Modification method of gelatin
A modified gelatin technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory biomedical materials, unsatisfactory application scenarios, incompatible chemical reagents, etc., and achieve easy control of reaction parameters, simple modification methods, and degradable strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
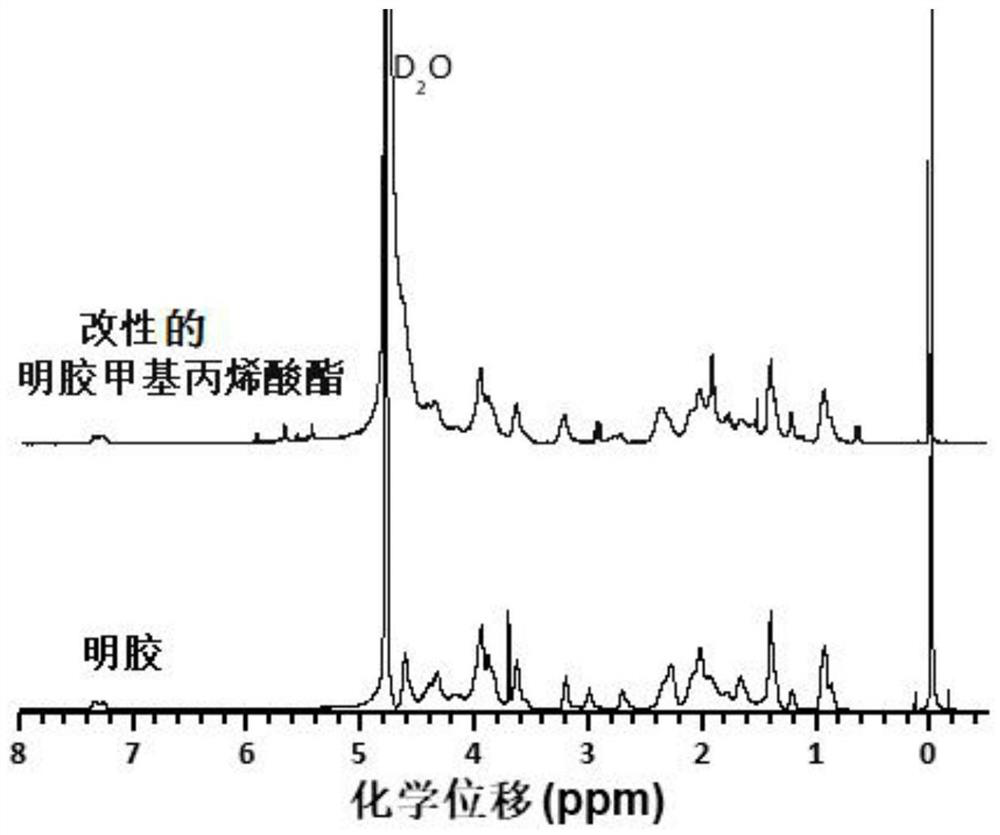
[0053] 10.0 g of gelatin was added to 100 mL of deionized water to a final concentration of 10% (w / v), and placed in a round bottom flask with a magnetic stirring bar. The resulting mixture was stirred moderately in a 50 °C water bath for 30 minutes to facilitate dissolution of the gelatin until the solution became clear when the gelatin was completely dissolved. Then, while stirring, slowly add 1.0 g of methacrylic anhydride (dropping speed: 0.02 mL / min) into the round bottom flask to obtain methacrylate functionalized gelatin, i.e. modified gelatin methacrylic acid ester. Due to the addition of methacrylic anhydride, the solution will become homogeneous and opaque, make sure to stir well during the reaction, while minimizing the absorption of air, because insufficient stirring will lead to phase separation of the solution. After the addition of methacrylic anhydride was complete, the reaction was stirred for 5 hours while using 7 mL of 1M NaHCO 3 The solution adjusted the ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] 10.0 g of gelatin was added to 100 mL of deionized water to a final concentration of 10% (w / v), and placed in a round bottom flask with a magnetic stirring bar. The resulting mixture was stirred moderately in a 50 °C water bath for 30 minutes to facilitate dissolution of the gelatin until the solution became clear when the gelatin was completely dissolved. Then, while vigorously stirring, slowly add 0.6 g of methacrylic anhydride (dropping rate: 0.30 mL / min) into the round bottom flask to obtain methacrylate functionalized gelatin, namely modified gelatin methyl Acrylate. Due to the addition of methacrylic anhydride, the solution will become homogeneous and opaque, make sure to stir well during the reaction while minimizing the absorption of air. After the addition of methacrylic anhydride was complete, the reaction was stirred for 3 hours while using 5 mL of 1M NaHCO 3 The solution adjusted the pH of the reaction solution to 7. After the reaction, transfer the react...
