Fusion protein for catalyzing glucose to synthesize D-psicose and construction method thereof
A technology of psicose and fusion protein, applied in chemical instruments and methods, methods based on microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, difficult process and complicated purification of chemical synthesis methods, and achieve The effect of reducing production cost, not easy to pollute, process safety and environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
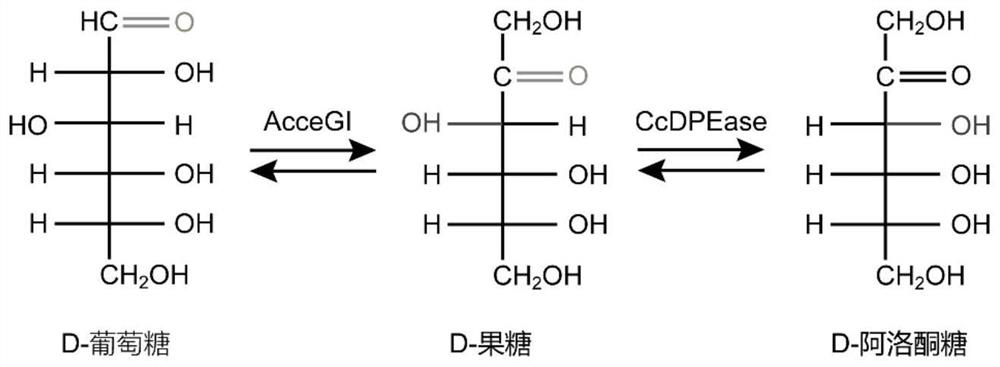
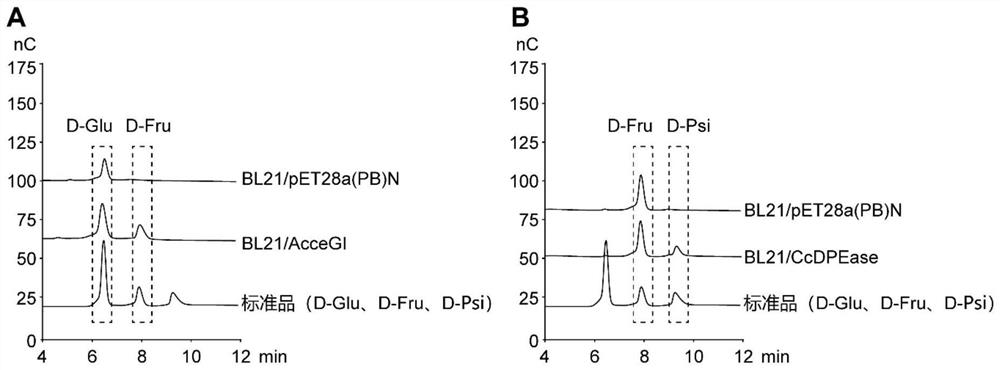
[0027] Example 1: Functional verification of glucose isomerase and D-psicose isomerase
[0028] Escherichia coli BL21 / AcceGI and D-psicose 3-epimerase encoding genes (CcDPEase, SEQ ID NO: 16) containing the gene encoding glucose isomerase (AcceGI, SEQ ID NO: 15) and D-psicose 3-epimerase, respectively BL21 / CcDPEase was cultured overnight in LB medium at 37°C and 200rpm, and transferred to a 250mL conical flask containing 25mL of fresh LB medium at an inoculum of 4% (v / v) at 37°C and 200rpm. Cultured to log phase. IPTG with a final concentration of 500 μM was added, and the culture was continued at 25° C. and 200 rpm for 8 h to express the gene of glucose isomerase and D-psicose 3-epimerase. Glucose and D-fructose were added respectively to verify the functions of glucose isomerase and D-psicose isomerase. E. coli BL21 / pET28a(PB)N with empty plasmid pET28a(PB)N was used as blank control, and other operating conditions were the same.
