Composite material taking two-dimensional bio-based material as skeleton unit and processing technology of composite material
A profile and slurry technology, applied in the field of bio-based composite materials, can solve problems such as poor fluidity, low mechanical properties, toughness, and large decline in plastic strength, and achieve low cost, raw materials, and cost-effective advantages.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073]1, selected by commercial sale 80 (thickness 0.1mm) g / m2Kraft paper (the same grams of kraft paper material is the same, no filler, reflection, wherein the cellulose content is 76.24%, the acid-free wood content is 5.76%) Tailor to a certain piece of paper 1, select a plastic film (0.01-0.1mm) Tarrel 2, <100 ° C drying in the same size of the sheet 1.
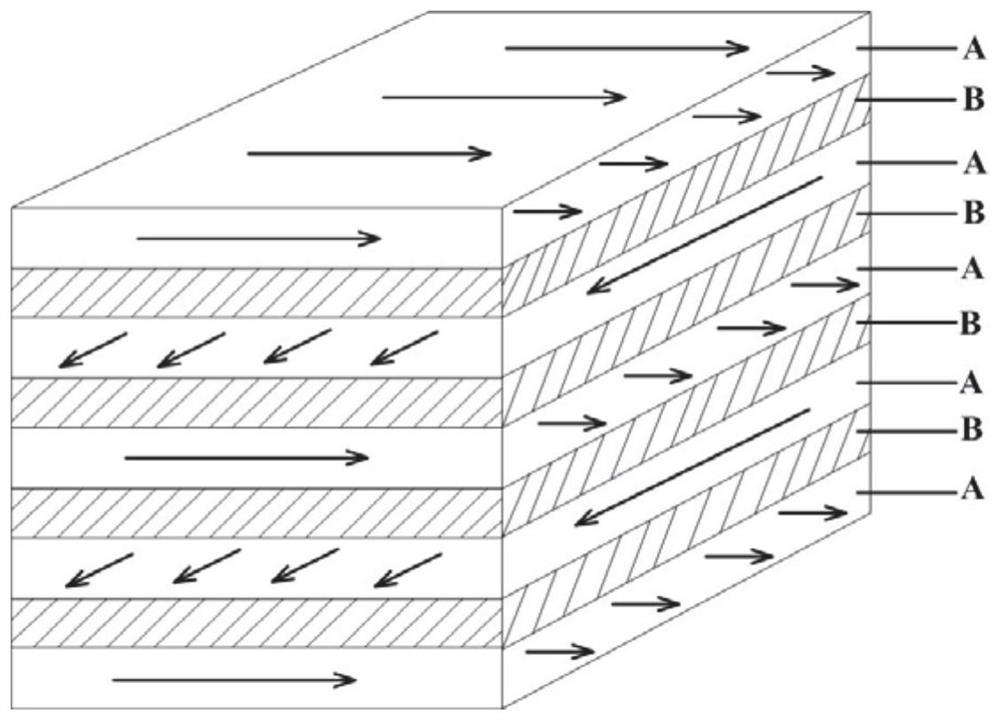
[0074]2. Take 26 sheets 1 and 25 sheets 2 alternately transversely gave a paper skeleton substrate for resin-paper-based composites. Structural schematic view of the paper skeleton substrate of the resin-paper-based compositefigure 1 .
[0075]3, the paper skeleton substrate is hot, and the product is allowed to cool to get the product.
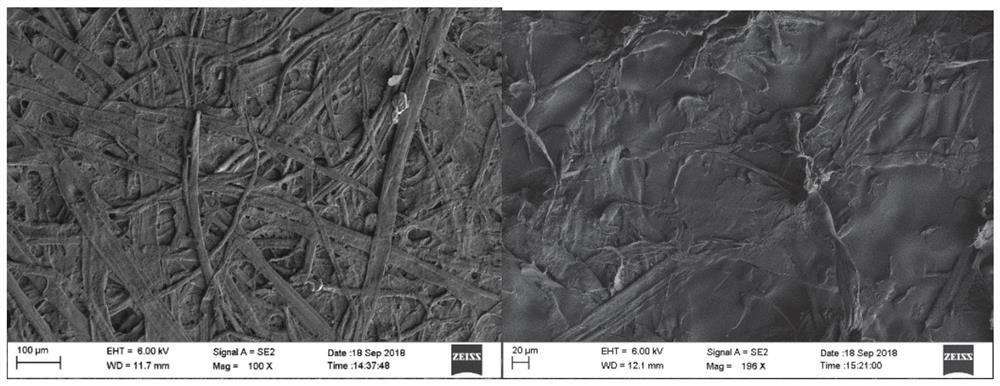
[0076]4, 80g / m2Kraft paper electron microscopy and 20% PP added amount PP-paper-based composite electron microscopic mapfigure 2 .
