A kind of serum-free medium and application for large-scale cultivation of cho cells
A technology of serum-free culture medium and culture medium, which is applied in the cultivation process, animal cells, tissue culture, etc., to achieve the effect of simple ingredients, low cost, and improvement of clumping phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The preparation of embodiment 1 culture medium and cell line
[0052] Basal medium: DMEM / F12 is a commercial basal medium commonly used in cell culture. The medium is composed of glucose, amino acids, vitamins, inorganic salts and other substances. Available from Sigma, GIBCO, etc.
[0053] On the basis of DMEM / F12, three kinds of serum-free medium for culturing CHO cells of the present invention with different concentration ratios were prepared.
[0054] Component, concentration mg / L Experimental example 1 Experimental example 2 Experimental example 3 AEO-9 100 200 150 cholesterol linoleate 5 10 7 Vitamin C 5 10 8 insulin 2 5 3 Transferrin 5 7 6 Ethanolamine 2 5 3 Lecithin 3 6 5 Choline Sulfate 10 40 25
[0055] Trace elements are all added in the above-mentioned experimental examples 1-3, and the final concentrations of each component of the trace elements are respectively: zinc sulf...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Batch suspension culture of rCHO-GS cells in a 5-liter stirred tank bioreactor
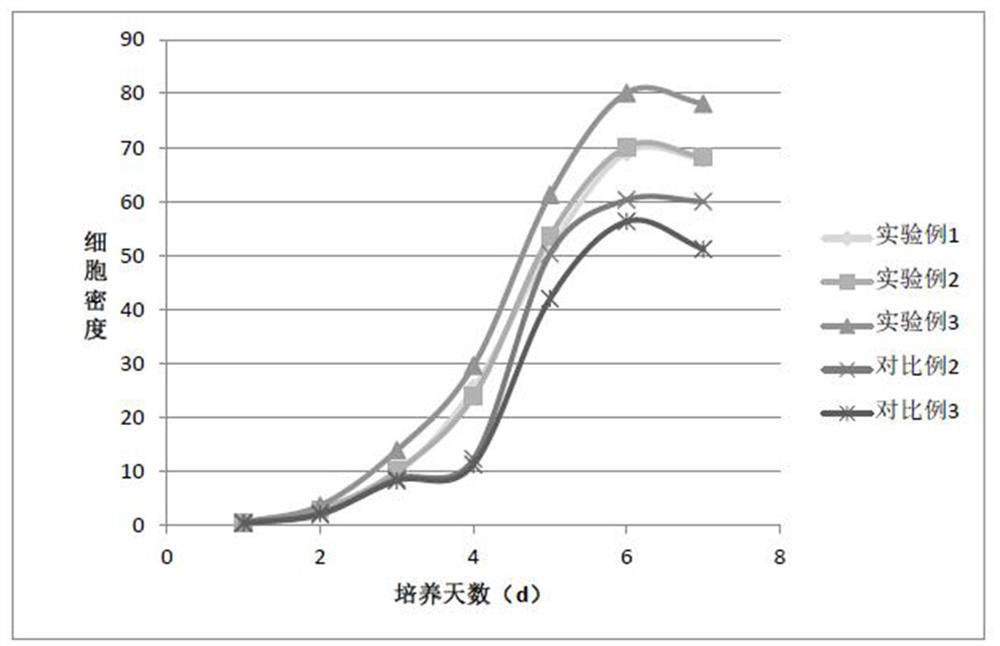
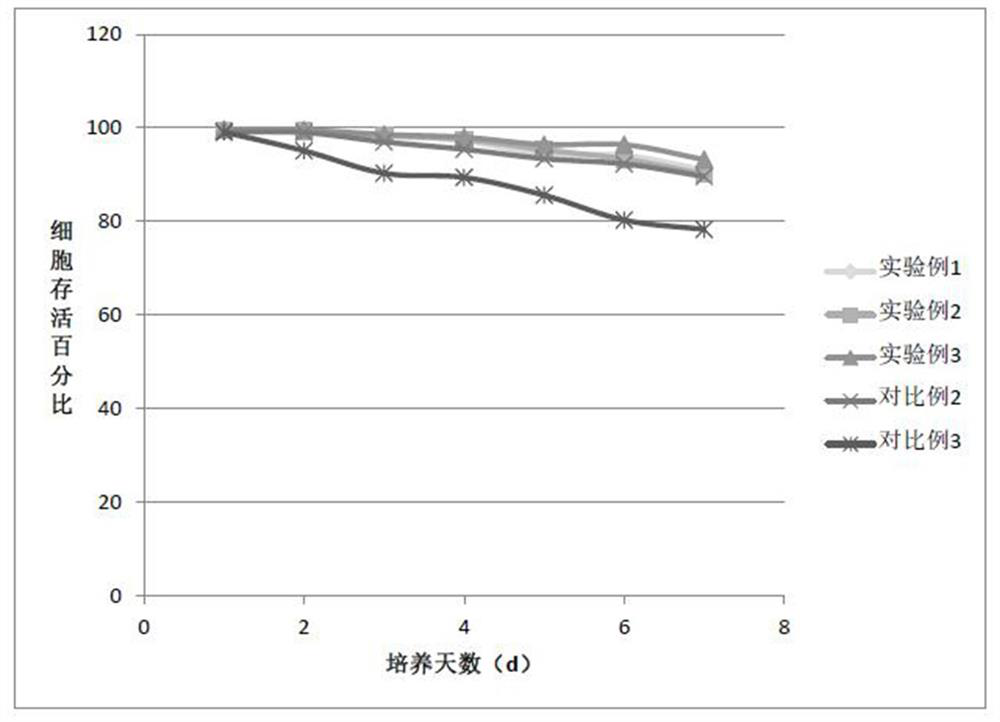
[0062] Cell culture: rCHO-GS cells were suspended and cultured in the medium of Experimental Example 1, Experimental Example 2, Experimental Example 3, Comparative Example 2, and Comparative Example 3 in a 250-m1 stirring flask, at a rate of 3 × 10. 5 cells / ml were inoculated into a 5L stirred tank bioreactor, and the above-mentioned medium was added to the set working volume of 5L. The temperature was set to 37°C, the dissolved oxygen concentration was controlled at 30-50%, the pH was controlled at 7.1-7.2, and the stirring speed was set at 60-70r / min. Samples were taken every day, and the cells were counted with a hemocytometer, and each sample was counted 3 times. , take the average value, and determine the viability of cells by trypan blue exclusion method. The whole culture process lasted 7d. The different results using the above 5 media are shown in Tables 2, 3 and figur...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3 Suspension culture of wild-type CHO cells
[0068] Experimental Example 3 and Comparative Example 3 in Example 2 were repeated, except that rCHO-GS cells were replaced with wild-type CHO cells, ie, CHO-K1ATCC Cat.NO.CC1-61. The experimental results showed that, using the medium of Experimental Example 3, the wild-type CHO cells reached the maximum cell density of 79.5×10 on the sixth day. 6 / mL, Comparative Example 3 also reached the maximum cell density on the sixth day, but only 58.1 × 10 6 / mL. After 7 days of culture, using the medium of Experimental Example 3, the survival rate of wild-type CHO cells was always above 90%. However, using the medium of Comparative Example 3, the survival rate of wild-type CHO cells was only 75.9% on day 7 of culture. It can be seen that using the serum-free medium of the present invention to cultivate rCHO-GS or wild-type CHO cells can achieve better results. Compared with the commercially available CHO serum-free medium ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com