Treatment of ammonium chloride waste-water zero-displacement in rare-earth production
A treatment method and ammonium chloride technology, applied in the field of ammonium halide, can solve the problems of high impurity content of solid ammonium chloride, difficult to obtain application prospects, low economic benefits, etc. The process is simple and reasonable, and the effect of improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
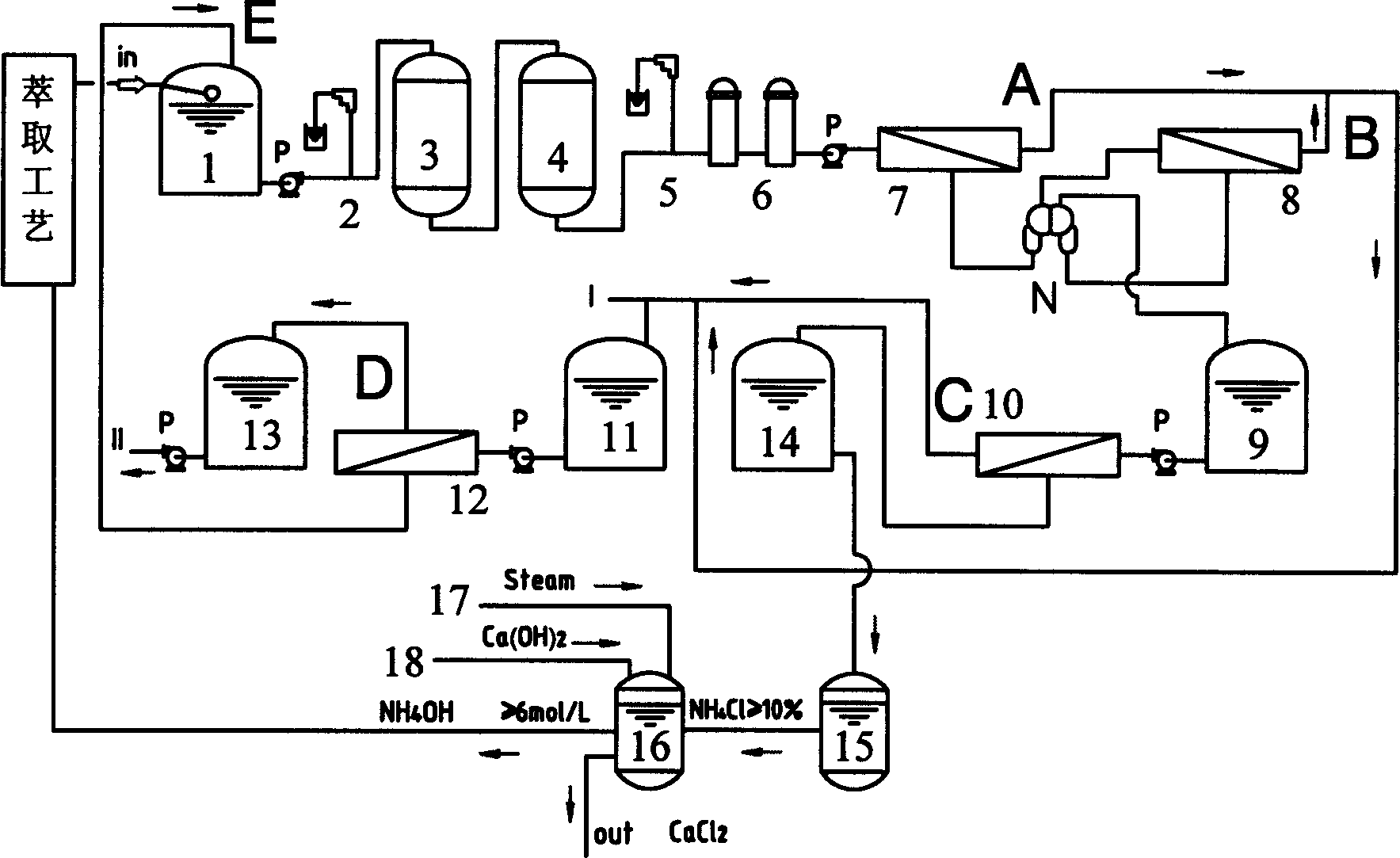
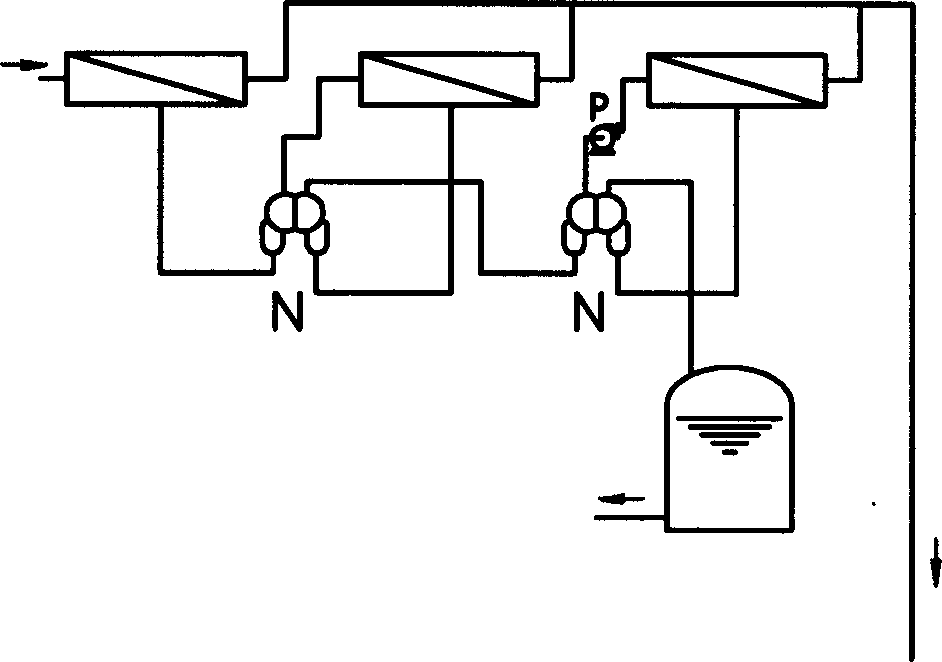
[0036] The process equipment and process of this example are as follows: figure 1 shown. The above-mentioned rare earth ore ammonium chloride wastewater is first purified and pretreated, and 5 tons of water liquid (its wastewater sampling composition is shown in Table 1) is input into the raw water tank 1 through flocculation, filtered in the multimedia filter 3 to remove impurities, activated carbon filter 4 Medium adsorption filtration, the water pollution index SDI of the effluent is ≤4.8. The flocculant is polyacrylamide, which is filtered through the secondary fine filter 6 to remove impurities. Then pump into the first-stage reverse osmosis devices 7 and 8, desalination and concentration are carried out at a pressure of 3.2Mpa and a water temperature of 15°C. This is an 8" roll-type composite membrane reverse osmosis brackish water desalination device, and its structure is a double reverse osmosis device. , the compound structure section is set as the front and back tw...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The ammonium chloride wastewater produced by a rare earth company in Northwest China has undergone chemical sedimentation, softening, filtration, and activated carbon adsorption. The water quality analysis report is shown in Table 2.
