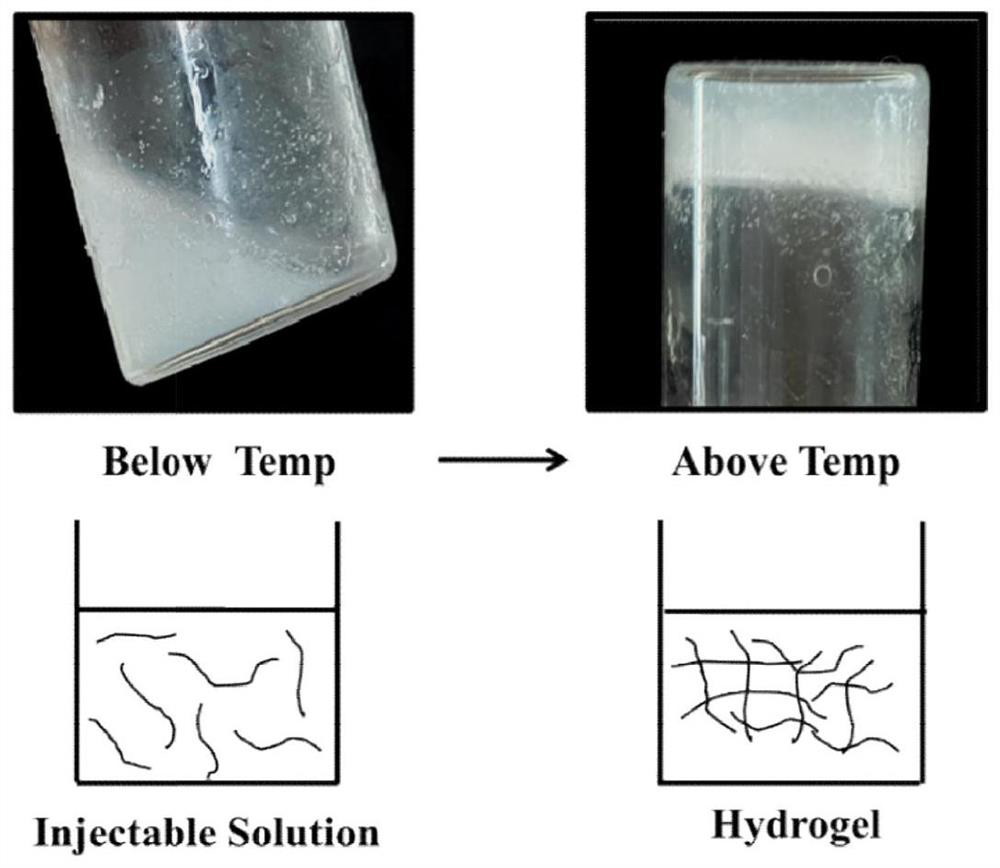
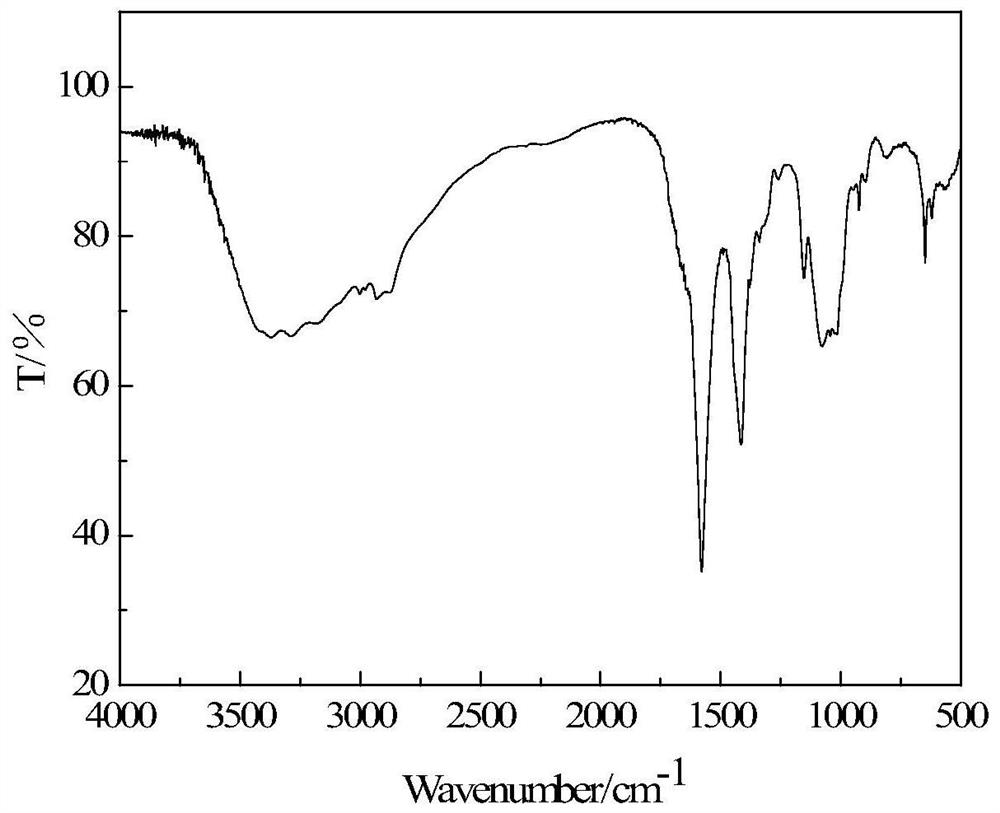
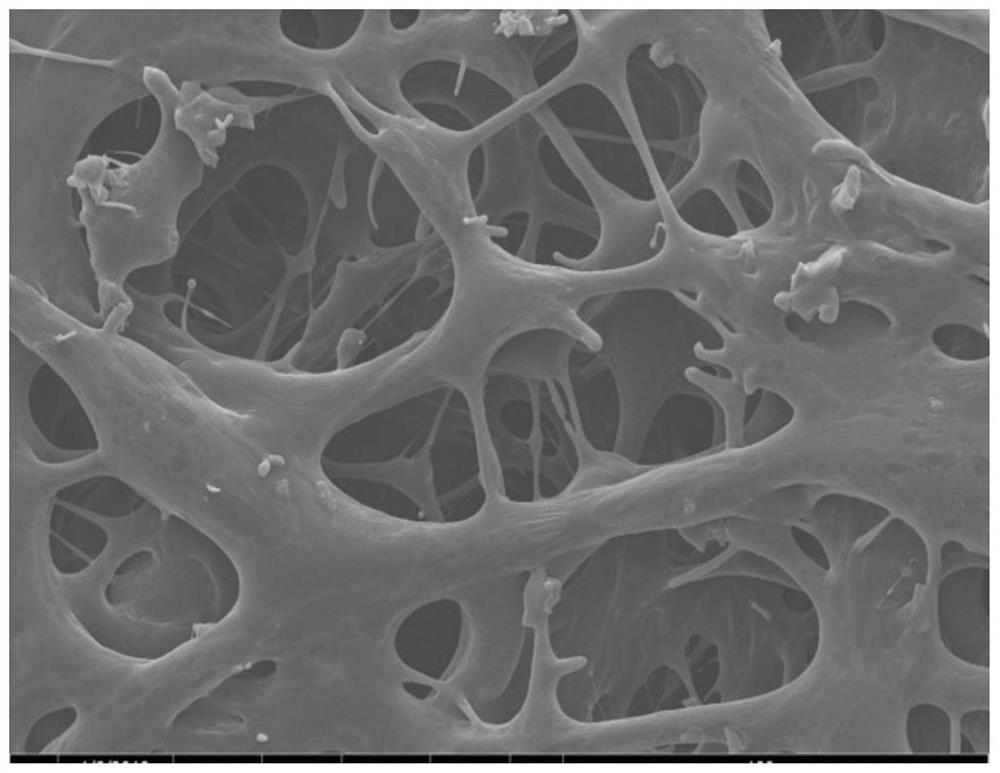
Preparation method and application of implantable in-situ formed chitosan hydrogel
A technology of in-situ molding and chitosan, which can be applied to medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulas, etc., and can solve problems such as safety retention that limits the development of implantable materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A kind of preparation method of chitosan hydrogel that can be implanted in situ molding of the present invention, specifically implement according to the following steps:
[0050] Step 1, chitosan is dissolved in the acetic acid solution, obtains the acetic acid solution of chitosan;
[0051] The massfraction of acetic acid solution is 1%; The concentration of chitosan in acetic acid solution is 20mg / mL;
[0052] Step 2, using N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAm) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AMPS) free radical polymerization to prepare polyanionic PNAM, specifically:
[0053] Dissolve the monomer NIPAm and the monomer AMPS in the mixed solvent, and then put the initiator under N 2 Protected, and added dropwise to the mixed solvent under constant temperature stirring at 60°C. After the dropwise addition, the sealed system was reacted for 24 hours, and the reaction liquid was transferred to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500Da for dialysis ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A kind of preparation method of chitosan hydrogel that can be implanted in situ molding of the present invention, specifically implement according to the following steps:
[0063] Step 1, chitosan is dissolved in the acetic acid solution, obtains the acetic acid solution of chitosan;
