Porous molybdenum carbide and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of molybdenum carbide and molybdenum source, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve problems such as complex reaction process, and achieve the effects of good repeatability, convenient operation and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Add a small amount of water to dissolve the untreated ammonium molybdate and magnesium chloride (the molar ratio of molybdenum and copper is 1:1), then mix the two solutions evenly, pre-freeze at -40 °C for 3 hours, and then vacuum to below 50pa, Freeze-dry for 12h, put the freeze-dried sample into one side of the effective heating area in the quartz tube in the tube furnace, then pass methane gas, heat up quickly to 1000 °C, and then move the molybdenum source and magnesium source mixture to the tube In the effective heating area in the furnace, the reaction is carried out in a heat preservation state for 10 minutes, cooled to room temperature after the reaction, and washed with 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid to remove magnesium to obtain porous molybdenum carbide.
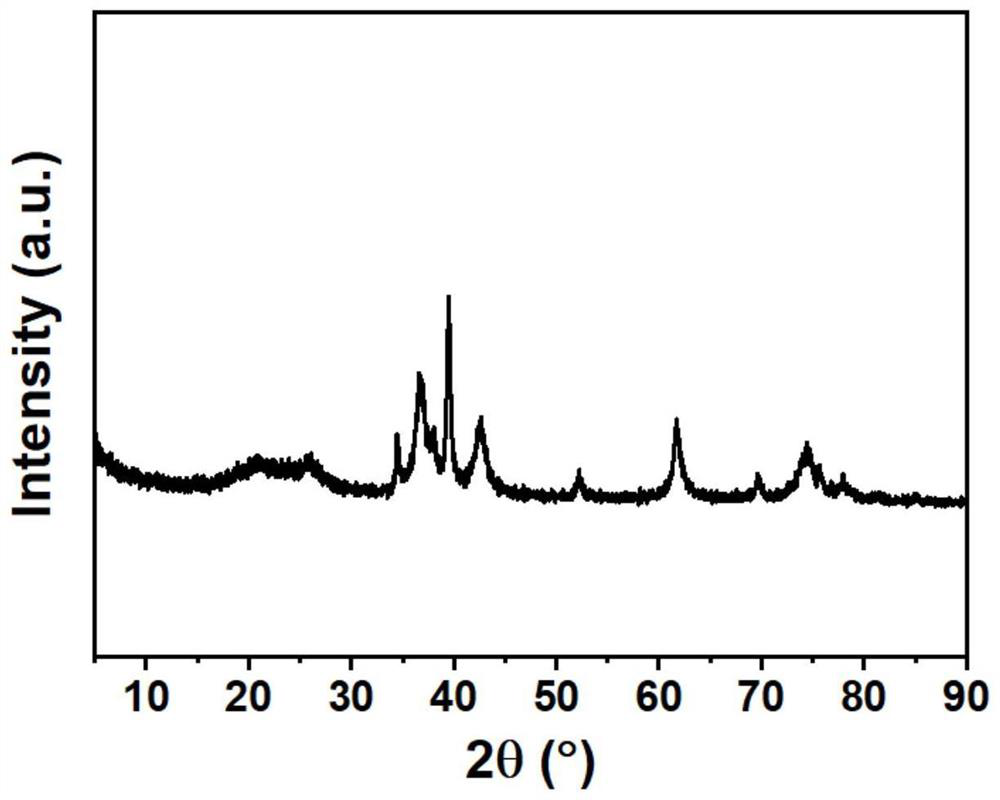
