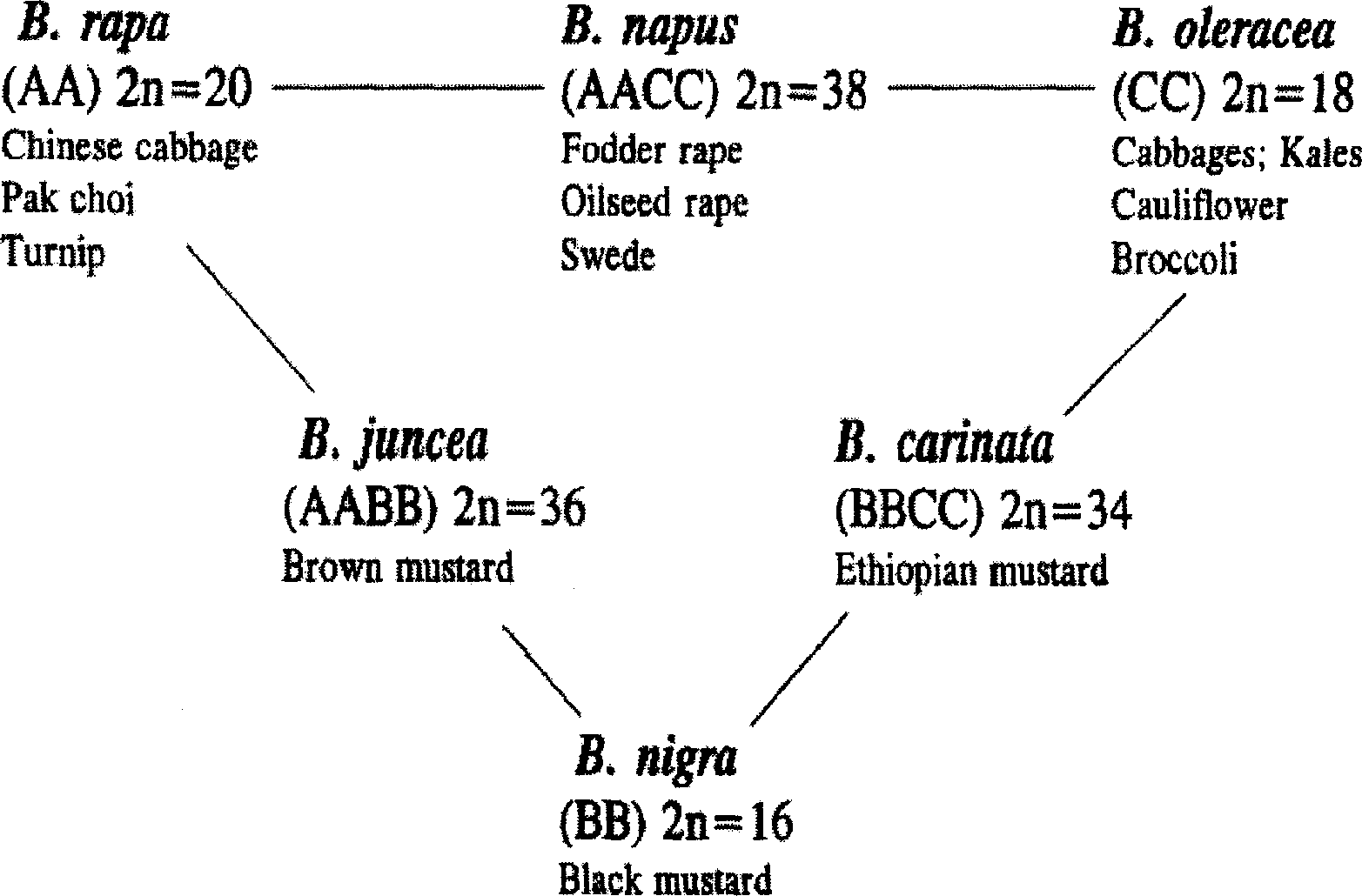
Directional gene transfer method of cabbage type rape C chromosome set
A Brassica napus and transgenic technology is applied in the field of ecological safety research of transgenic plants, and can solve the problems of transfer of exogenous target genes, difficulty of transgenic Brassica napus, identification of exogenous genes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Transgenic bark kale (B.oleracea var.alboglabra)
[0061] 1 Genetic transformation of kale
[0062] 1.1 Agrobacterium preparation
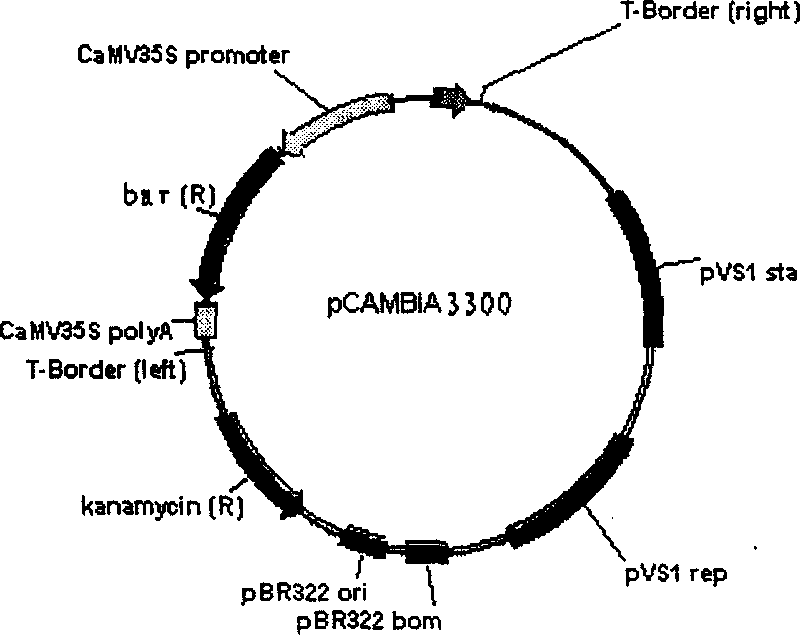
[0063] The Agrobacterium strain LBA4404 containing the bar gene expression vector pCAMBIA3300 plasmid was streak-inoculated on the YEB plate medium supplemented with 50mg / L kanamycin, and cultured upside down at 28°C for 2-3 days. After the colony grows, pick a single colony from the YEB plate, inoculate it in 5ml YEB (containing 50 mg / L kanamycin) liquid medium, place it on a shaker at 200 rpm, and cultivate overnight at 28°C. Take the bacterial solution and inoculate it on the YEB plate supplemented with 50 mg / L kanamycin, and incubate it upside down at 28°C for 2 days. For each experiment, take a single colony and inoculate it on the YEB plate medium supplemented with 50mg / L kanamycin, culture it at 28°C for 1-2 days, and wash the bacteria with 1 / 2MS liquid medium (pH5.4) , and dilute the bacterial solution to OD600=0.08 as the bacter...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Synthesis of Brassica napus with C Chromosome Transgenic Bar Gene
[0075] 1.1 Artificial synthesis of Brassica napus as female parent
