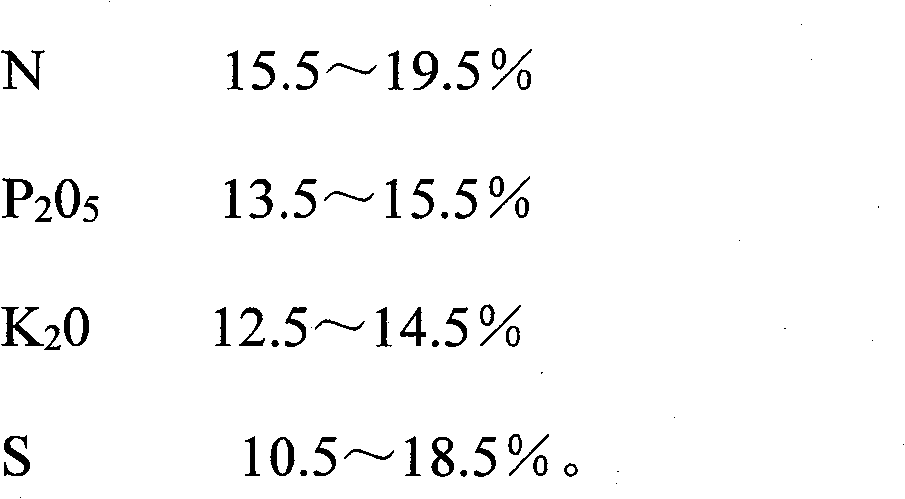High nitrogen sulfur base nitrogen phosphorus potassium slow release composite fertilizer and its production method
A technology of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and high nitrogen and sulfur, which is applied in the field of compound fertilizers, can solve problems such as the inability to adjust nutrients, the easy loss of fertilizers, and the inability to increase the nitrogen ratio, and achieve the effects of strong market competitiveness, improved quality, and increased utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Production of high-nitrogen-sulfur-based NPK compound fertilizer: S 18 -N 16 -P 15 -K 13 , (where N≥16%, S≥12%, CL-<3%, N, P, K single nutrient ±0.5)
[0035] Pick
[0036] 98% sulfuric acid 0.560t
[0037] 100%P 2 o 5 Phosphoric acid 0.153t——(using 26% dilute phosphoric acid, which contains 100% P 2 o 5 )
[0038] 60%K 2 O Potassium chloride 0.214t——(referring to containing 60% K in pure potassium chloride 2 O)
[0039] 99.5% liquid ammonia 0.134t
[0040] 38% N urea formaldehyde 0.106t——(urea formaldehyde contains 38% N)
[0041] 10-50-0 ammonium phosphate /
[0042] 46% N urea 0.044t (for coating) --- (refers to 46% N in urea)
[0043] Anticaking agent 0.001t
[0044] The above are the raw materials needed to produce one ton of compound fertilizer
[0045] Excessive 98% concentrated sulfuric acid is used to decompose potassium chloride at a relatively low temperature (130°C) to obtain potassium bisulfate solution, which is mixed with 26% dilute phosp...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Production of high-nitrogen, sulfur-based NPK slow-release compound fertilizer: S 15 -N 17 -P 14 -K 14 , N+P 2 o 5 +K 2 O≥45% (of which N≥16%, S≥12%, CL - <3%, N, P, K single nutrient ±0.5)
[0049] Pick
[0050] 98% sulfuric acid 0.460t
[0051] 100%P 2 o 5 Phosphoric acid 0.126t
[0052] 60%K 2 O potassium chloride 0.236t
[0053] 99.5% liquid ammonia 0.111t
[0054] 38% N urea formaldehyde 0.168t
[0055] 10-50-0 ammonium phosphate 0.028t
[0056] 46% N urea 0.044t
[0057] Anticaking agent 0.001t
[0058] The above are the raw materials needed to produce one ton of compound fertilizer
[0059] According to the above process route, three times of chemical synthesis, one time of nitrogen supplementation, one time of spraying anti-caking agent, and the finished product is obtained after metering and packaging.
Embodiment 3
[0061] Production of high-nitrogen-sulfur-based NPK compound fertilizer: S 11 -N 19 -P 14 -K 13 , N+P 2 o 5 +K 2 O≥45% (of which N≥16%, CL - <3%, N, P, K single nutrient ±0.5)
[0062] Pick
[0063] 98% sulfuric acid 0.330t
[0064] 100%P 2 o 5 Phosphoric acid 0.090t
[0065] 60%K 2 O potassium chloride 0.226t
[0066] 99.5% liquid ammonia 0.079t
[0067] 38% N urea formaldehyde 0.256t
[0068] 10—50-0 ammonium phosphate 0.100t
[0069] 46% N urea 0.044t
[0070] Anticaking agent 0.001t
[0071] The above are the raw materials needed to produce one ton of compound fertilizer
[0072] According to the above process route, three times of chemical synthesis, one time of nitrogen supplementation, one time of spraying anti-caking agent, and the finished product is obtained after metering and packaging.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com