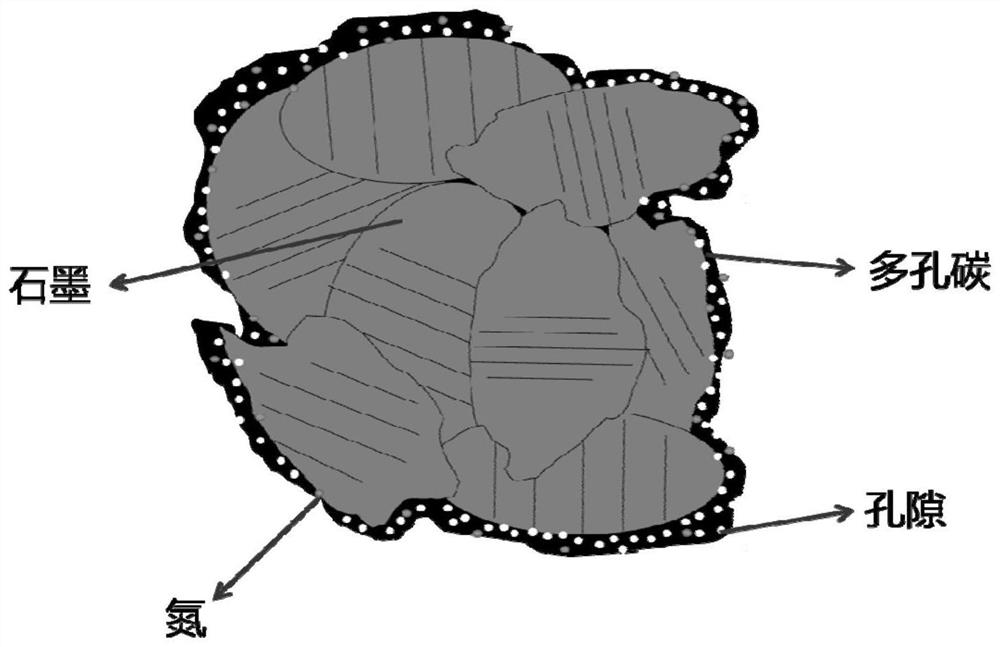
Graphite modification method and application of graphite in lithium ion battery
A graphite and modification technology, applied in graphite, battery electrodes, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, unsuitable for industrial production, complicated preparation process, etc., achieve simple method, excellent kinetic performance, and increase rate performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] (1) Potassium hydroxide and particle size d50 are 12 μm artificial graphite secondary particles (specific surface area is 1.2m 2 / g, 5T compaction density is 2.05g / cm 3 , graphitization degree is 94%) carry out VC homogeneous mixing according to weight ratio 15:85, put the evenly mixed mixture into pusher kiln, under nitrogen atmosphere, heat up to 900 ℃ with 3 ℃ / min heating rate to carry out carbonization, Keep warm for 4 hours, cool down naturally, and obtain a graphite material with a porous surface;
[0050] (2) Mix the surface porous graphite material and ammonium chloride with VC at a mass ratio of 90:10, put them into a pusher kiln for carbonization, and raise the temperature to 1100°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min in a nitrogen atmosphere , the carbonization time is 5h, and the finished product is obtained by sieving after natural cooling.
Embodiment 2
[0052] (1) Sodium carbonate and particle size d50 are 12 μm artificial graphite secondary particles (specific surface area is 1.2m 2 / g, 5T compaction density is 2.05g / cm 3 , degree of graphitization is 94%) uniformly mixed with VC according to the weight ratio of 20:80, put the uniformly mixed mixture into the rotary furnace, and raise the temperature to 1000°C at a heating rate of 4°C / min under nitrogen atmosphere for carbonization, heat preservation 2h, natural cooling down, obtain the graphite material with porous surface;
[0053] (2) Mix the surface porous graphite material and ammonium chloride with VC at a mass ratio of 85:15, put them into a rotary furnace for carbonization after mixing, and raise the temperature to 1200°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min under an argon atmosphere , the carbonization time is 1.5h, and the finished product is obtained by sieving after natural cooling.
Embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Potassium hydroxide and particle size d50 are 18 μ m artificial graphite secondary particles (specific surface area 1.2, 5T compaction density is 2.06, degree of graphitization 94%) carry out VC uniform mixing by weight ratio 25:75, will mix homogeneously Put the mixture into a rotary furnace, heat up to 800°C under a nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 5°C / min for carbonization, keep it warm for 5 hours, and cool down naturally to obtain a graphite material with a porous surface;
[0056] (2) Mix the surface porous graphite material and urea with VC at a mass ratio of 80:20, put them into a rotary furnace for carbonization after mixing, and raise the temperature to 1000°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min under an argon atmosphere, and carbonize The time is 4 hours, and the finished product is obtained by sieving after natural cooling.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compaction density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com