[0076]Seven Chinese cabbage varieties including Heiyebai, Rongyouai Kangqing, Tezao 50 cabbage moss, golden cabbage, red cabbage, Chaoshan sweet cabbage and double-low cabbage rape were used as female parents, and the bar gene transgenic Chinese kale was used as crops. The male parent is interspecifically crossed. 4-7 days after pollination, the fertilized ovary was taken for disinfection, and the ovary was cultured, and the medium was MS medium containing 500 mg / L hydrolyzed casein. After the ovary was cultured for 40 days, the seeds were peeled off from the mature pods and transferred to MS medium for germination. When seedlings germinate from the seeds, the seedlings are excised and transplanted on MS medium containing 0.01% colchicine for 7-10 days to perform chromosome doubling. Then, the seedlings were transferred to the mediu...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Molecular verification of bar gene located on chromosome C of Brassica napus
[0085] Genome Southern blotting analysis: Take about 20 μg of total genomic DNA from transgenic kale, C chromosome transgenic Brassica napus and non-transgenic rapeseed, digest them completely with endonuclease EcoR I, and run them on 0.8% agarose gel For electrophoresis separation, the DNA of plasmid pCAMBIA3300 was used as a positive control. The procedures of prehybridization, hybridization and membrane washing were carried out according to the method reported by Sharpe et al. (1995). The probe used was a 0.5 kb fragment of the bar gene amplified by plasmid PCR, and the detection was performed using a Digoxigenin labeling kit (Roche Diagnostics, Swiss).
[0086] Randomly select three PCR and Basta Genomic Southern blot analysis of the positive synthetic rapeseed line (same transgenic male parent) and its male parent showed that the exogenous bar gene had been integrated into the genome...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com