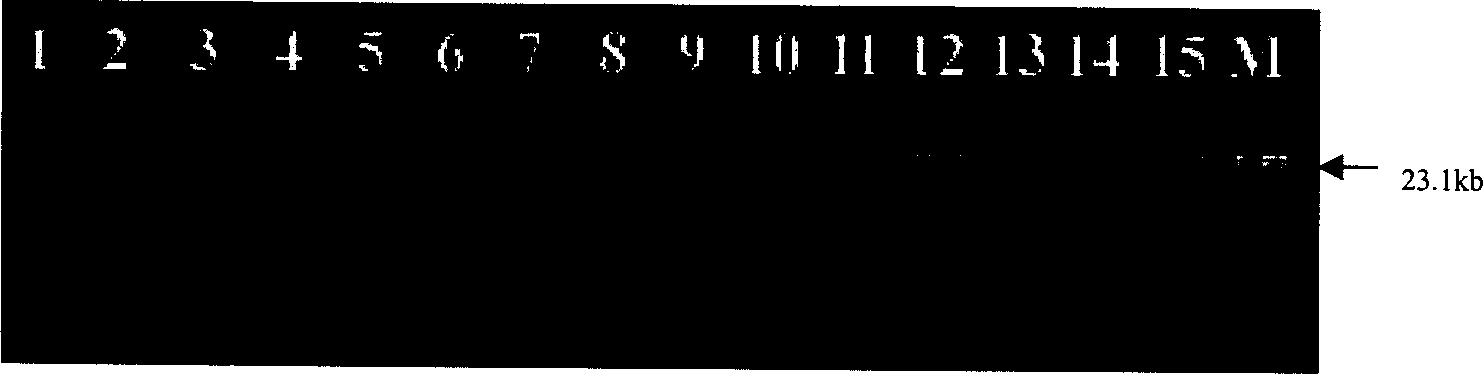Process for separating nucleic acid from biological particles by solid-phase carrier
A technology of biological particles and solid-phase carriers, applied in the fields of sugar derivatives, organic chemistry, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of many steps and difficult miniaturization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Separation of macromolecular DNA. Take the adsorption of DNA fragments with nano-magnetic microspheres as an example: add 40 μl of 15 mg / ml nano-magnetic microsphere suspension and 0.4 μg / μl double-stranded DNA molecular weight marker (marker ) (Hind III digestion) 15μl, shake gently on the vortex shaker for 15s, then add 4mol L -1 80μl of NaI solution, after shaking slightly for 15s, let stand for 3 minutes. Then add 100 μl of isopropanol as a suction aid, shake slightly for 5 seconds, and then let stand for 2 minutes. The magnetic spheres were fixed with a magnetic separation rack, the supernatant was discarded, and the nanomagnetic spheres that had adsorbed DNA were washed twice with 100 μl of 70% ethanol. Add 50 μl of TE solution (10mol L -1 Tris.Cl, 1mmol L -1 EDTA). The DNA was eluted from the magnetic beads in a water bath at 62°C for 12 minutes. Then the magnetic ball is separated from the TE solution, and the obtained TE solution is subjected t...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: Separation of genomic (genomic) DNA of Escherichia coli with nano-magnetic microspheres.
[0024] The samples were plasmid-free E. coli strains cultured overnight. Take 300 μl of the harvested cell culture solution, and then add 50 μl of nano-magnetic microsphere suspension. After shaking and mixing, use a magnetic separation rack to separate the magnetic beads, and discard the supernatant. Add 300 μl cell lysate (3mol / l NaI, 4mol / l urea, 30g / l Triton-100 (trinitrotoluene), 10mmol / l EDTA (pH6.5), 25mmol / l Tris·HCl (pH6.5) to the magnetic ball .5)) (the same below), shake well, and let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes. Add 300 μl of isopropanol. Slightly oscillate on a vortex shaker for 15 s, and let stand at room temperature for 5 min. Fix the magnetic beads with a magnetic separation rack, discard the supernatant, and wash the magnetic beads twice with 70% ethanol. Then add the above 100 μl TE solution (pH=6.0), and let it stand at room temperatu...
Embodiment 3
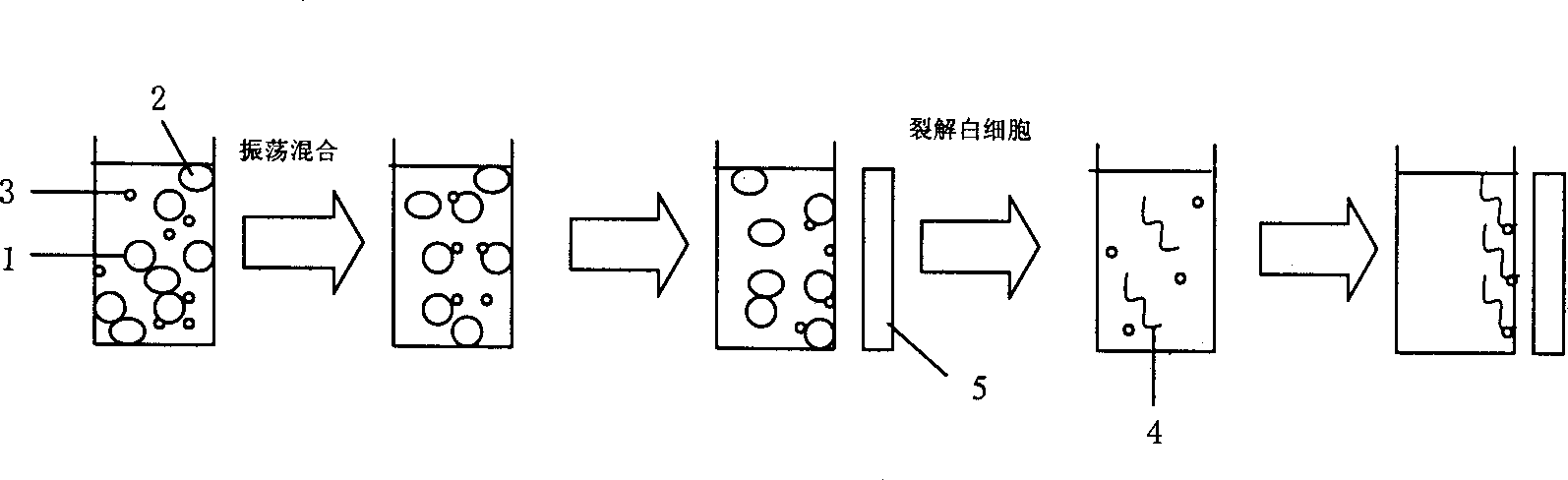
[0025] Example 3: Adsorption and separation of leukocytes in whole blood by nano-magnetic microspheres and extraction of DNA therein.
[0026] Whole blood used in this experiment was provided by healthy blood donors, and anticoagulated with 1 / 6 volume of blood ACD (23mmol / l citric acid, 80mmol / l glucose, 45mmol / l sodium citrate). Take an appropriate amount of 300 μl of blood, add 50 μl of the above-mentioned magnetic microsphere solution (suspended with the above pH=6.0 TE solution), oscillate slightly on a vortex shaker for 15 s, and after standing at room temperature for 3 min, fix the magnetic beads with a magnetic separation rack. Discard other parts. Add 300 μl of cell lysate, shake and mix well, and let stand at room temperature for 2 minutes. Then add 300 μl isopropanol, shake and mix well, and let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes. Fix the magnetic beads with a magnetic separation rack and discard the supernatant. After washing the magnetic ball twice with 70%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com