[0041] serial number
[0042] The pretreatment method is the same as Example 1. At an inlet water temperature of 31.5°C and an operating pressure of 5.0Mpa, a 2.5" membrane module is used, and the rest of the process flow is the same as Example 1. See figure 2 . When the permeate flux of the third-stage reverse osmosis device is 400mL / min, the concentration of ammonium chloride in the concentrate is 68046.2mg / L, and the concentration of the permeate is 16mg / L. The ammonium chloride concentrated solution concentrated by the above-mentioned reverse osmosis was passed through the solution, and the ammonia was distilled to obtain ammonia water with a concentration of 6.2 mol / L.
Embodiment 3
[0045] The ammonium chloride wastewater produced by a rare earth factory in Northwest China was subjected to chemical sedimentation, softening, filtration, and activated carbon adsorption similar to Example 2. The water quality analysis report is shown in Table 3.
[0046] At an inlet water temperature of 36.5°C and an operating pressure of 6.5Mpa, a 2.5″ membrane module is used, and the process flow is the same as Example 1. When the permeate flux of the third-stage reverse osmosis device is 560mL / min, the concentration of the concentrated solution is 83312mg / L. The liquid concentration is 18mg / L. The above-mentioned reverse osmosis concentrated ammonium chloride solution is passed through a three-effect evaporator, and after it is concentrated to 11%, it is passed through an ammonia distillation absorption tower, and saturated Ca(OH) 2 Solution, distill ammonia to obtain the ammoniacal liquor of 6.5mol / L concentration. No waste discharge.
[0047] The treatment metho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com