[0029] Add glucose at a final concentrat...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Construction and functional analysis of fusion proteins
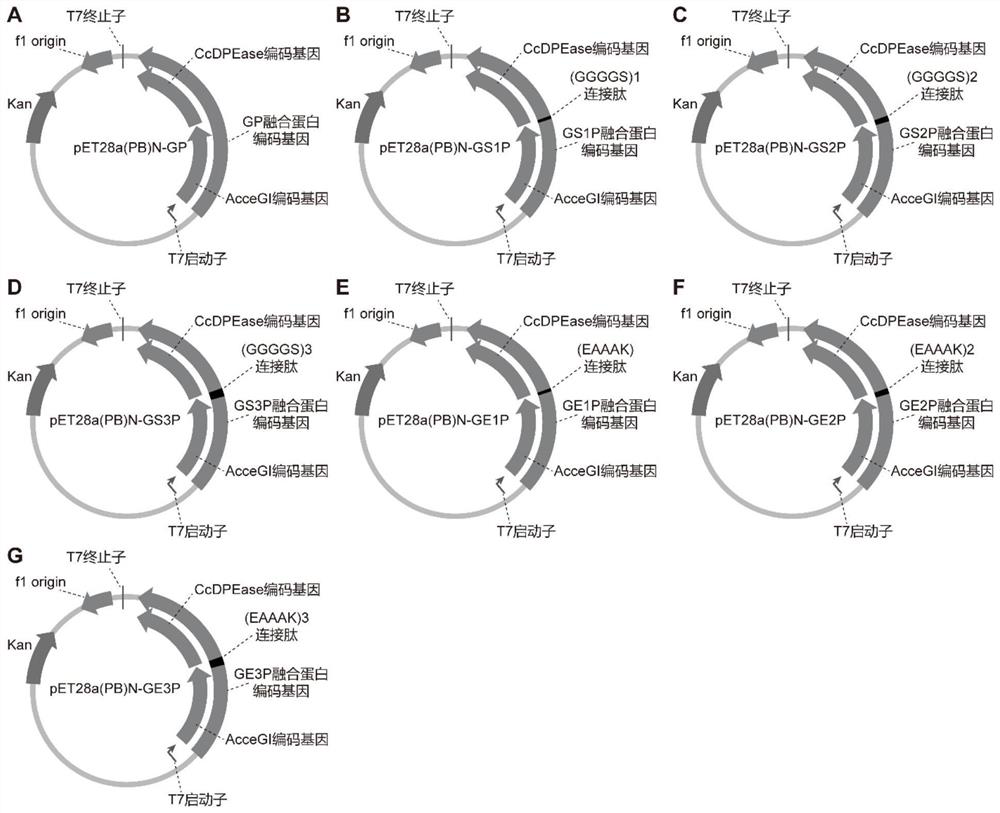
[0034] The gene encoding glucose isomerase (AcceGI, SEQ ID NO: 15) derived from Acidothermus cellulolyticus 11B and D-psicose 3-epimerase (CcDPEase, SEQ ID NO: 16) derived from Clostridium cellulolyticum H10 ), respectively cloned into the vector pET28a(PB)N between the BamHI and HindIII sites of the vector pET28a(PB)N or the BamHI site of the vector pET28a(PB)N-CcDPEase (see primers) Table 1) to obtain recombinant plasmids pET28a(PB)N-GP, pET28a(PB)N-GS1P, pET28a(PB)N-GS2P, pET28a(PB)N-GS3P, pET28a(PB)N-GE1P, pET28a(PB)N-GE1P ) N-GE2P and pET28a(PB)N-GE3P (see Table 2 for the linking peptides used, and the plasmid map is shown in image 3 shown). Among them, the expression of all pathway genes is controlled by T7 promoter and T7 terminator. The recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 / GP, BL21 / GS1P, BL21 / GS2P, BL21 / GS3P, BL21 / GE1...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Optimization of reaction conditions for the generation of D-psicose from glucose catalyzed by fusion proteins GE3P and GS3P
[0046] In order to improve the yield and conversion rate of the one-step conversion of glucose to D-psicose catalyzed by the fusion protein, the present invention further optimizes the reaction conditions for converting D-psicose.
[0047] The invention optimizes the reaction conditions for the conversion of glucose to D-psicose: the temperature range of the reaction is 45-85° C., the pH range of the reaction is 4.5-8.5, and the concentration of the substrate glucose is 100 g / L. The results showed that the optimum reaction temperature was 65°C ( Image 6 A), the optimum reaction pH is 7.5 ( Image 6 B).
[0048] Under the above optimal conditions, the yield of D-psicose can reach 5.69 g / L. The results show that the method for catalyzing the generation of D-psicose from glucose by using the fusion protein constructed in the present i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com