Preparation method of CZTS thin-film solar cell back electrode with modification layer
A technology for solar cells and modified layers, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of destroying the stability of Mo electrodes, affecting carrier collection, and falling off of Mo electrodes, so as to improve carrier transport performance, increase photoelectric conversion efficiency, reduce The effect of grain boundary defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
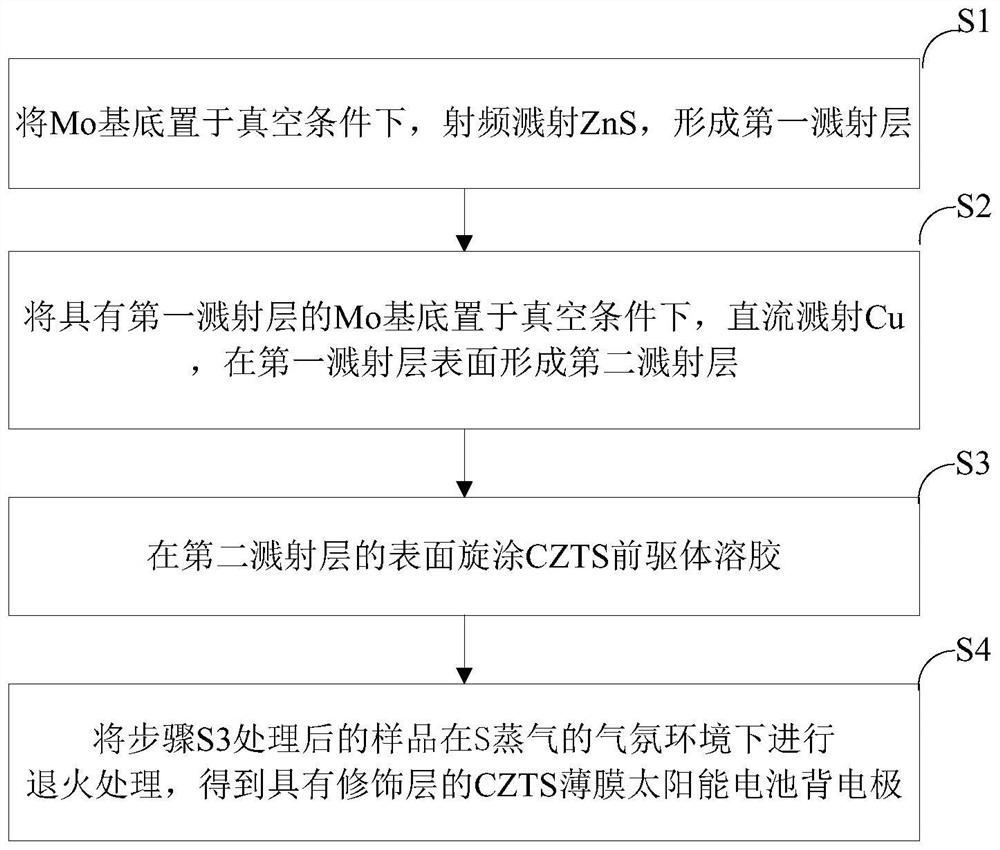
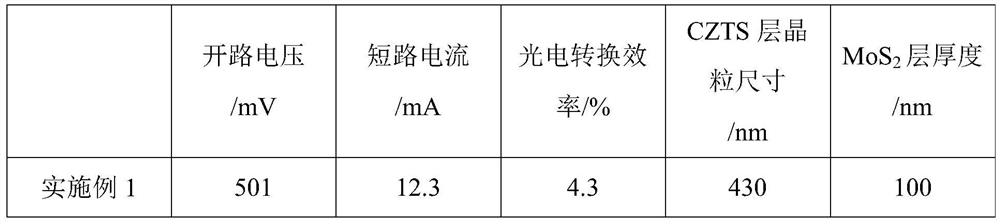
[0030] (1) Place the Mo substrate in a vacuum chamber, use ZnS target radio frequency sputtering to sputter the first sputtering layer, the sputtering power is 80W, the sputtering pressure is 1Pa, and the sputtering time is 2s;
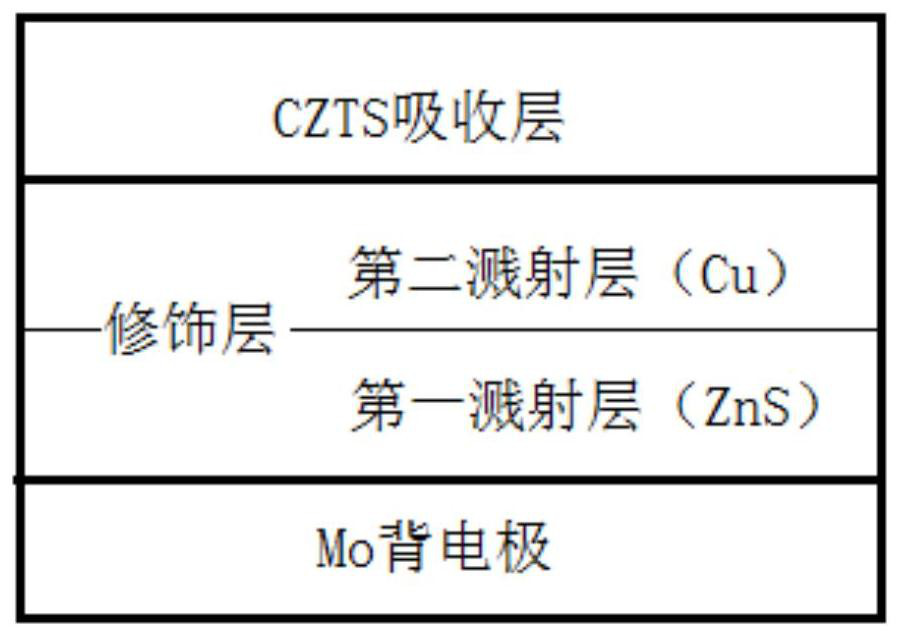
[0031] (2) Place the Mo substrate with the first sputtering layer in a vacuum chamber, and use a Cu target to direct-current sputter the second sputtering layer, the sputtering power is 40W, the sputtering pressure is 1Pa, and the sputtering time is 1s. Mo back electrode with modification layer;
[0032] (3) Prepare CZTS precursor sol at a temperature of 50°C, the solvent is ethylene glycol methyl ether, the additive is triethanolamine (the volume ratio of additive to solvent is 1:50), and the metal salt is Cu, Zn, Sn chloride Compounds, the molar concentrations of metal atoms are: 0.05M, 0.03M and 0.025M. The CZTS precursor sol is spin-coated on the Mo back electrode with the modified layer treated in step (2) to form a CZTS film.
[0033] (4) Plac...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Place the Mo substrate in a vacuum chamber, use ZnS target radio frequency sputtering to sputter the first sputtering layer, the sputtering power is 60W, the sputtering pressure is 0.5Pa, and the sputtering time is 3s;
