Preparation method of slowly digestible starch with loose structure
A slow-digesting starch and loosening technology, applied in the field of starch processing, can solve the problems of high molecular weight, low palatability and high hardness of modified products, and achieve the effect of improving bad taste and expanding practical application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A preparation method of SDS with loose structure, the steps are as follows:
[0024] (1) Enzyme extrusion: prepare cornstarch with a high branched chain ratio: 8:1 (w / w), and adjust its moisture content to 20wt%. Gradient heating co-extrusion of high-temperature-resistant α-amylase solution (5U / g) and compounded corn starch: the temperature distribution is 60°C, 70°C, 80°C, 90°C and 100°C, and the screw speed is set 250r / min;
[0025] (2) Transglycoside reaction: Add 90 U / g of glucosidase to the amyloid prepared in step (1), stir in acetate buffer (pH 5.2) at 50°C for 12 hours, and then bake Dry to a moisture content of 30wt%;
[0026] (3) Temperature-controlled crystallization: the dried amyloid was lowered to 10°C at a cooling rate of 0.1°C / min, and stored at this temperature for 8 days. Grinding after freeze-drying, and passing through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain the SDS with loose structure;
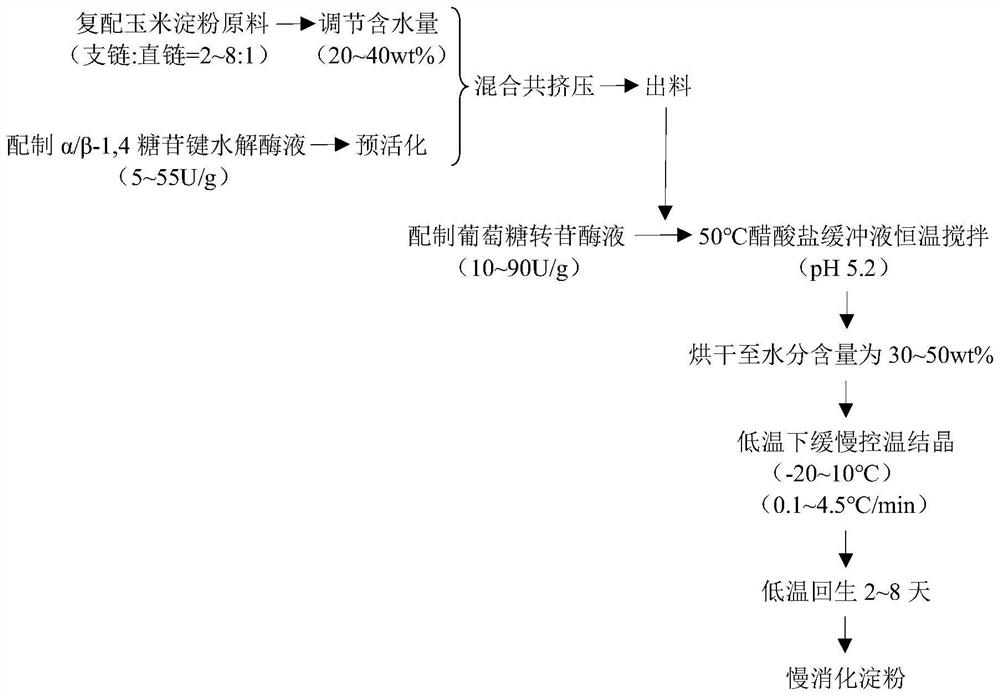
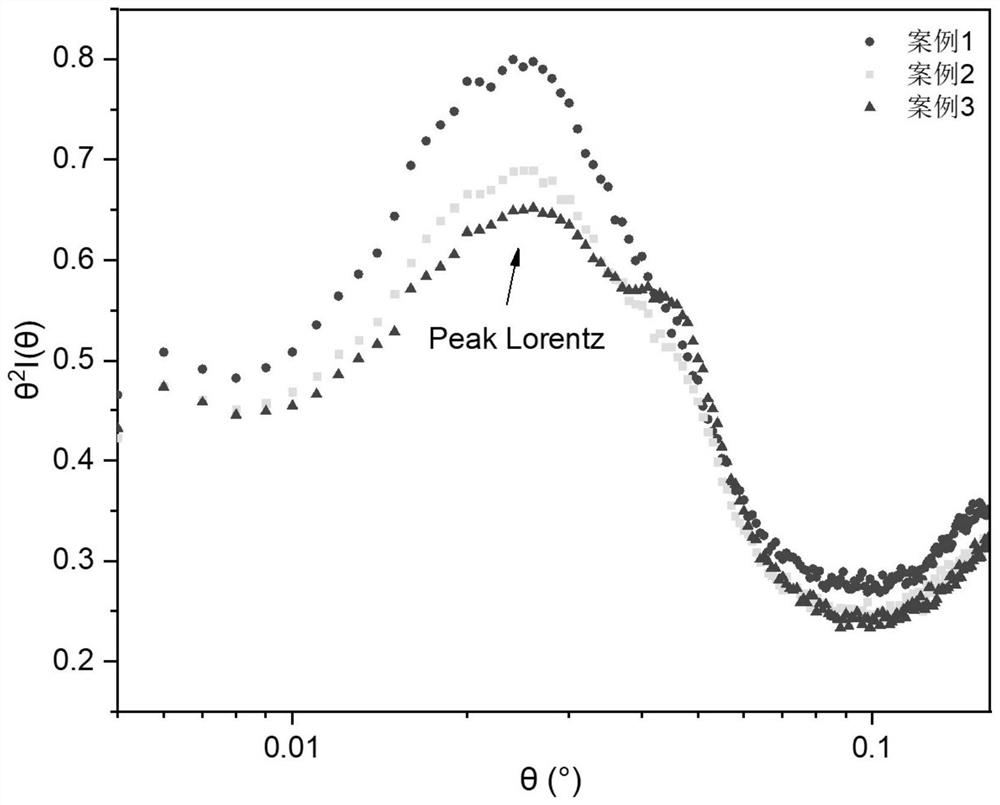
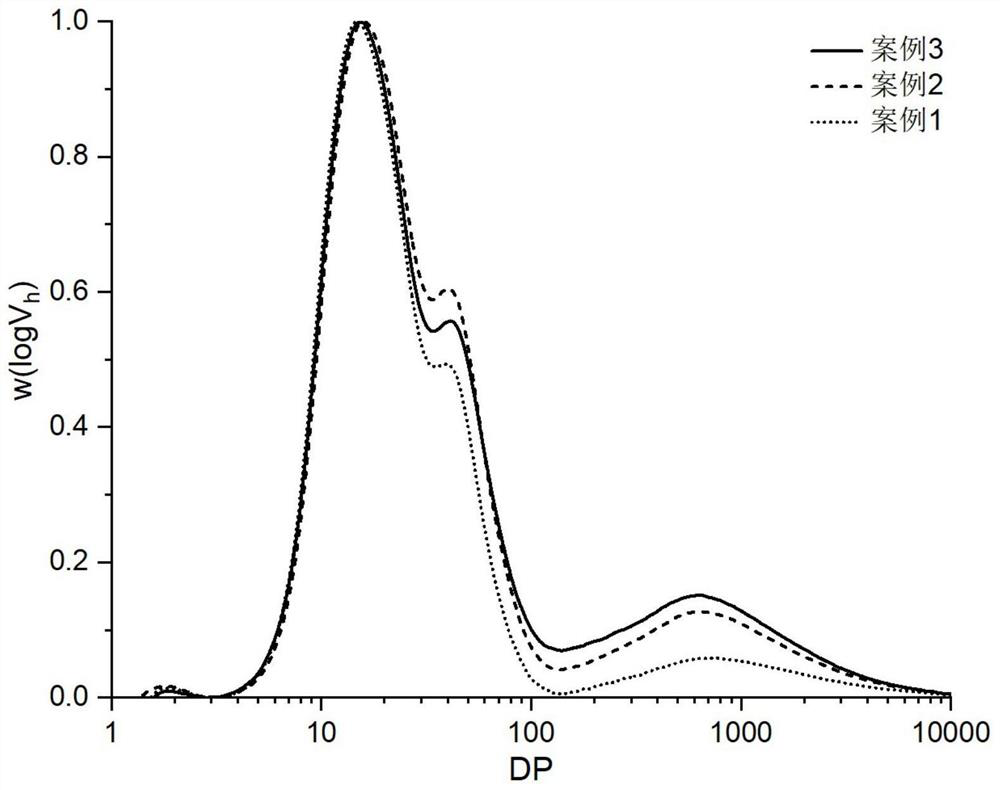
[0027] (4) Long-term detection of crystals: small angle X-ray scatteri...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A preparation method of SDS with loose structure, the steps are as follows:
[0038] (1) Extrusion with enzyme: prepare cornstarch with high branched chain ratio: 5:1 (w / w), and adjust its moisture content to 30wt%. The medium temperature α-amylase solution (25U / g) and the compounded corn starch were subjected to gradient temperature co-extrusion: the temperature zone distribution was 50°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C and 90°C, and the screw speed was set to 150r / min;