[0077]5. Profile performance prepared under various conditions is shown in Table 1.
[0078]Table 1 80g / m2Preparation conditions and product performance of PP-paper based...
Embodiment 2
[0087]1, elected 70 (thickness 0.08mm) g / m2Homemade non-admissil, the non-filled kraft paper (the same grams of kraft paper material is the same, wherein the cellulose content is 58.98%, the acid is not soluble, the lactose content is 23.96%) Tailor to a certain specification sheet 1, select commercially available PP Plastic film (0.01-0.1mm) Tailor 2, <100 ° C drying in the same size of the sheet 1, select the commercially available PVA, the degree of polymerization of 1700-1800, the molecular weight 84000-89000, the 3% solution, and take the film 2 Quantitative infiltration PVA solution, <70 ° C drying to obtain film 3 for use.
[0088]2, take 26 sheet of paper 1, with 25 sheet 2 or film 3 alternately cross and vertically gave a paper skeleton substrate of the resin-paper-based composite.
[0089]3, the paper skeleton base material is thermocompressed, and the product is allowed to obtain the product, and the product performance under various conditions is shown in Table 3-5.
[0090]4, ...
Embodiment 3
[0103]1, elected 70 (thickness 0.08mm) g / m2Kraft paper (wherein the cellulose content is 58.98%, the acid-free wood content is 23.96%) Trip into a certain specification sheet 1, select a commercially available PVC film (0.01-0.1mm) Trip into a film with the same specification of the sheet 1 2, 100 ° C drying spare.
[0104]2, capture the sheet 1 and the film 2 vertically to 25 sheets of the paper skeleton substrate to obtain a resin-paper-based composite material.
[0105]3, the paper skeleton substrate is thermocompressed, and the product obtained by the preparation of the product, the performance of the materials obtained is shown in Table 6.
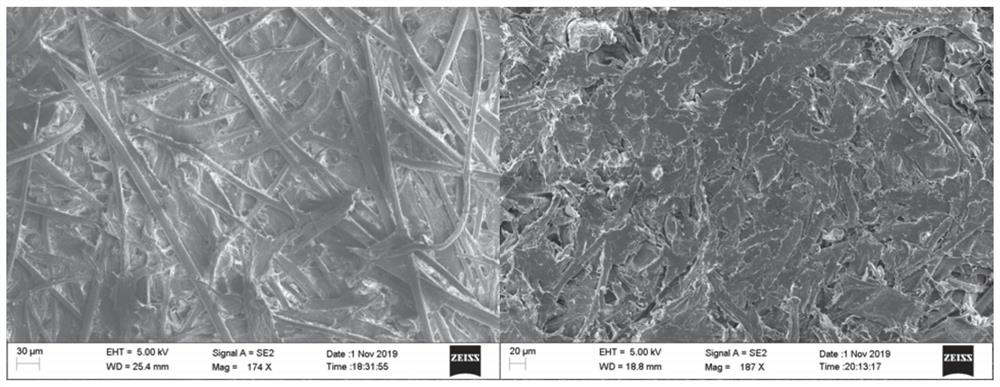
[0106]4, 70g / m2Kraft paper electron microscopy and 40% PVC added amount of PVC-paper-based composite electron microscopyFigure 4 .
[0107]Table 6 70g / m2Self-made kraft paper for raw material PVC-paper-based material preparation conditions and product performance
[0108]
[0109]As can be seen from Table 6, 70 g / m can be used2The natural paper is ra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com