Novel technique for preparing ethylene glycol
A ethylene glycol and new process technology, applied in the new process field of ethylene glycol production, can solve the problems of flammability, increased energy consumption, shortage, etc., and achieve the advantages of reducing operating costs, simplifying process flow, and improving production efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
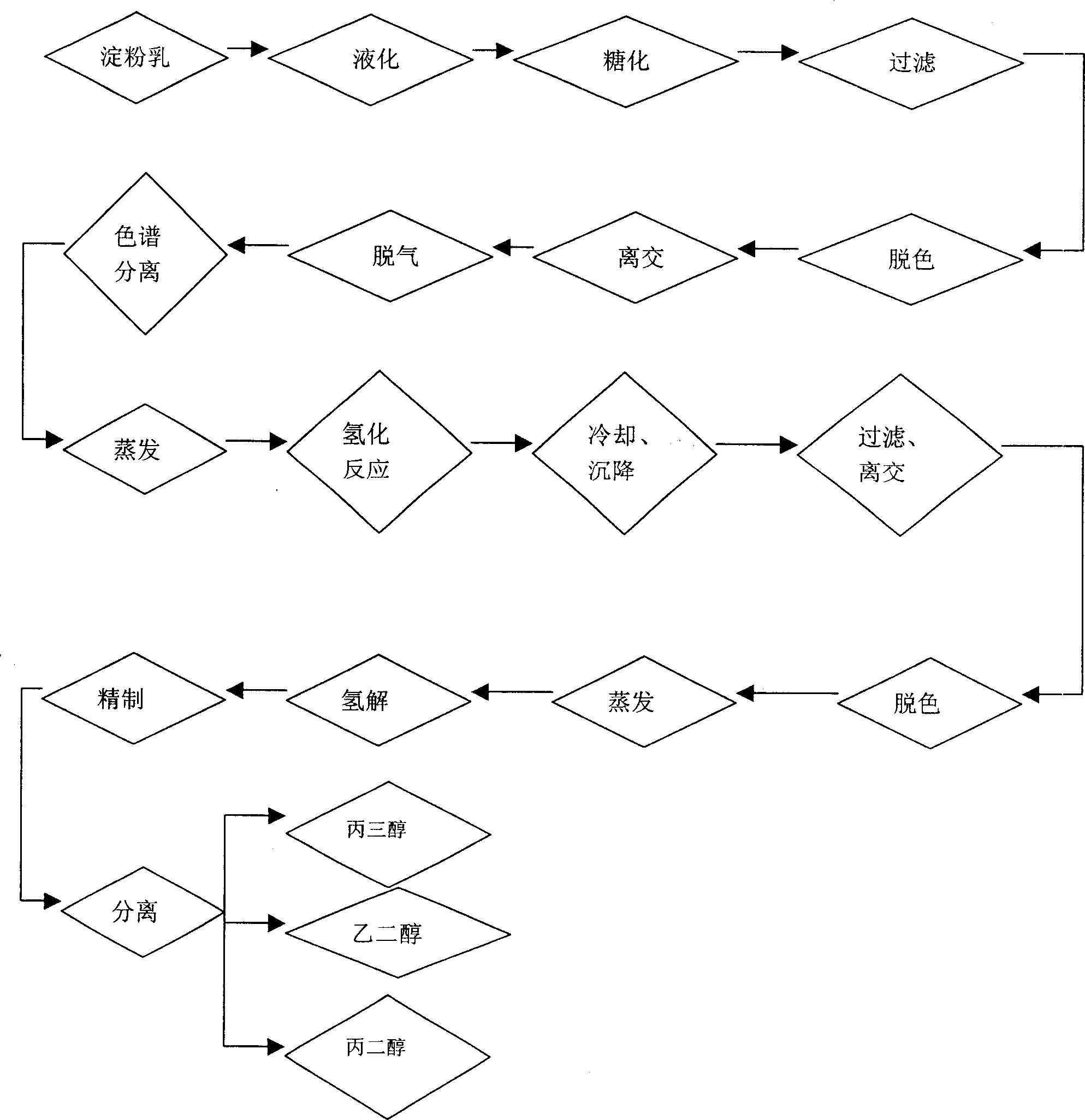
[0018] Example 1: As shown in the attached figure, the preparation of glucose syrup with DX value: the cornstarch milk is subjected to liquefaction, saccharification, filtration, decolorization, separation and other processes and then enters the simulated moving bed chromatographic separation system for separation to obtain DX 99.5%. glucose syrup. The feed dry matter entering the chromatographic separation system is 60%, and the temperature is 60°C.
[0019] Hydrogenation reaction: Evaporate high DX value glucose syrup to 50% dry matter, use nickel as a catalyst, carry out hydrogenation reaction at 150°C, pH 8.2, and pressure 4.5Mpa to obtain 97% sorbitol solution.
[0020] Refining of sorbitol solution: the sorbitol solution after the hydrogenation reaction is cooled, settled, filtered, separated and decolorized, and evaporated to 50%.
[0021] Hydrogenolysis of sorbitol: under the conditions of pH 10, temperature 230°C and pressure 2500 psig, using Ni / Ru as catalyst, hydro...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: As shown in the accompanying drawings, the preparation of glucose syrup with DX value: the cornstarch milk is put into the simulated moving bed chromatographic separation system for separation after liquefaction, saccharification, filtration, decolorization, separation and other processes to obtain DX 99% Glucose syrup, wherein the feed dry matter entering the chromatographic separation system is 50%, and the temperature is 70°C.
[0024] Hydrogenation reaction: Evaporate high DX value glucose syrup to 50% dry matter, use nickel as a catalyst, carry out hydrogenation reaction at 140°C, pH 7.5, and pressure 3.5Mpa to obtain 96% sorbitol solution.
[0025] Refining of sorbitol solution: the sorbitol solution after the hydrogenation reaction is cooled, settled, filtered, separated and decolorized, and evaporated to 50%.
[0026] Hydrogenolysis of sorbitol: under the conditions of pH 9, temperature 190°C and pressure 2000 psig, using Co / Re as catalyst, hydrogenol...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: As shown in the attached figure, the preparation of glucose syrup with DX value: After the corn starch milk is liquefied, saccharified, filtered, decolorized, and separated, it is separated into a simulated moving bed chromatographic separation system to obtain DX 99.7%. glucose syrup. The feed dry matter entering the chromatographic separation system is 70%, and the temperature is 80°C.
[0029] Hydrogenation reaction: Evaporate high DX value glucose syrup to 50% dry matter, use nickel as a catalyst, carry out hydrogenation reaction at 160°C, pH 8.5, and pressure 5.5Mpa to obtain 98% sorbitol solution.
[0030] Refining of sorbitol solution: the sorbitol solution after the hydrogenation reaction is cooled, settled, filtered, separated and decolorized, and evaporated to 50%.
[0031] Hydrogenolysis of sorbitol: under the conditions of pH 11, temperature 250°C and pressure 4000 psig, using Ru as a catalyst, hydrogenolysis for 6 hrs to obtain a mixture of ethy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com