[0039] (2) Transglycoside reaction: Add 50 U / g of glucosidase to the amyloid prepared in step (1), stir in acetate buffer solution (pH 5.2) at 50°C for 12 hours at a constant temperature, and then bake Dry to a moisture content of 40wt%;
[0040] (3) Temperature-controlled crystallization: the dried amyloid was lowered to 0°C at a cooling rate of 2.5°C / min, and stored at this temperature for 5 days. Grinding after freeze-drying, and passing through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain the SDS with loose structure;
[0041]...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A preparation method of SDS with loose structure, the steps are as follows:
[0052] (1) Enzyme extrusion: prepare cornstarch with a high branched chain ratio: 2:1 (w / w), and adjust its moisture content to 40wt%. The β-amylase solution (55U / g) and the compounded corn starch were subjected to gradient temperature co-extrusion: the temperature zone distribution was 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, 70°C and 80°C, and the screw speed was set at 50r / min;
[0053] (2) Transglycoside reaction: Add 10 U / g of glucosidase to the amyloid prepared in step (1), stir in acetate buffer (pH 5.2) at 50°C for 12 hours, and then bake Dry to a moisture content of 50wt%;
[0054] (3) Temperature-controlled crystallization: the dried amyloid was lowered to -20°C at a cooling rate of 4.5°C / min, and stored at this temperature for 2 days. Grinding after freeze-drying, and passing through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain the SDS with loose structure;
[0055] (4) Crystal long-term detection: SAXS was used to de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com