Tissue engineering liver based on plant acellular scaffold and preparation method
A decellularized scaffold and tissue engineering technology, which is applied in the field of tissue engineering liver and preparation based on plant decellularized scaffolds, can solve the problems of limited usability, achieve suitable porosity and hydrophilicity, high biocompatibility, and simple method Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Preparation of tissue engineered liver based on plant decellularized scaffolds
[0024] A tissue-engineered liver on a plant decellularized scaffold is prepared by the following method, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0025] S1, intercept the stem of cress with a hollow hole-like structure and clean it;
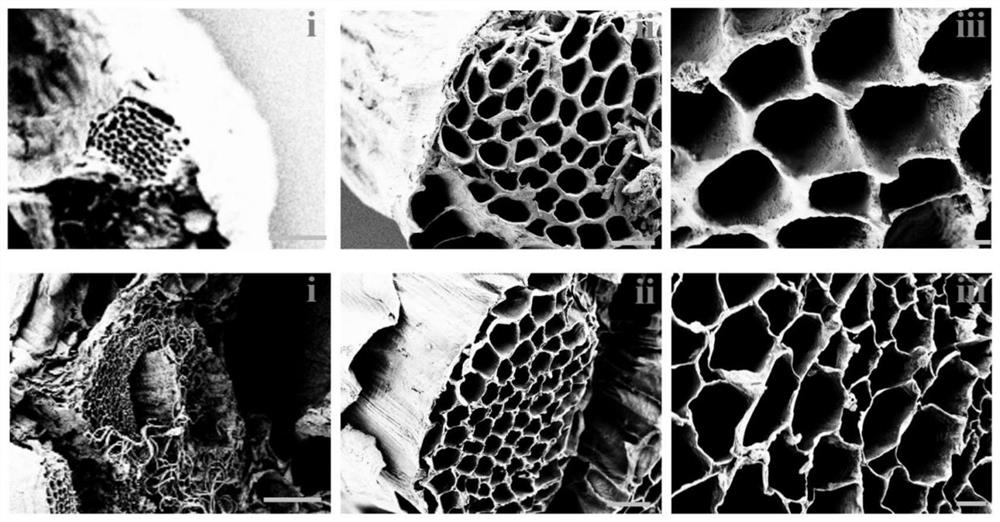
[0026] S2. Submerge the celery stems in 10wt% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution for 5 days, and change the solvent every day; The stems were rinsed for two days to obtain decellularized scaffolds, and it could be observed that the fresh celery tissue changed from green to transparent (the tissue cell components were removed); the obtained decellularized scaffolds were washed with PBS solution, and the residual solvent components were used to provide suitable the environment in which cells live; figure 1 The porous structure of the natural celery stem and the prepared decellularized scaffold was shown;
[0027] S3. Mix the hepatocyte mixture wi...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 Test of compatibility of tissue engineering liver based on plant decellularized scaffolds
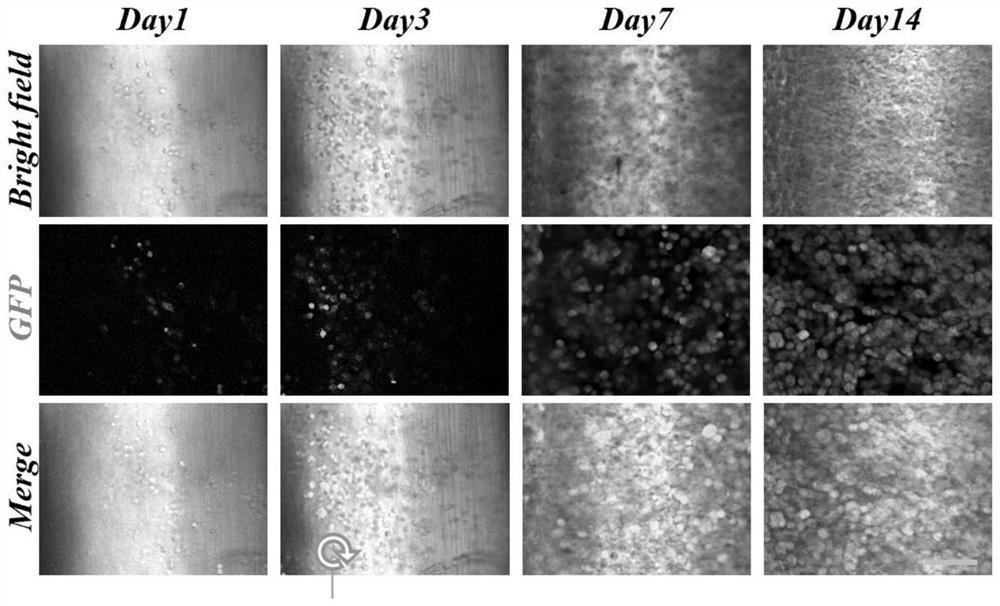
