Polymer and corrosion resistant material
A technology of polymers and compounds, applied in the field of polyhydroxystyrene derivatives, can solve the problems of substrate dependence, poor solvent retention ability, and poor adhesion during the delay period of poor resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0330] Synthesis of poly[p-(1-ethoxyethoxy)styrene / p-hydroxystyrene]
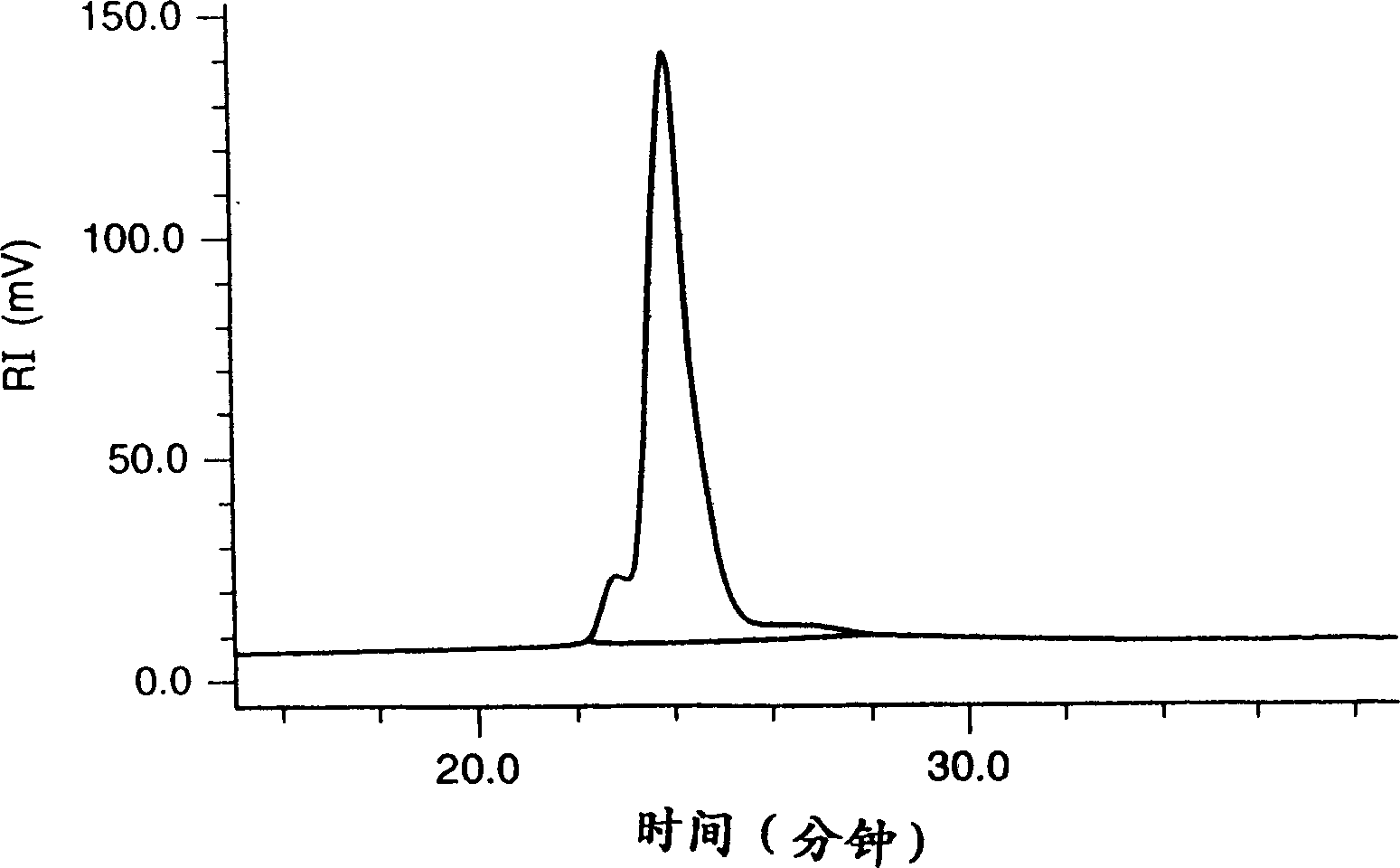
[0331] (1) Suspend 15.9 g of poly(p-tert-butoxystyrene) [manufactured by Nippon Soda Co., Ltd.; Mw about 21,000; molecular weight distribution (dispersion index) 1.16] in isopropanol and add 30 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid, followed by reflux and stirring for 4 hours. After cooling, the reaction solution was poured into 3000 ml of water for crystallization. Crystal precipitates were filtered off, washed with water and dried under reduced pressure to obtain 10.5 g of poly(p-hydroxystyrene) white powder crystals.
[0332] (2) The poly(p-hydroxystyrene) obtained in (1) above was dissolved in 80 ml of ethyl acetate in an amount of 8 g and 2.4 g of ethyl vinyl ether. After adding a catalytic amount of pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate, the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. After the reaction, the reaction solution was concentrated at room temperature under reduced pressure, and the residu...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0334] Synthesis of poly[p-(1-methoxyethoxy)styrene / p-hydroxystyrene].
[0335] The poly(p-hydroxystyrene) obtained by the method described in Preparation Example 1 (1) was reacted in an amount of 8 g and 2.2 g of methyl vinyl ether in the same manner as described in Preparation Example 2 (1). And aftertreatment, obtain the white powder of 8.6g poly [p-(1-methoxyethoxy) styrene / p-hydroxystyrene] without crystallization. The ratio of p-(1-methoxyethoxy)styrene to p-hydroxystyrene in the resulting polymer was about 4:6 as measured by 'H-NMR. Its Mw is about 17000 and its dispersion index is 1.16 (GPC method, polystyrene as calibration).
preparation Embodiment 3
[0337] Synthesis of poly[p-(1-ethoxyethoxy)styrene / p-hydroxystyrene / p-isobutoxycarbonyloxystyrene].
[0338] (1) Poly(p-hydroxystyrene) [manufactured by Nippon Soda Co., Ltd.; Mw about 8200, dispersion index 1.05] was dissolved in 70 ml of ethyl acetate in an amount of 18.0 g. Then, 3.5 g of diisobutyl dicarbonate synthesized from isobutyl chlorocarbonate and 3.0 g of triethylamine were added, and the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 4 hours. After the reaction, ethyl acetate was distilled off under reduced pressure and the residue was dissolved in 70 ml of acetone. After pouring 1000 ml of water, crystals precipitated out. The crystal precipitate was filtered off, washed with water and dried under reduced pressure to obtain 13.5 g of white powder crystals of poly(p-hydroxystyrene / p-isobutoxycarbonyloxystyrene). The ratio of p-hydroxystyrene units to p-isobutoxycarbonyloxystyrene units was about 92:8 as measured by 'H-NMR.
[0339] (2) The poly(p-hydroxystyr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dispersion index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dispersion index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dispersion index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com