Method for rapidly dyeing biological sample and acquiring three-dimensional data
A biological sample, rapid dyeing technology, applied in the field of biomedical photonics, can solve the problems of limited types of dyes, slow signal acquisition process, incomplete dyeing, etc., to reduce syneresis, accelerate dyeing efficiency, and improve acquisition. The effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
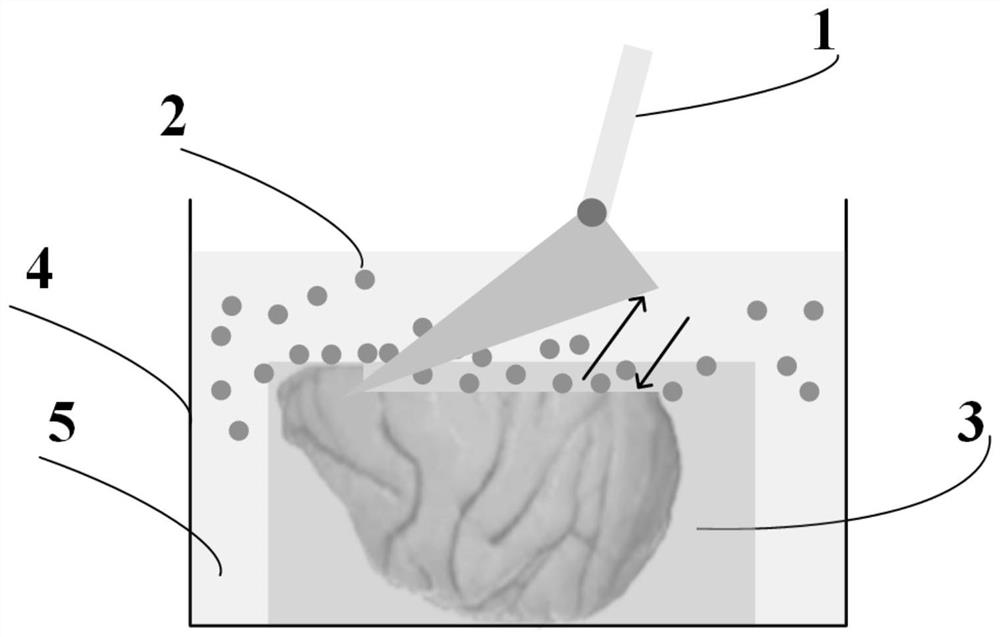
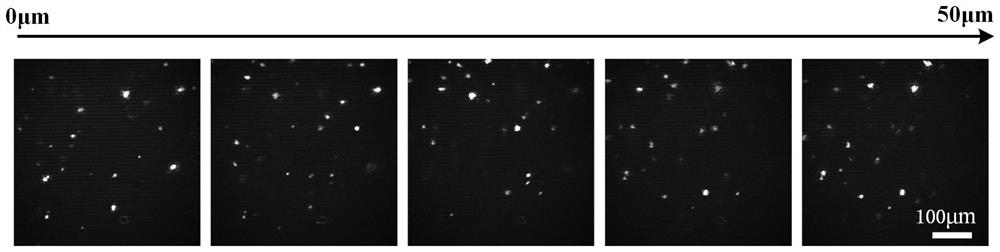
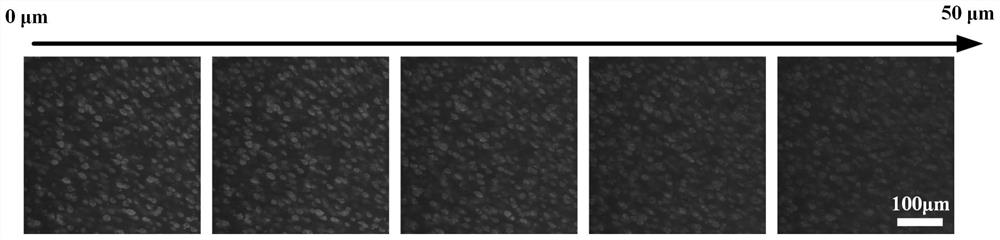
[0068] The imaging solution in Example 1 was composed of an aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.25 wt% Thioflavin S, 30 wt% fructose, 20 wt% urea and 20v / v% DMSO. The biological sample tissue is the brain tissue of 5XFAD transgenic mice, which has the pathological characteristics of β-amyloid plaques, and the three-dimensional data acquisition is completed according to the following steps:
[0069] S1, mice were anesthetized and then perfused. The perfusion solution was firstly 0.01M phosphate buffer solution, and then 4% paraformaldehyde solution, and the brain was taken as the biological sample tissue. The biological sample tissue was soaked in 4% paraformaldehyde solution and fixed for 24 hours until the sample hardened.
[0070] S2. Perform pretreatment on the acquired biological sample tissue, that is, immerse the biological sample tissue in an imaging solution for at least 24 hours. During this process, the imaging solution dehydrates the biological sample tissue...
Embodiment 2
[0082] The imaging solution in Example 2 is composed of 2ug / ml PI (propidium iodide), 30wt% fructose, 20wt% urea and 20v / v% dimethyl sulfoxide aqueous solution. The biological sample tissue is wild-type C57 mouse brain tissue, and the three-dimensional data collection is completed according to the following steps:
[0083] S1, mice were anesthetized and then perfused. The perfusion solution was firstly 0.01M phosphate buffer solution, and then 4% paraformaldehyde solution, and the brain was taken as the biological sample tissue. The biological sample tissue was soaked in 4% paraformaldehyde solution and fixed for 24 hours until the sample hardened.
[0084] S2. Perform pretreatment on the acquired biological sample tissue, that is, immerse the biological sample tissue in an imaging solution for at least 24 hours. During this process, the imaging solution dehydrates the biological sample tissue and makes the surface transparent and stained.
[0085] S3, embedding the pretreat...
Embodiment 3
[0096] The imaging solution in Example 3 was composed of DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), 30wt% fructose, and 20wt% urea at a concentration of 1ug / ml. The biological sample tissue is wild-type C57 mouse brain tissue, and the three-dimensional data collection is completed according to the following steps:
[0097] S1, mice were anesthetized and then perfused. The perfusion solution was firstly 0.01M phosphate buffer solution, and then 4% paraformaldehyde solution, and the brain was taken as the biological sample tissue. The biological sample tissue was soaked in 4% paraformaldehyde solution and fixed for 24 hours until the sample hardened.
[0098] S2. Perform pretreatment on the acquired biological sample tissue, that is, immerse the biological sample tissue in an imaging solution for at least 24 hours. During this process, the imaging solution dehydrates the biological sample tissue and makes the surface transparent and stained.
[0099] S3, embedding the pretreated bi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com