Embodiment 3
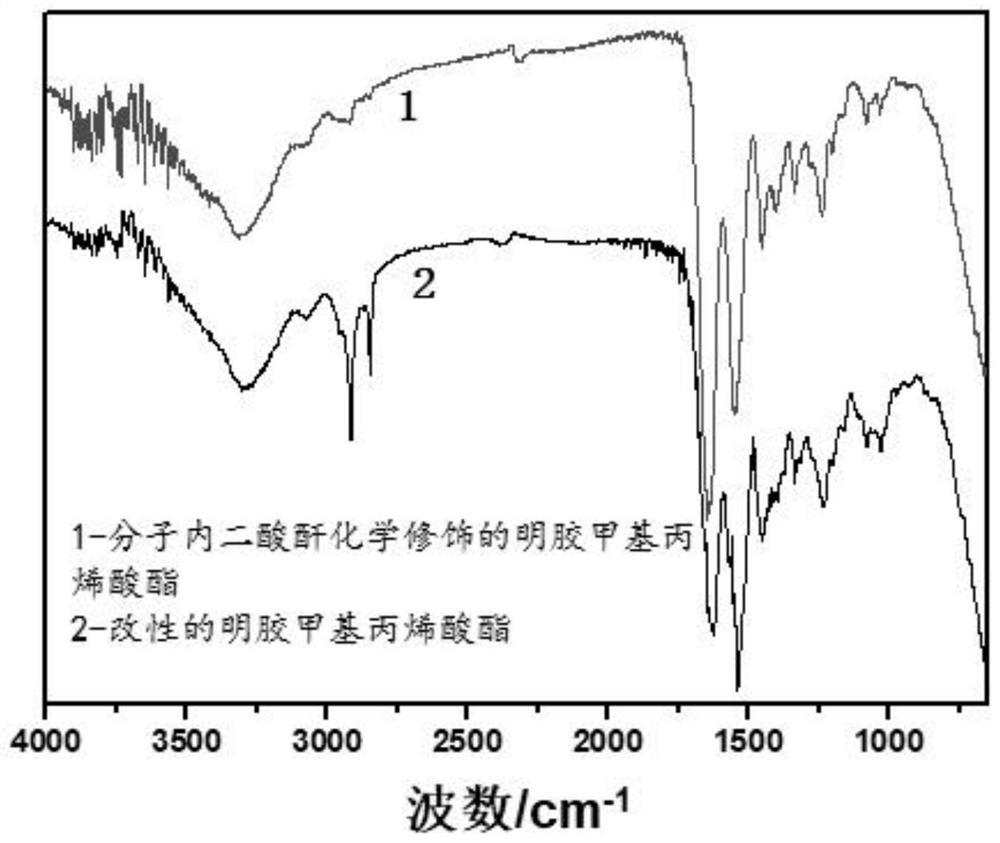
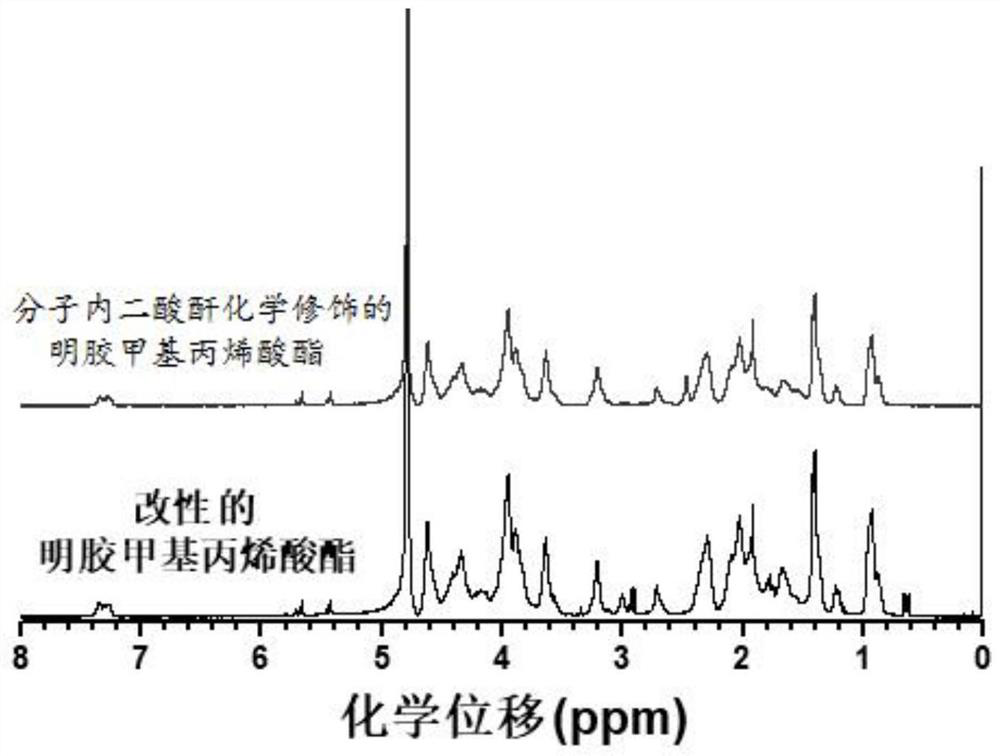
[0058] Take 1.0 g of the modified gelatin methacrylate with a medium degree of substitution obtained in Example 1 and dissolve it in 20 mL of deionized water, heat and stir in a water bath at 50° C. for 40 minutes to dissolve the modified gelatin methacrylate to form a uniform modified gelatin methacrylate. Aqueous gelatin methacrylate aqueous solution, prepared as a solution with a mass fraction of 5%; add 0.5mL triethylamine to adjust the pH value of the reaction solution to 8, and dissolve 0.5g succinic anhydride in 10mL dimethyl sulfoxide Add it into the uniform and transparent solution, the dropping rate is 0.1g / min, so that the molar ratio of the modified gelatin methacrylate to succinic anhydride is 1:10, and the reaction temperature is 50°C under magnetic stirring for 18h, with 0.1 The HCl solution of M adjusts the pH value of the reaction solution to neutrality. The obtained crude product was centrifuged at 3500g for 3 minutes, and the supernatant was dialyzed in deio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com