R-T-B type alloy, production method of r-t-b type alloy flake, permanent magnet, and fine powder for manufacturing the same
A technology of permanent magnets and alloy sheets, which is applied in the fields of magnetic objects, inductors/transformers/magnets, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of powder particle size distribution expansion and alloy crushing stability deterioration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
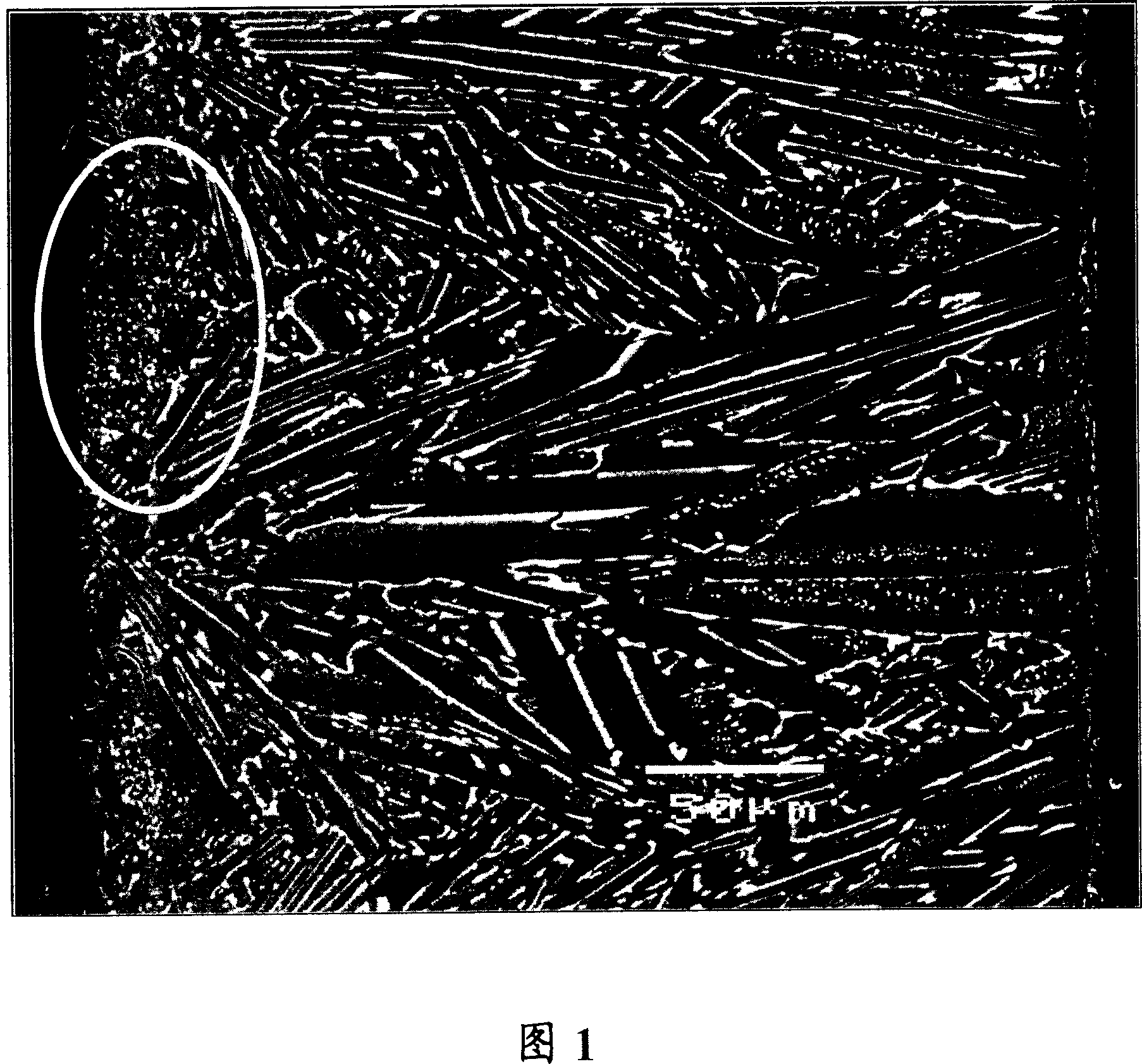
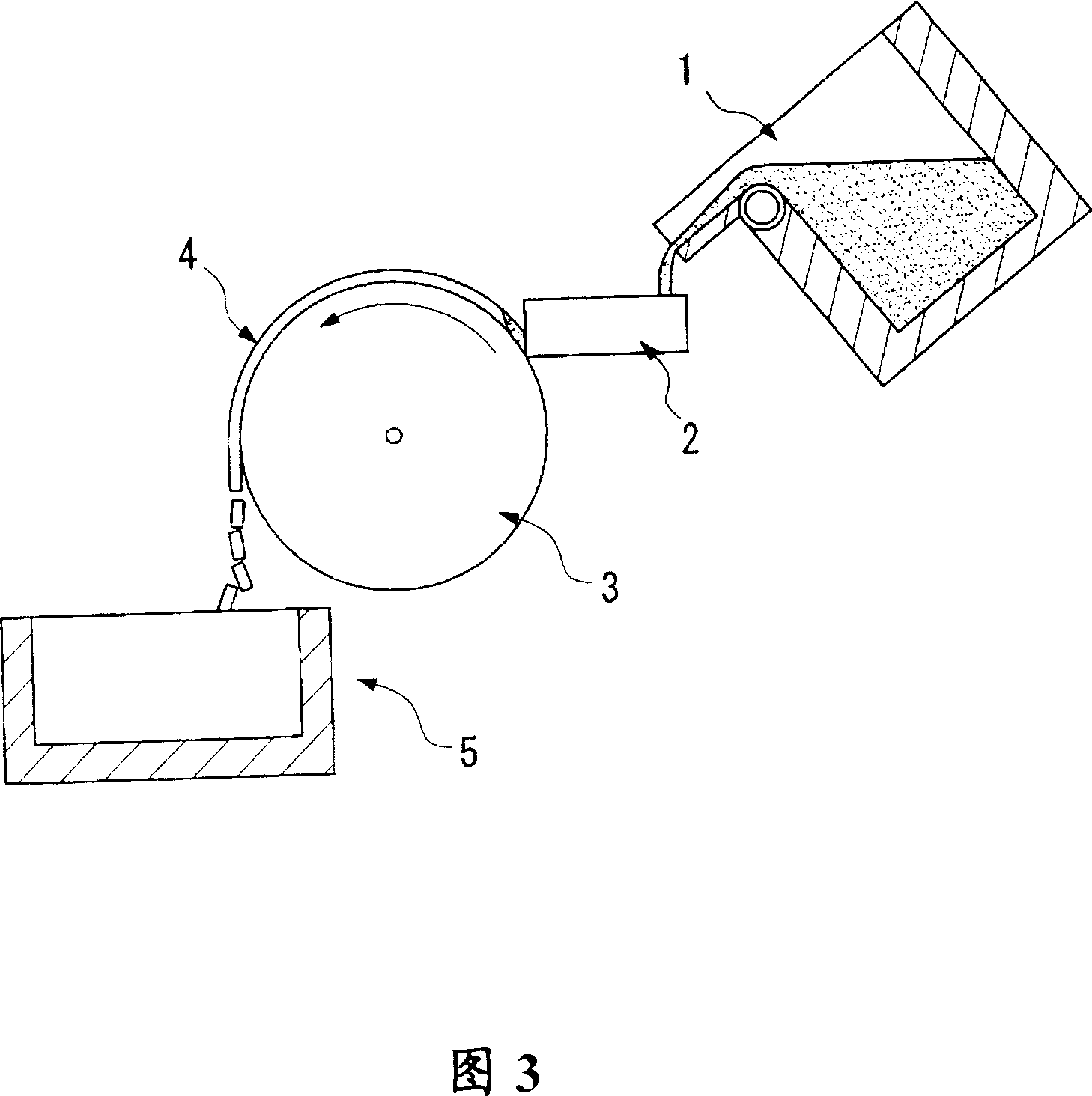
[0089] Raw metal neodymium, dysprosium metal, ferroboron, cobalt, aluminum, copper and iron are weighed to give an alloy composition comprising 22% of Nd, 9% of Dy, 0.95% of B, 1% of Co, 0.3% of Al and 0.1 of Cu, the rest being Fe, alloy components were melted in an alumina crucible at 1 atm in an argon atmosphere by using a high-frequency melting furnace, and the molten alloy was cast by an SC method to manufacture alloy flakes.
[0090] The turning roll used for casting had a diameter of 600 mm, was made of an alloy obtained by mixing trace amounts of Cr and Zr with copper, and was water-cooled inside. The peripheral velocity of the roll at the time of casting was 1.3 m / sec, the average supply rate of the molten alloy to the cast roll was 28 g / sec per 1 cm width, and the average temperature of the alloy when it was separated from the cast roll was measured by a radiation thermometer and found to be 890°C. In the measured values, the difference between the highest temperature...
