Adsorption and microelectrolysis cooperative treatment method for coking reverse osmosis concentrated wastewater
A technology of reverse osmosis concentration and synergistic treatment, applied in the fields of energy wastewater treatment, special compound water treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of lack of effectiveness evaluation, membrane pollution, difficulty in crystallization and purification, etc., and achieve green and low-consumption treatment. efficiency, improve processing efficiency, and save cost and consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
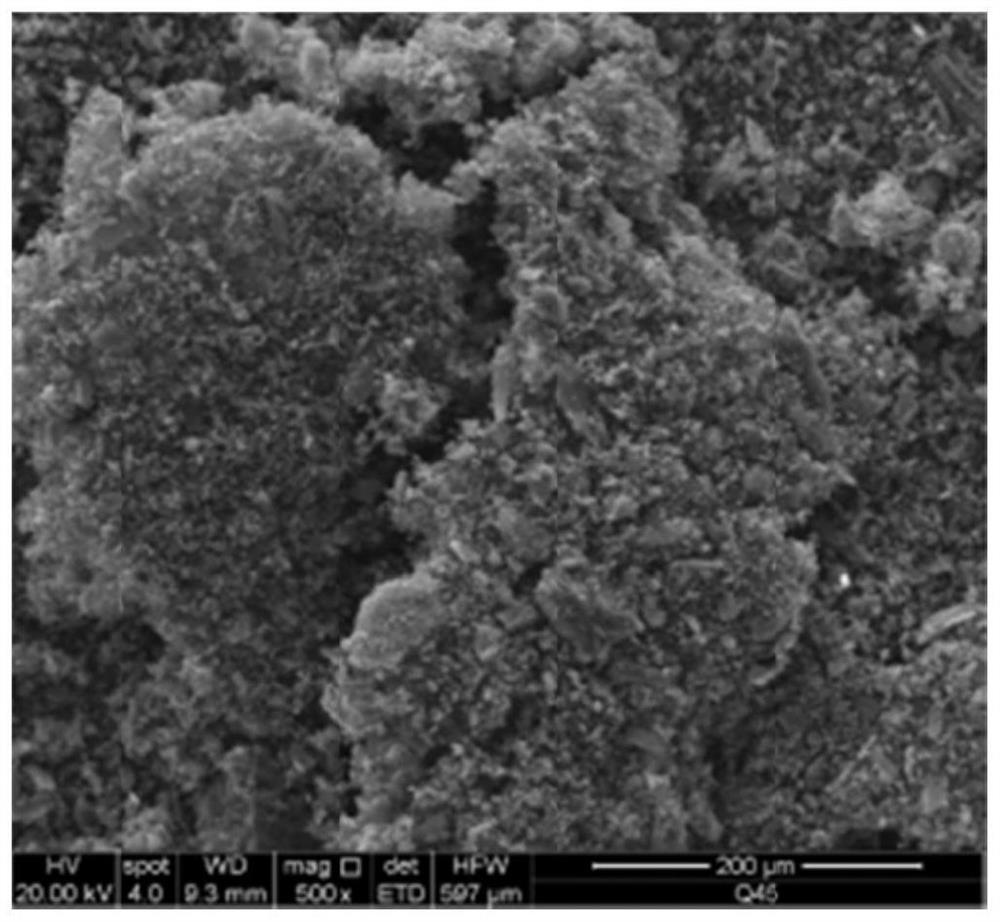
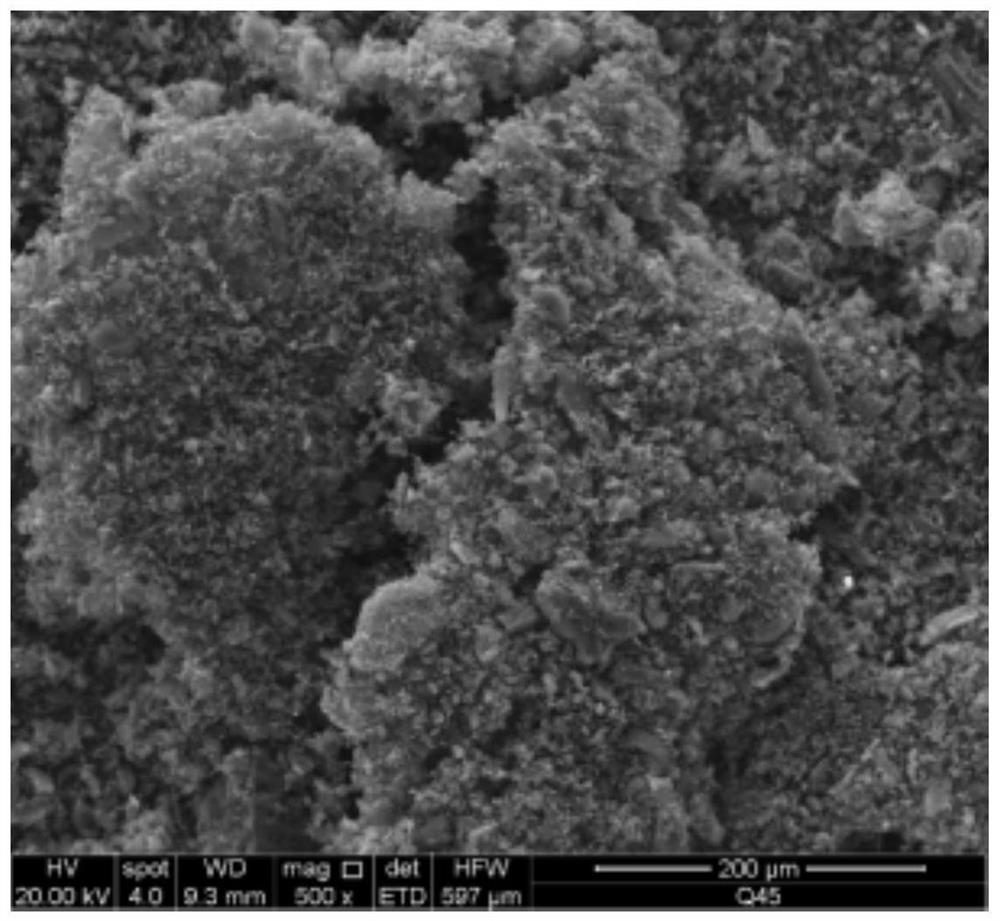
[0045] The present invention is an adsorption micro-electrolysis synergistic treatment method for coking reverse osmosis concentrated wastewater, which combines activated carbon adsorption, iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and Fenton reaction, and comprises the following steps:
[0046] Step 1, treatment of activated carbon.
[0047] Commercial activated carbon (5 g) was boiled with 30% sodium hypochlorite for 2 hours, then filtered with deionized water and dried for 6 hours. The pretreated AC was reacted with 0.1M mild oxidant (citric acid, tartaric acid, malic acid and salicylic acid mixed) in a 1000ml round bottom flask, specifically the mixture was continuously stirred at 125°C for 14h. After cooling, the mixture was washed with deionized water, keeping the pH of the wash at 7.0 to remove unreacted acid, then the product O-AC was filtered and dried at 80°C.
[0048] The treated activated carbon has larger pore size and adsorption capacity than the original activated carbon....
Embodiment 1
[0072] Step 1. Activated carbon of category P-1400-Y was treated as described previously.
[0073] Step 2, take 4 L of coking reverse osmosis concentrated wastewater, dropwise add 1 mol / L of H 2 SO 4 The solution was measured with a pH meter to bring the pH to 2. After aeration at 2min / L for 30min, 0.6g / L of activated carbon was added to carry out the adsorption reaction for 30min, which could enrich 70.34% of the organic matter in the water.
[0074] Step 3, take 100 mL of wastewater after adsorption, and under the condition of aeration for 2 min / L in the whole process, carry out the reaction in a solution with a mass ratio of iron to carbon of 1:2, adjust the pH to 2 and carry out micro-electrolysis reaction for 3 h, take 100 mL of filtered effluent, Add 30% H directly to the solution 2 O 2 The solution was 0.2 mL, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 8.5 with 40% NaOH solution after aeration reaction (2 L / min) for 2 h. After the precipitation is no longer produce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com