[0064] The massfraction of acetic acid solution is 1%;
[0065] The concentration of chitosan in acetic acid solution is 15mg / mL; the viscosity of chitosan is medium viscosity chitosan;
[0066] Step 2, using N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAm) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AMPS) free radical polymerization to prepare polyanionic PNAM, specifically:
[0067] Dissolve the monomer NIPAm and the monomer AMPS in the mixed solvent, and then put the initiator under N 2 Protected, and added dropwise to the mixed solvent under constant temperature stirring at 60°C. After the dropwise addition, the sealed system was reacted for 24 hours, and the reaction liquid was transferred to a di...
Embodiment 3
[0076] A kind of preparation method of chitosan hydrogel that can be implanted in situ molding of the present invention, specifically implement according to the following steps:
[0077] Step 1, chitosan is dissolved in the acetic acid solution, obtains the acetic acid solution of chitosan;
[0078] The massfraction of acetic acid solution is 1%;
[0079] The concentration of chitosan in acetic acid solution is 20mg / mL; chitosan is high viscosity chitosan (>400mPa.s);
[0080] Step 2, using N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAm) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AMPS) free radical polymerization to prepare polyanionic PNAM, specifically:
[0081] Dissolve the monomer NIPAm and the monomer AMPS in the mixed solvent, and then put the initiator under N 2 Protected, and added dropwise to the mixed solvent under constant temperature stirring at 60°C. After the dropwise addition, the sealed system was reacted for 24 hours, and the reaction liquid was transferred to a dialysis ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com