example 2
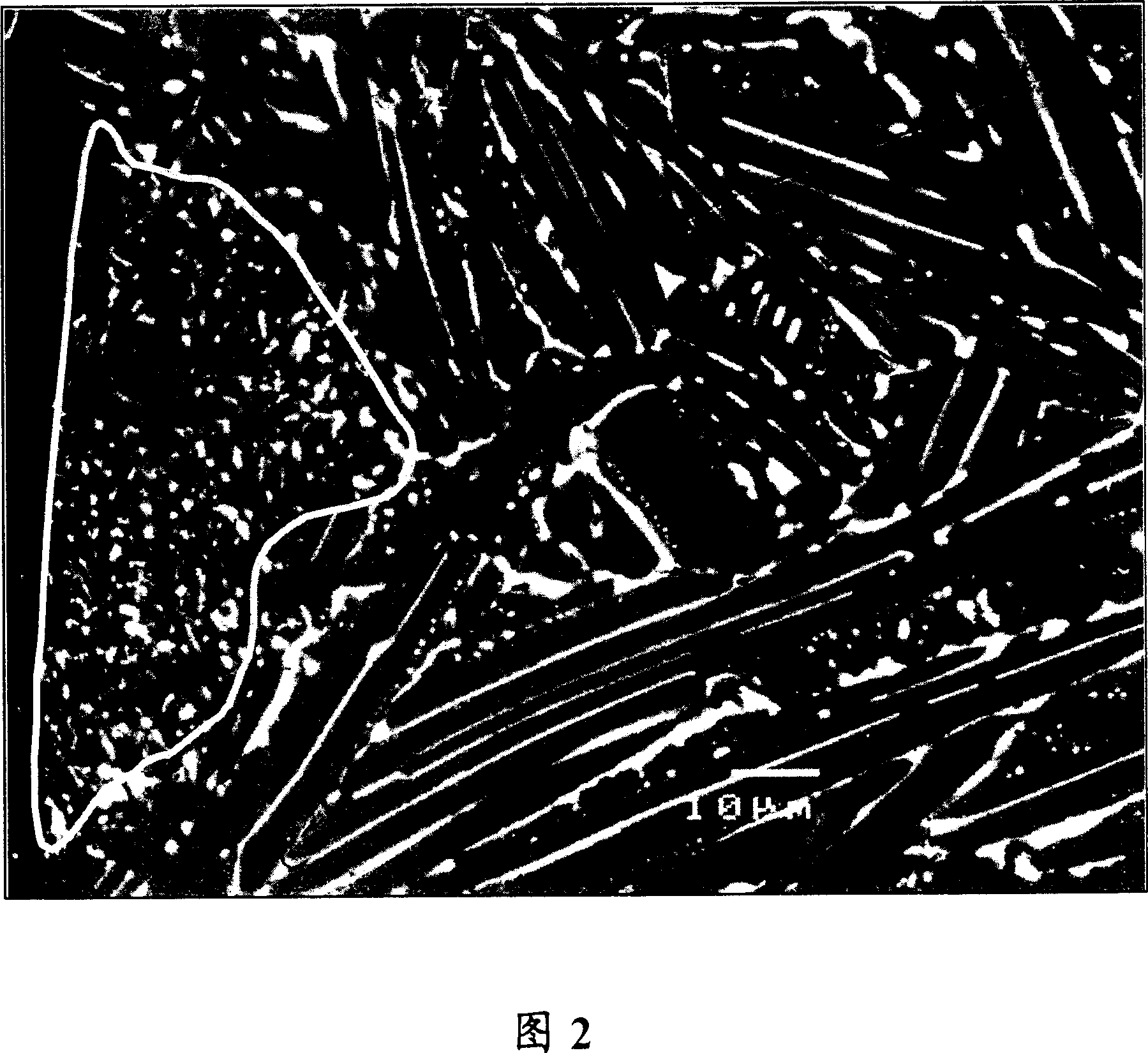
[0101] Metal neodymium, metal praseodymium, boron iron, cobalt, aluminum, copper and iron are mixed to give an alloy composition comprising, by weight, 26.0% of Nd, 5.0% of Pr, 0.95% of B, 1.0% of Co, 0.3% of Al and 0.1 of Cu, the rest being Fe, and melting and casting by the SC method were performed in the same manner as in Example 1. However, the peripheral velocity of the roll at the time of casting was 1.3 m / sec, the average supply rate of the molten alloy to the casting roll was 28 g / sec per 1 cm width, and the average temperature of the alloy at the time of separation from the casting roll measured by a radiation thermometer was 850°C, And the difference between the highest temperature and the lowest temperature of the measured temperatures is 20°C. Since the alloy's R 2 T 14 The melting point of phase B is about 1140°C, so the difference from the average separation temperature is 290°C. Also, the average cooling rate of the R-T-B series alloy on the casting roll was ...
example 3
[0111] The alloy flakes obtained in Example 1 were subjected to hydrogen cracking and pulverized by a jet mill. The conditions in the hydrogen absorption step which is the preceding step of the hydrogen cracking step were 100% hydrogen atmosphere, a pressure of 2 atm and a holding time of 1 hour. The temperature of the metal ribbon at the start of the hydrogen absorption reaction was 25°C. The conditions in the dehydrogenation step which is a subsequent step were 500° C. and a holding time of 1 hour in a vacuum atmosphere of 0.133 hPa. Subsequently, 0.07% by mass of zinc stearate powder was added to the powder obtained above, and the obtained powder was thoroughly mixed by a V-blender under a nitrogen atmosphere of 100%, and then pulverized by a jet mill. The atmosphere during pulverization was a nitrogen atmosphere mixed with 4000 ppm of oxygen. Afterwards, the powders were thoroughly mixed again by V-blender under 100% nitrogen atmosphere. The oxygen concentration in the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com