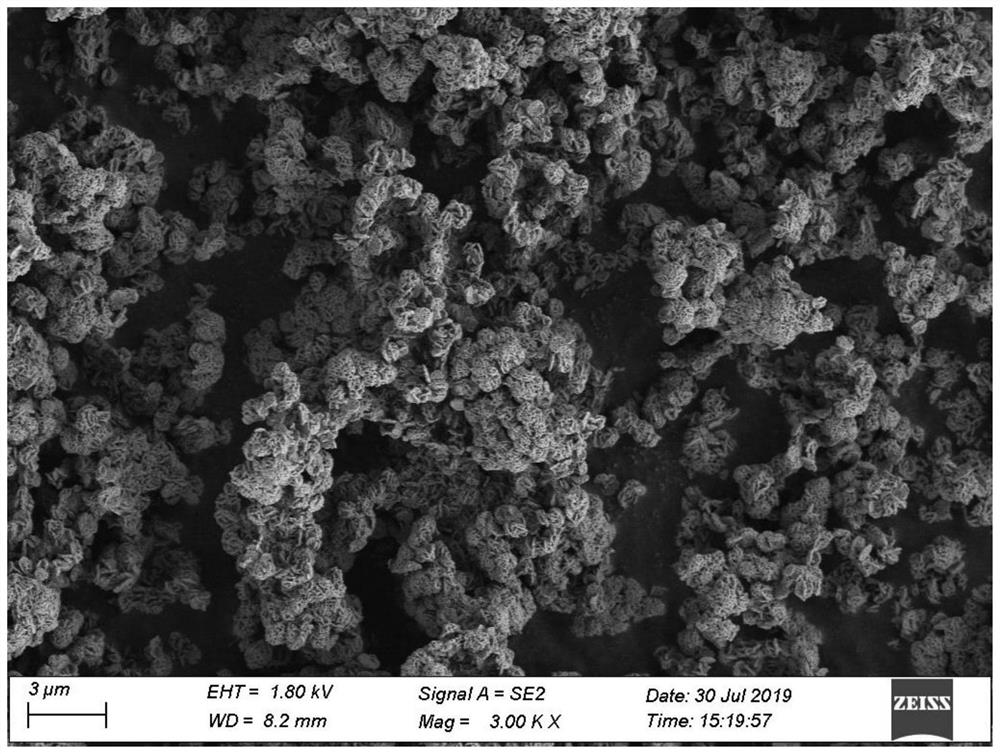
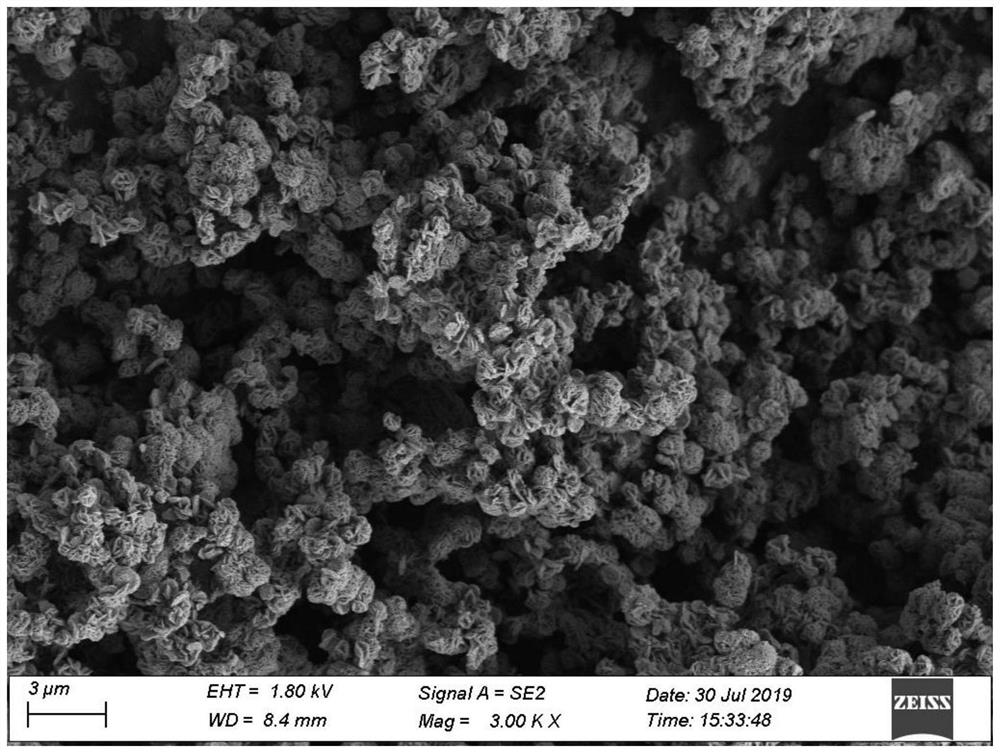
Method for synthesizing iron phosphate by utilizing titanium dioxide byproduct ferrous sulfate
A technology of ferrous sulfate and ferric phosphate, used in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of neglecting the control of sulfur content, potential safety hazards, complicated operations, etc., to improve the utilization rate and increase the concentration. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 of the present invention is: a method for synthesizing ferric phosphate by using ferrous sulfate, a by-product of titanium dioxide, comprising the following steps:
[0047] S1: Pretreatment: Control the temperature at 70°C, add ammonia water with a mass concentration of 30% to the titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate solution, adjust the pH value to 4.2, and press filter to obtain a mass concentration of iron element of 101g / The ferrous sulfate raw material solution of L;
[0048] Add a hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass concentration of 30% into the ferrous sulfate raw material solution, control the molar ratio of hydrogen peroxide and iron element in the ferrous sulfate raw material solution to be 0.6:1, and oxidize all ferrous ions into iron ions Finally, add an appropriate amount of pure water to obtain a ferric sulfate raw material solution with a mass concentration of iron element of 56g / L;
[0049] According to the solid-to-liquid ratio ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2 of the present invention is: a method for synthesizing ferric phosphate by using titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate, comprising the following steps:
[0054] S1: Pretreatment: Control the temperature at 80°C, add a sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 25% to the titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate solution, adjust the pH value to 5.0, and press filter to obtain the mass concentration of iron element as The ferrous sulfate raw material liquid of 87g / L;
[0055] Add a hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass concentration of 30% into the ferrous sulfate raw material solution, control the molar ratio of hydrogen peroxide and iron element in the ferrous sulfate raw material solution to be 0.6:1, and oxidize all ferrous ions into iron ions Finally, add an appropriate amount of pure water to obtain a ferric sulfate raw material solution with a mass concentration of iron element of 67g / L;
[0056] According to the solid-to-liquid ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment three of the present invention is: a method for synthesizing ferric phosphate by using ferrous sulfate as a by-product of titanium dioxide, comprising the following steps:
[0061] S1: Pre-treatment: Control the temperature of the titanium dioxide by-product ferrous sulfate solution to 60°C, add ammonia water with a mass concentration of 30% to the ferrous sulfate solution, adjust the pH value to 3.8, and press filter to obtain the quality of iron element Concentration is the ferrous sulfate raw material solution of 105g / L;
[0062] Add a hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass concentration of 30% into the ferrous sulfate raw material solution, control the molar ratio of hydrogen peroxide and iron element in the ferrous sulfate raw material solution to be 0.6:1, and oxidize all ferrous ions into iron ions Finally, add an appropriate amount of pure water to obtain a ferric sulfate raw material solution with a mass concentration of iron element of 44.8g / L;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com