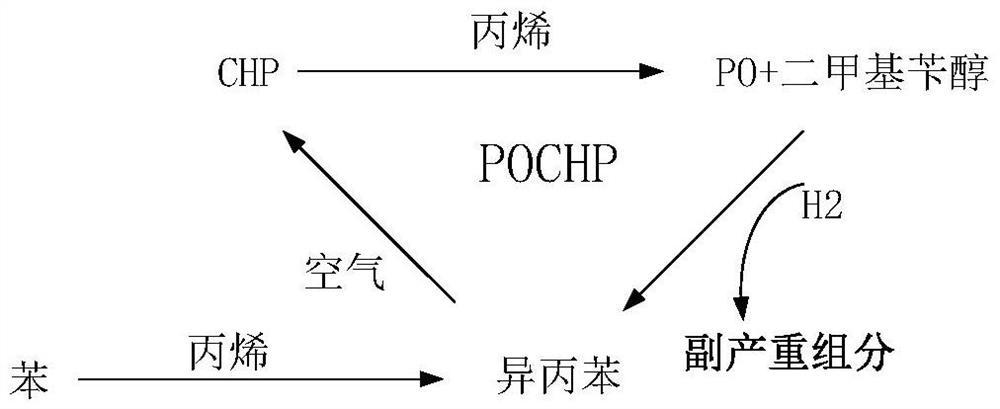
A method for reducing the unit consumption of cumene in the process of producing propylene oxide by co-oxidation of cumene
A technology of propylene oxide and co-oxidation method, which is applied in the production of bulk chemicals, chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of cumene loss, economic benefit reduction, and increased cumene loss, etc. achieve low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] The preparation of palladium / foamed carbon catalyst in the embodiment:
[0045] The foamed carbon prepared by using coal and coal-based substances as raw materials is used as a carrier: 99.5 g of the prepared foamed carbon is taken and placed in a three-necked bottle, and a small amount of distilled water is added for dispersion. The chloropalladium acid solution containing 0.5 g of Pd was added to a three-necked flask under stirring conditions at 40 °C in a water bath for adsorption. After adsorption, excess formaldehyde was added to a water bath at 60 °C for reduction for 6 hours. After suction filtration and washing, it was dried at 400 °C for 4 hours under nitrogen atmosphere. The carbon foam supported Pd catalyst A was obtained, and the loading amount of Pd was 0.5%.
[0046] Catalyst B with a Pd loading of 0.1% was prepared by changing the loadings of the carrier and chloropalladic acid.
Embodiment 1
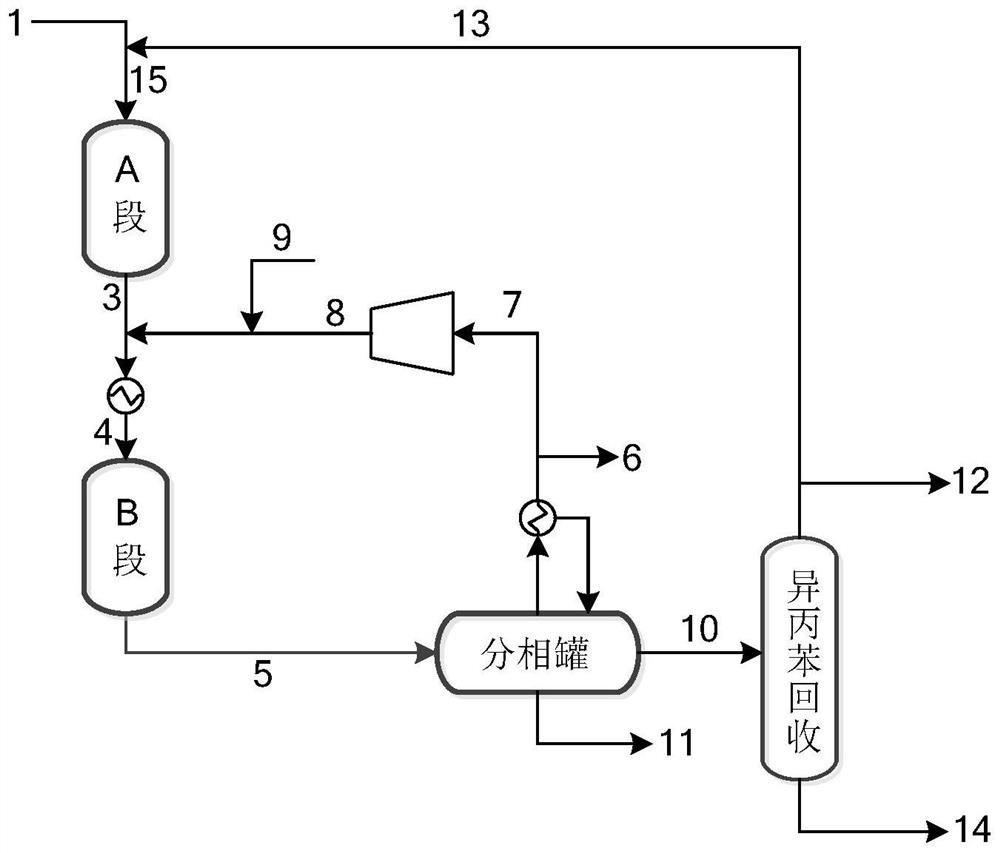
[0048] The cumene heavy component stream 1 obtained by rectifying and recovering cumene in the dimethylbenzyl alcohol hydrogenolysis reaction solution contains 9.0% cumene, 21.0% dimethylbenzyl alcohol, 24.0% 2 - Phenyl-n-propanol, 45% cumene.
[0049] The hydrogenation reactor was charged with 0.5% Pd-loaded catalyst A on foamed carbon.
[0050] (a) The cumene heavy component stream 1 enters from the upper end of the cracking reactor. The temperature of the cracking reactor is 300°C, the reaction pressure is 1.0MPaG, and the volumetric space velocity is 2.0h -1 , wherein heavy components such as cumene take place rapid cracking reaction to generate the logistics 3 containing cumene, α-methylstyrene (AMS);
[0051] (b) material 3 obtains material 4 after being cooled to 50 ℃, material 4 enters the hydrogenation reactor of loading palladium / foamed carbon catalyst A together with circulating hydrogen material 8, fresh hydrogen and feeds material 9, in material 4, α- The hydrog...
Embodiment 2~9
[0055] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0056] Change the pressure, temperature, space velocity of the reactor. The hydrogenation catalyst used was catalyst B. The specific reaction conditions and results are shown in Table 2.
[0057] Table 2 Results of Examples 1 to 9
[0058]
[0059] In the above table, the conversion rates of dimethylbenzyl alcohol and cumene all represent the total reaction effect after passing through the cracking reactor and the hydrogenation reactor. Wherein the dimethyl benzyl alcohol conversion rate test method: measure the mass concentration of the dimethyl benzyl alcohol of logistics 1, logistics 10 respectively, calculate according to the following formula,
[0060]
[0061] Wherein n is the mass flow rate of stream 10 and stream 1, which can be simply calculated according to the following formula. In Examples 1 to 9, n≈3. Since a small amount of water is generated during the cracking reaction, the flow rate calculated by the followi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com