[0036] (2) Place the Mo substrate with the first sputtering layer in a vacuum chamber, and use a Cu target to direct-current sputter the second sputtering layer, the sputtering power is 30W, the sputtering pressure is 1Pa, and the sputtering time is 1s. Mo back electrode with modification layer;
[0037] (3) Prepare CZTS precursor sol at a temperature of 40°C, the solvent is ethylene glycol methyl ether, the additive is monoethanolamine (the volume ratio of additive to solvent is 1:25), and the metal salt is nitric acid of Cu, Zn, and Sn Compounds, the molar concentrations of metal atoms are: 0.03M, 0.02M and 0.015M. The CZTS precursor sol is spin-coated on the Mo back electrode with the modified layer treated in step (2) to form a CZTS film.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Place the Mo substrate in a vacuum chamber, use ZnS target radio frequency sputtering for the first sputtering layer, the sputtering power is 40W, the sputtering pressure is 3Pa, and the sputtering time is 5s;
[0041](2) Place the Mo substrate with the first sputtering layer in the vacuum chamber, use the Cu target to sputter the second sputtering layer with direct current, the sputtering power is 20W, the sputtering pressure is 1Pa, and the sputtering time is 2s, the obtained Mo back electrode with modification layer;
[0042] (3) Prepare CZTS precursor sol at a temperature of 60°C, the solvent is N,N-dimethylformamide, the additive is diethanolamine (the volume ratio of additive to solvent is 1:40), and the metal salt is Cu, Zn , Sn sulfate, the molar concentration of metal atoms are: 0.14M, 0.11M and 0.07M. The CZTS precursor sol is spin-coated on the Mo back electrode with the modified layer treated in step (2) to form a CZTS film.
[0043] (4) Place the samp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com