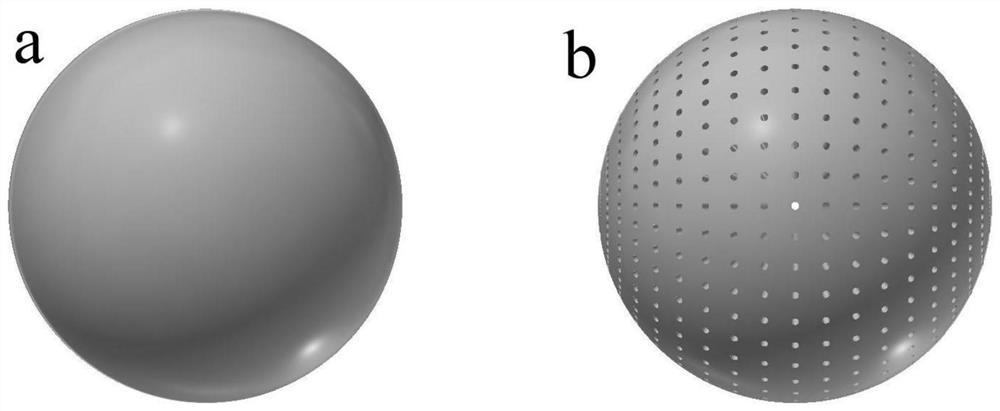
[0101] 2) Then use the 3D printing equipment to print the above-mentioned 3D printing mixture in batches according to the preset programming procedure to prepare honeycomb pellets with a particle size of 10mm, and then place the honeycomb pellets in an oven at 105°C to dry for 3 hours .
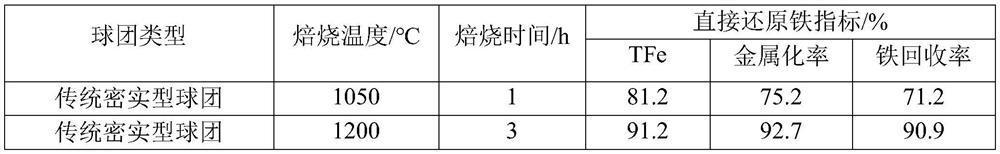
[0102] 3) Then put the above-mentioned dried honeycomb pellets in a muffle furnace to preheat at 600°C for 15 minutes, then raise the temperature of the muffle furnace to 1050°C for roasting for 1 hour, and then directly cool with cold water to obtain roasted ore...
Embodiment 2
[0111] 1) Take 120 parts of magnetite ore powder in Liaoning, 3.5 parts of bentonite in Hunan, 0.18 parts of nano-sized titanium dioxide, 0.12 parts of micron-sized vanadium pentoxide, 0.12 parts of micron-sized cerium dioxide, and 28 parts of coal powder in proportion. Stir and mix evenly, and add 0.8 parts of high elastic modulus polyethylene fiber in batches 4 times during the stirring process to obtain the final 3D printing mixture.
[0112] 2) Then use the 3D printing equipment to print the above-mentioned 3D printing mixture in batches according to the preset programming procedure to prepare honeycomb pellets with a particle size of 12mm, and then place the honeycomb pellets in an oven at 105°C to dry for 3 hours .
[0113] 3) Then put the above-mentioned dried honeycomb pellets in a muffle furnace to preheat at 800°C for 10 minutes, then raise the temperature of the muffle furnace to 1000°C and roast for 1.5 hours, then cool directly with cold water to obtain roasting ...
Embodiment 3
[0121] 1) 120 parts of mixed ore powder (1:1 ratio) of magnetite in Liaoning and hematite concentrate in Australia, 4.0 parts of bentonite in Hunan, 0.2 parts of nano-sized titanium dioxide, and micron-sized pentoxide were measured in proportion. 0.1 part of vanadium, 0.04 part of micron-sized tungsten trioxide, 0.08 part of micron-sized cerium oxide, and 30 parts of coal powder are stirred and mixed evenly. During the stirring process, 0.8 parts of polyurethane elastic fiber are added in batches to obtain the final 3D printing mixture. material.
[0122] 2) Then use the 3D printing equipment to print the above-mentioned 3D printing mixture in batches according to the preset programming procedure to obtain honeycomb pellets with a particle size of 11mm, and then place the honeycomb pellets in an oven at 105°C to dry for 3 hours .
[0123] 3) Then put the above-mentioned dried honeycomb pellets in a muffle furnace for preheating at 700°C for 12 minutes, then raise the temperat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com