Method for preparing functional filling material of superfine calcium carbonate powder
A technology of fine calcium carbonate and filling materials, applied in the direction of calcium carbonate/strontium/barium, etc., can solve the problems of long reaction time, large product particle size, expensive production equipment, etc., achieve simple production process and equipment, and narrow particle size distribution range , low energy consumption and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Weigh 0.005mol of calcium chloride and sodium bicarbonate powder, add to 100mL of deionized water and stir thoroughly; put it into a microwave reactor, and react for 60 minutes under the action of a microwave with a power of 140W; suction filter the solid product, Wash with deionized water and dry to obtain the product submicron calcium carbonate powder.
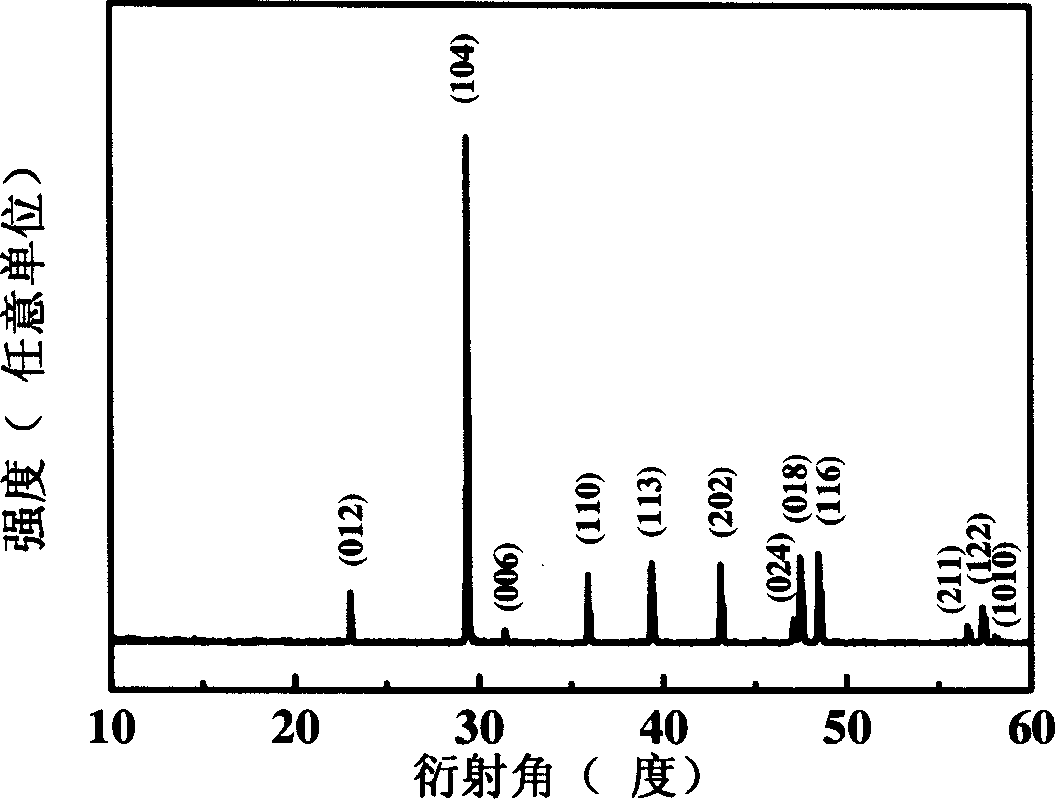
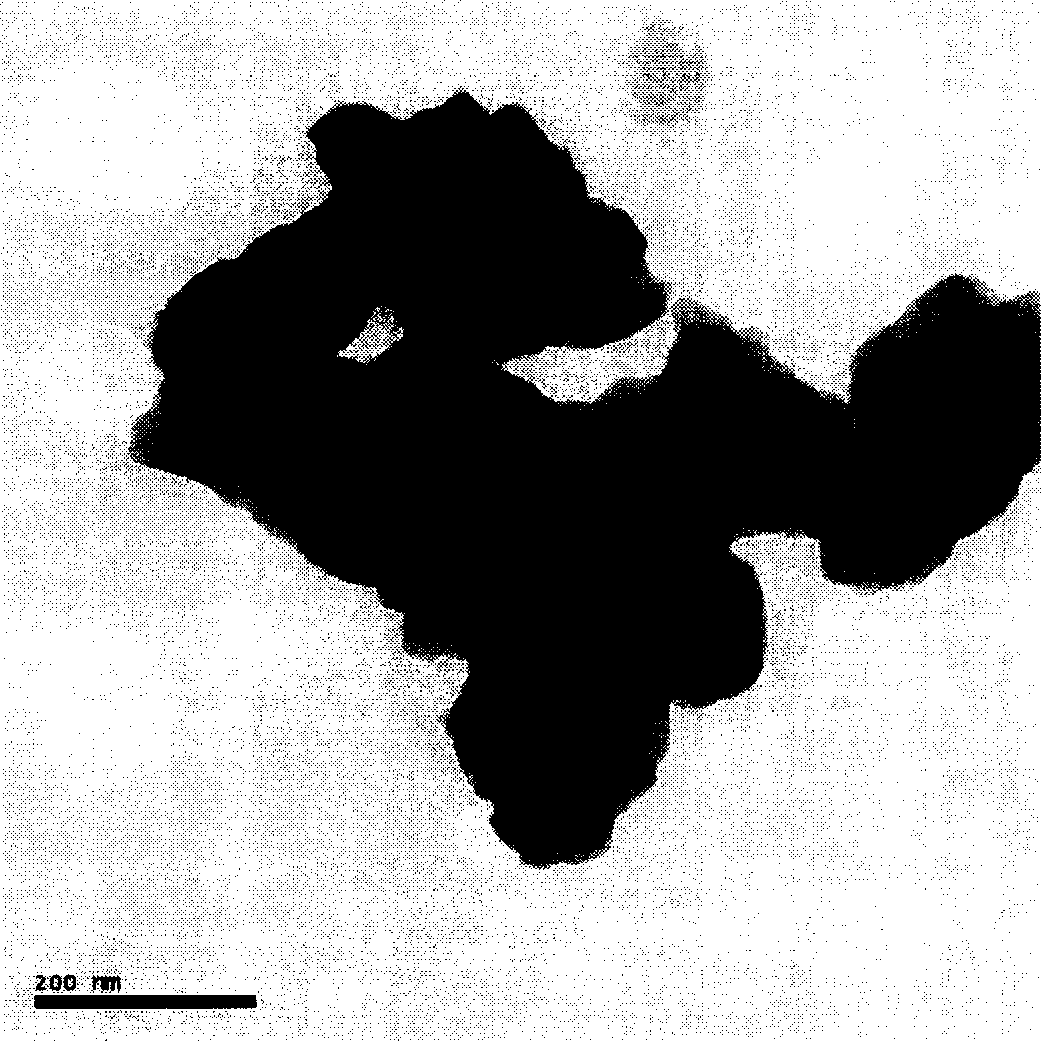
[0019] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the German Bruker D8Advance X-ray powder diffractometer (CuK α Radiation, λ = 1.5406 Ȧ) to determine the crystal structure of the prepared material; the morphology and size of the product were observed with a Tecnai 12 transmission electron microscope (TEM, 120kV) from Philips Company in the Netherlands.
[0020] The results showed that:
[0021] figure 1 : the X-ray diffraction pattern of the manufactured product of Example 1 of the present invention. All its X-ray diffraction peaks correspond to (012), (104), (006), (110), (113), (202), (024), (018) of Mitsubishi ph...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Weigh 0.005mol of calcium nitrate and sodium bicarbonate powder, add to 100mL deionized water and stir fully; put it into a microwave reactor, and react for 60 minutes under the action of a microwave with a power of 140W; suction filter the solid product, and use Wash with deionized water and dry to obtain the product submicron calcium carbonate powder.