[0037] According to the X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) results ( figure 1 ) characterizes the product obtained in this example as molybdenum carbide.
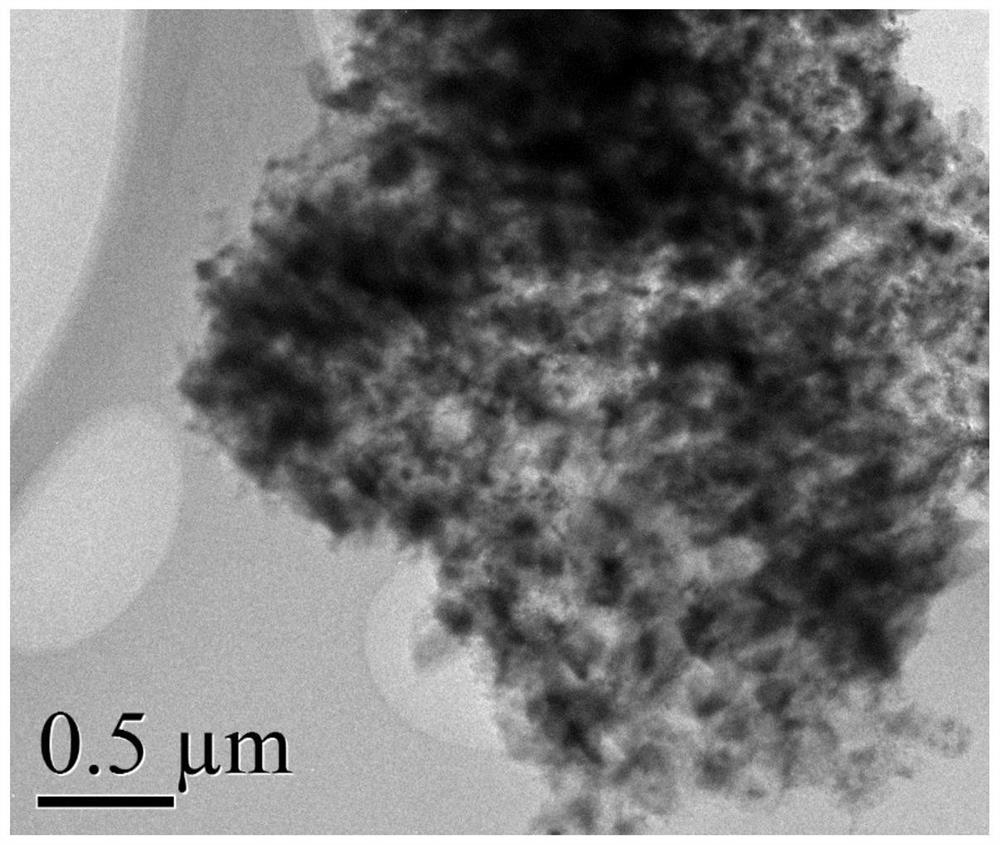
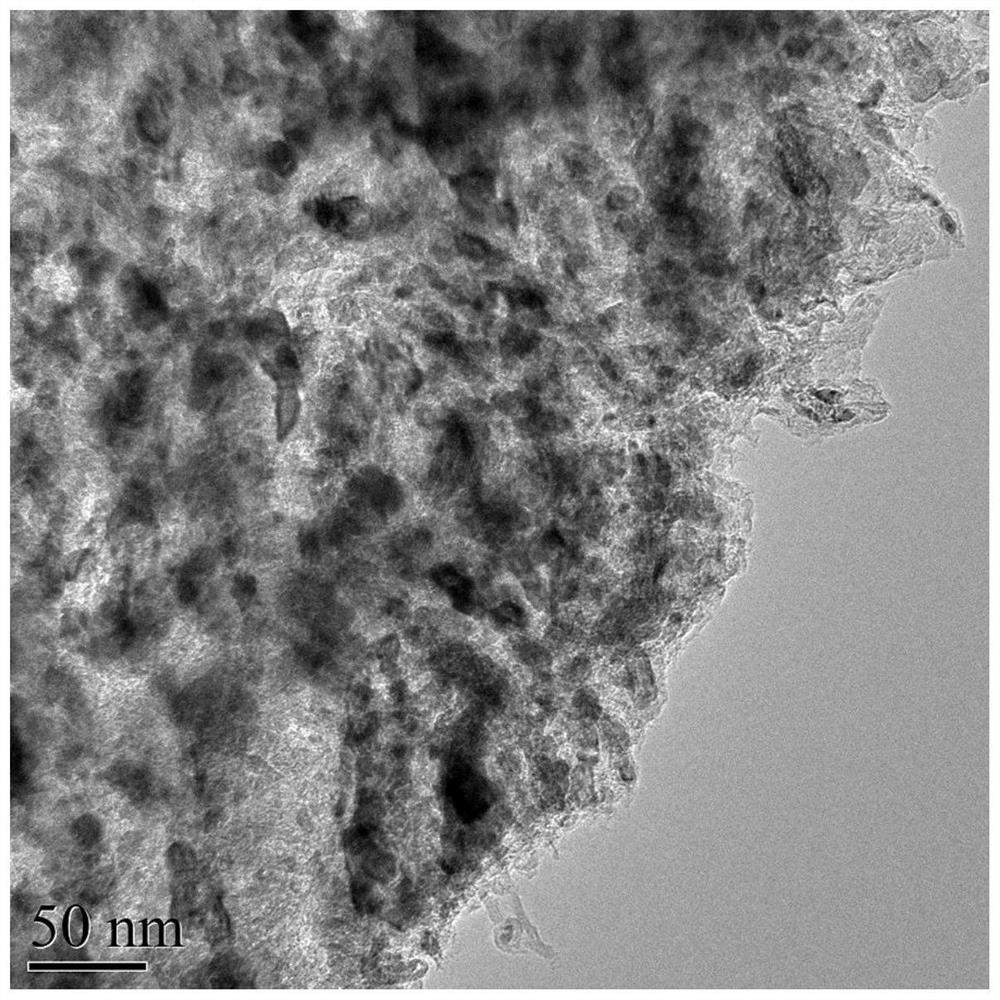
[0038] Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) as figu...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Porous molybdenum carbide prepared according to the method in Example 1. The difference is that the reaction temperature is 1200°C. After the reaction, the tube furnace is closed, cooled to room temperature, and after the magnesium element is removed by acid washing, porous molybdenum carbide is obtained.
[0041] The product obtained in this example is similar to the result of Example 1, and porous molybdenum carbide is also prepared.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Porous molybdenum carbide prepared according to the method in Example 1. The difference is that the reaction temperature is 900°C. After the reaction, the tube furnace is closed, cooled to room temperature, and after the magnesium element is removed by acid washing, porous molybdenum carbide is obtained.
[0044] The product obtained in this example is similar to the result of Example 1, and porous molybdenum carbide is also prepared.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com