Pichia pastoris engineering bacteria for producing inositol and fermentation method
A technology of Pichia pastoris and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the field of bioengineering to achieve the effect of enhancing inositol synthesis capacity and improving supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Construction of Pichia pastoris engineering strains overexpressing endogenous and exogenous inositol synthesis key enzyme genes and knocking out inositol transporter genes
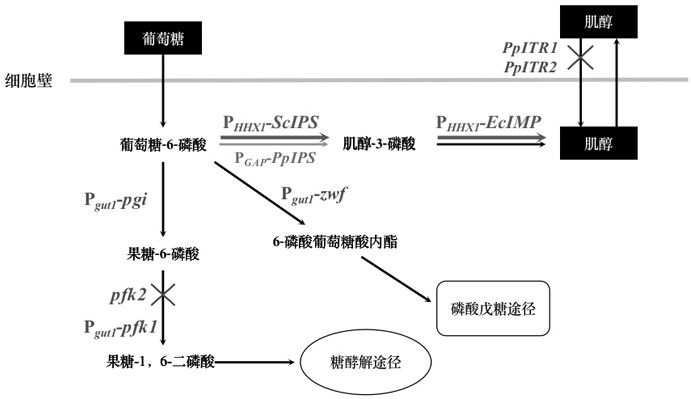
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, glucose is transported into cells to generate glucose-6-phosphate, and then glucose-6-phosphate is catalyzed by inositol-1-phosphate synthase and inositol monophosphatase to generate inositol, and finally excess inositol will be secreted outside the cell. Extracellular myo-inositol can be absorbed into the cell through two inositol transporters (PpITR1 and PpITR2), while excessive intracellular myo-inositol will affect the expression of myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase and myo-inositol monophosphatase and activity. Therefore, the ability of Pichia pastoris to accumulate inositol can be effectively improved by overexpressing endogenous and exogenous inositol synthesis key enzyme genes and knocking out inositol transporter genes.
[0039] use mazF - ...
Embodiment 2
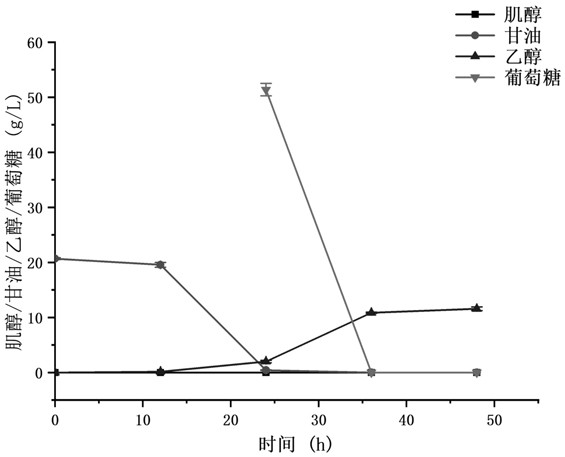
[0055] Example 2 Increased inositol production by reducing glycolytic flux
[0056] The precursor of inositol synthesis is glucose-6-phosphate, and glucose-6-phosphate can also enter the glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway for metabolism, so reducing the glycolytic metabolic flow helps to increase the glucose-6-phosphate supply. fructose-6-phosphate kinase gene pfk1 and pfk2 It is a key gene in glycolysis. Knocking out one of the genes can reduce the carbon metabolism flow of glycolysis while ensuring the normal growth of bacteria.
[0057] 1. Construction pfk2 gene editing plasmid
[0058] Amplification of fructose-6-phosphate kinase 2 gene by PCR pfk2 For the homologous arm fragments on both sides, the target gene after gel electrophoresis was gel recovered, and the obtained fragment was ligated with the enzyme-cut JQ vector, transformed into Escherichia coli Trans10 by heat shock, recovered at 37°C for 30 min, and coated Cloth LB plates (containing ampicillin...
Embodiment 3
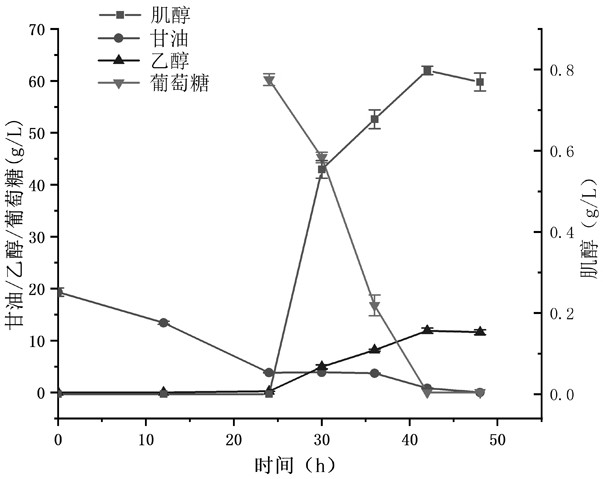
[0063] Example 3 Further improving inositol production by dynamically regulating glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathways
[0064] It is proved by Example 2 that reducing the glycolytic metabolic flux helps to increase the supply of glucose-6-phosphate, thereby increasing the production of inositol. Therefore, in order to further increase the supply of glucose-6-phosphate, glycerol-inducible promoters are used to regulate the expression of the gene encoding glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in the glycolytic pathway. pgi , the gene encoding fructose-6-phosphate kinase 1 pfk1 and the gene encoding glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the pentose phosphate pathway zwf , the resulting strains were unaffected when grown in glycerol as a carbon source medium, but were affected by carbon metabolism inhibition when grown in a medium containing glucose pgi , pfk1 and zwf The expression of is blocked, thereby reducing the metabolic flux of the glycolysis and pentose phosphate pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com