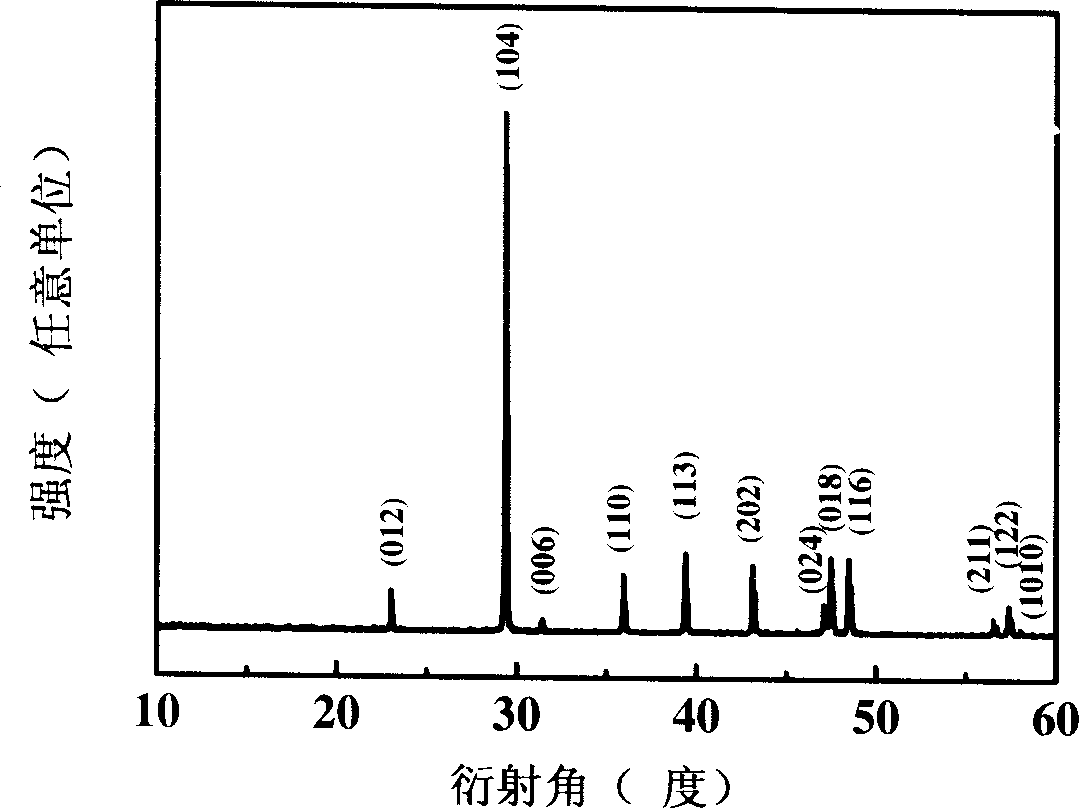
[0025] Such as image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, the German Bruker D8 Advance X-ray powder diffractometer (CuK α Radiation, λ = 1.5406 Ȧ) to determine the crystal structure of the prepared material; the morphology and size of the product were observed with a Tecnai 12 transmission electron microscope (TEM, 120kV) from Philips Company in the Netherlands.
[0026] The results showed that:
[0027] image 3 : the X-ray diffraction pattern of the product made in Example 2 of the present invention. All its X-ray diffraction peaks correspond to (012), (104), (006), (110), (113), (202), (024), (018) of Mitsubishi phase calc...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Weigh 0.005mol of calcium acetate and sodium bicarbonate powder, add to 100mL of deionized water and stir thoroughly; put it into a microwave reactor, and react for 60 minutes under the action of a microwave with a power of 140W; suction filter the solid product, and use Wash with deionized water and dry to obtain the product submicron calcium carbonate powder.
[0031] Such as Figure 5 , Image 6 As shown, the German Bruker D8 Advance X-ray powder diffractometer (CuK α Radiation, λ = 1.5406 Ȧ) to determine the crystal structure of the prepared material; the morphology and size of the product were observed with a Tecnai 12 transmission electron microscope (TEM, 120kV) from Philips Company in the Netherlands.
[0032] The results showed that:
[0033] Figure 5 : the X-ray diffraction figure of the manufactured product of the embodiment of the present invention 3. All its X-ray diffraction peaks correspond to (012), (104), (006), (110), (113), (202), (024), (018) o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com