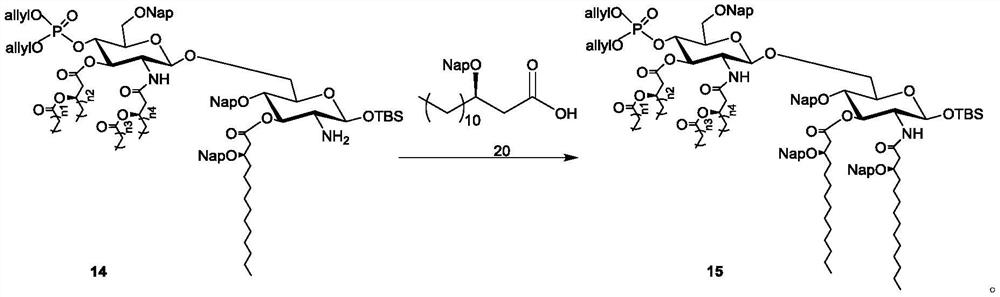
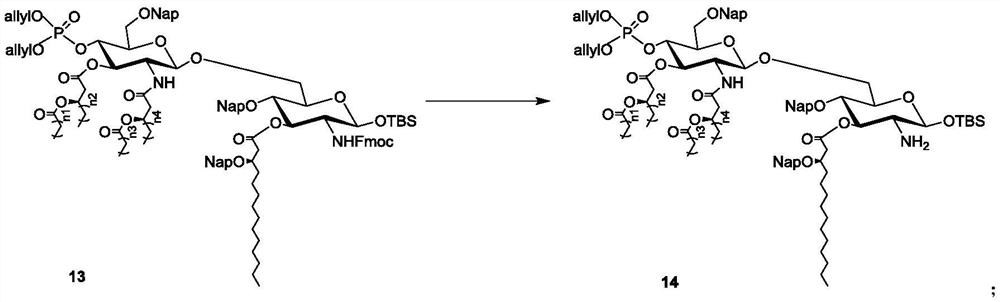
Intermediate, synthesis and application of vaccine adjuvant MPLA
A reaction and solvent technology, applied in the field of intermediates of vaccine adjuvant MPLA, can solve the problems of lack of preparation methods of vaccine adjuvant MPLA, and achieve the effect of short route and increased total yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0241] Preparation of starting compound 1
[0242]
[0243] Add 2-deoxy-1-oxo-(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl-2-[(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)carbonyl]amino-3,4 , 6-triacetyl-β-D-glucose (10g, 16.8mmol) was slowly added to a reaction flask of guanidine hydrochloride buffer solution (100mL, pH = 8), stirred at room temperature for 3.5h, and TLC detected that the raw material was consumed , the reaction solution was neutralized with a cationic resin, filtered and concentrated, the product was extracted with dichloromethane and saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, the organic layer was collected and concentrated to obtain 2-deoxy-1-oxo-(1,1-dimethylethyl) di Methylsilyl-2-[(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)carbonyl]amino-β-D-glucose (1-1, 8.23 g).
[0244] In a reaction flask, 1-1 and 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-naphthalene (5.1g, 25mmol, 1.5eq) were dissolved in 50mL of acetonitrile, and camphorsulfonic acid (0.39g, 1.69mmol, 0.1eq) was added , Stir at room temperature for 4h to react, add tri...
Embodiment 1
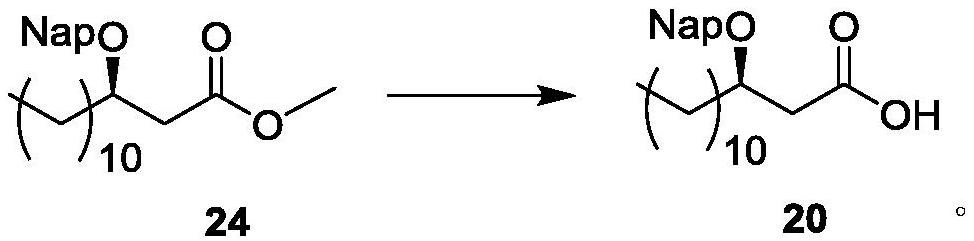
[0264] The preparation of embodiment 1 compound 24
[0265]
[0266] Compound 23 (10g, 39mmol, 1eq) and 2-naphthaldehyde (18.14g, 116mmol, 3eq) were dissolved in THF (100mL), and TMSOTf (6.88g, 31mmol, 0.8eq) was added under ice-cooling, (TMS) 2 O (37.68g, 232mmol, 6eq) and Et 3 SiH (15.7 g, 135 mmol, 3.5 eq). Reacted at 0°C for 1.5 hours, and the reaction solution was washed with CH 2 Cl 2 (150mL) and dilute with saturated NaHCO 3 washing. The organic layer was spin-dried and recrystallized (to obtain methylnaphthalene as a white solid at room temperature) (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 5:1), and filtered to remove impurities (methylnaphthalene). The filtrate (containing compound 24) was collected and spin-dried to obtain the crude product 24 as a pale yellow oily liquid, which was directly used in the next step without purification. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )0.89(3H,t,J6.7),1.27–1.64(18H,m),2.35(2H,dd,J8.4)2.49(1H,dd,J15.0,5.3),2.62(1H,dd,J15 .0,7.3),3.68(3H,s),...
Embodiment 2
[0267] The preparation of embodiment 2 compound 20
[0268]
[0269] Compound 24 prepared in Example 1 was dissolved in THF-H 2 O solution (5:1, 100 mL), was added aqueous lithium hydroxide solution (9.41 g, 224 mmol, 94 mL), and refluxed for 12 h. After the starting material disappeared, it was cooled to room temperature and quenched to pH 7 by adding 1.5M HCl aqueous solution. The mixture was washed with CH 2 Cl 2 (150mL) diluted with saturated NaHCO 3 washing. The organic phase was dried and spin-dried. Purification by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether / ethyl acetate=5:1) gave compound 20 (11.6 g, 77.9% yield in two steps, colorless syrup).
[0270] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ10.00 (1H, s, OH), 7.85 (4H, dd, J = 14.5, 10.8), 7.53 (3H, d, J = 4.2), 4.85–4.71 (2H, m, NapCH 2 O), 4.08–3.94 (1H, m, H-3), 2.76 (1H, dd, J = 15.2, 6.9, H-2), 2.64 (1H, dd, J = 15.2, 4.3, H-2), 1.84–1.58(2H,m,H-4),1.57–1.31(18H,m),1.00(3H,t,J=6.0).
[0271] 13 C NMR (101...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com