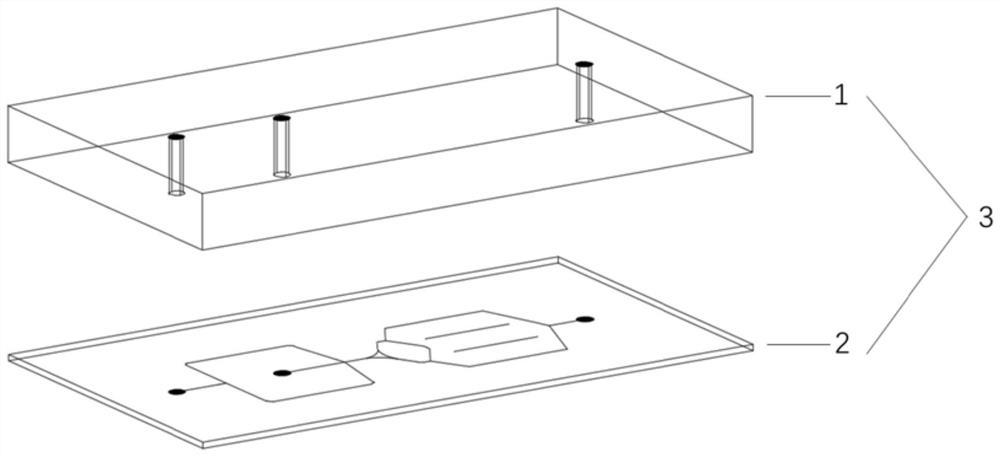
Photocuring micro-fluidic chip based on elastic support body and preparation method and application thereof
A microfluidic chip and elastic support technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, laboratory containers, laboratory utensils, etc., can solve chip cutting, punching, inconvenient connection of external pipelines, increasing equipment, processing technology Complexity and cost, poor flexibility of light-cured materials, etc., to achieve the effect of easy connection of external pipelines, good potential for mass production, and the elimination of PDMS mold processing links
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
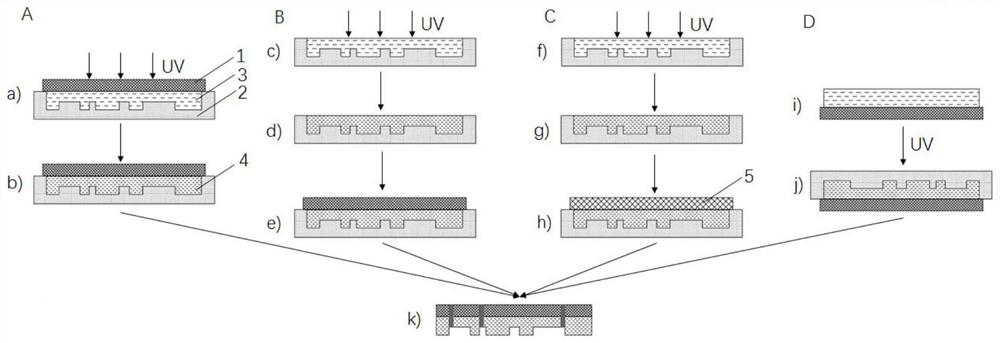
[0099] Example 1 Preparation of elastic support based on thiol-ene material:
[0100] a) Preparation solution: by mass percentage, 73% tetrakis (2-mercaptoacetic acid) pentaerythritol ester (Aladdin, P160529), 26% 1,3,5-triallyl-1,3,5- Triazine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione (Aladdin, T123406), 1% photoinitiator 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphenylphosphonic acid ethyl ester ( Aladdin, E186856) mixed well to obtain solution 1.
[0101] b) Pour the solution 1 prepared in step a) into and fill the groove with a depth of 3mm, cover it with a piece of clean glass and flatten it, and apply ultraviolet light (365nm, 2.5mW / cm 2 ), the irradiation time is 180s~200s.
[0102] c) After solidification, the thiol-ene solid is removed from the groove for later use.
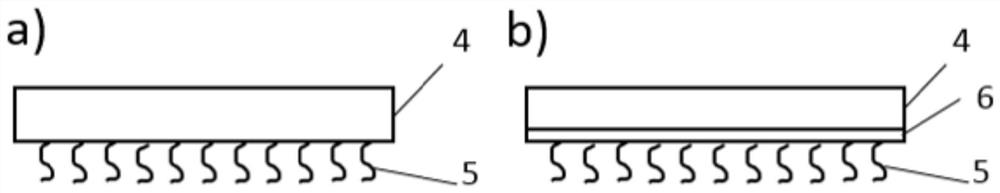
[0103] The thiol-ene solid (bulk layer) obtained in this example has good elasticity and has a photocurable functional group itself, which can be directly used as an elastic support.
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2 Preparation of elastic support based on polyurethane acrylate material:
[0105] a) Prepared solution: by mass percentage, 99% polyurethane acrylate (Changxing material company, 6115J-80), 1% photoinitiator 2-hydroxyl-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-acetone (Sigma, 405655) and mix well to obtain solution 2.
[0106] b) Pour the solution 2 prepared in step a) into the groove with a depth of 3mm, cover it with a piece of clean glass and flatten it, and apply ultraviolet light (365nm, 2.5mW / cm 2 ), the irradiation time is 340s~360s.
[0107] c) After curing, take out the polyurethane acrylate solid from the groove for later use.
[0108] The urethane acrylate solid (body layer) obtained in this embodiment has good elasticity, and has photocurable functional groups itself, and can be directly used as an elastic support.
Embodiment 3
[0109] Embodiment 3 PDMS surface modification acrylate functional group as elastic support body:
[0110] a) Mix PDMS prepolymer (Momentive, RTV615) and curing agent (Dow Corning, Sylgard184) at a mass ratio of 10:1, stir evenly, pour 30g into the injection tank, and heat and cure the whole for 2 hours.
[0111] b) After the thermally cured PDMS is subjected to plasma treatment (500V, 13.56MHz, 45s), it is immersed in a silane coupling agent solution (3-(methacryloyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane ethanol solution, volume fraction 10%), soak for 1 to 2 hours to ensure that the PDMS surface is modified with acrylate functional groups.
[0112] c) The PDMS in step b) was taken out, rinsed with ethanol, and dried with nitrogen gas for later use.
[0113] In this embodiment, the surface of the PDMS bulk layer is modified with photocurable functional groups and used as an elastic support.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com