[0029] In order to examine the biocompatibility of the decellularized scaffolds, the tissue engineered liver prepared in Example 1 was cultured for another 14 days, and the hepatocytes suspended in Matrigel were seeded on a 24-well plate as a control group. like figure 2 Cell numbers were determined using GFP staining as indicated. On the third day after seeding, the number of GFP-positive cells was higher than on the first day. In addition, the number of GFP-positive cells increased with the culture time, indicating that the decellularized scaffolds promoted cell proliferation, confirming their high biocompatibility.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 Characterization of liver function of tissue engineered liver based on plant decellularized scaffolds
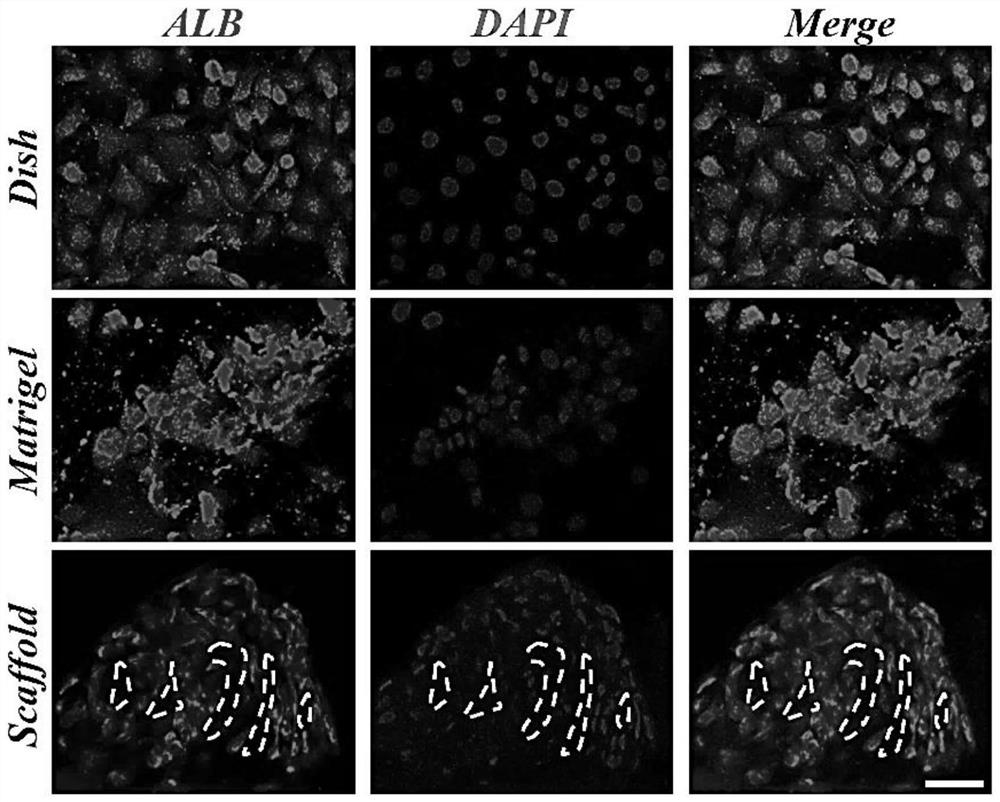
[0031] Due to the lack of extracellular matrix components and cell-to-cell interactions, hepatocytes lose their differentiated state over time when cultured in 2D dishes. However, the composition of Matrigel is heterogeneous, with more than 1500 different proteins in its composition, including the most common proteins such as laminin and type IV collagen. To assess the metabolic activity of transplanted hepatocytes in decellularized liver scaffolds, the albumin secretion, glycogen synthesis, and mRNA expression levels of key hepatic transcription factors and functional genes were quantitatively analyzed. like image 3 As shown, fluorescence images of albumin confirmed that the number of albumin-positive cells was greater in both the Matrigel and decellularized scaffold groups compared to the dish group. Hepatocyte-specific gene expression was performed dur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com