Hepatitis E virus vaccine and method
a technology for hepatitis e virus and vaccine, applied in the field of antigen and antibody vaccine compositions, can solve the problems of general unevenness of hev, and achieve the effect of neutralizing hepatitis e virus (hev) infection and preventing or treating hev infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
In vitro HEV Infection of Primary Human Hepatocytes
[0159] A. HEV Infection of Human Hepatocytes.
[0160] The HEV-infected cynomolgus monkey #73 stool pool (fourth passage) was used as an inoculum for infections of primary human hepatocytes. Various amounts of inoculum was diluted in 1 ml of serum-free medium (SFM) and applied to the culture during a 3 hr incubation period. This solution was then supplemented with 2 ml of fresh SFM and the entire mixture was incubated overnight. The next day, cell monolayers were washed with WME (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4) for three times and changed to fresh SFM, which was changed at two day intervals thereafter.
[0161] B. Immunofluorescence Staining Assay.
[0162] Primary cynomolgus monkey hepatocytes were isolated and plated in tissue culture plates with collagen-coated coverslips as described. Cells on coverslips were infected with either the HEV-infected cynomolgus monkey #73 stool pool or the NIH normal human serum three days after initial plating. The in...
example 3
Preparation of 406.3-2 and 406.4-2 Antigens
[0169] A TZKF1 plasmid (ET1.1), ATCC deposit number 67717, was digested with EcoRI to release the 1.33 kb HEV insert which was purified from the linearized plasmid by gel electrophoresis. The purified fragment was suspended in a standard digest buffer (0.5M Tris HCl, pH 7.5; 1 mg / ml BSA; 10 mM MnC12) to a concentration of about 1 mg / ml and digested with DNAse I at room temperature for about 5 minutes. These reaction conditions were determined from a prior calibration study, in which the incubation time required to produce predominantly 100-300 basepair fragments was determined. The material was extracted with phenol / chloroform before ethanol precipitation.
[0170] The fragments in the digest mixture were blunt-ended and ligated with EcoRI linkers. The resultant fragments were analyzed by electrophoresis (5-10V / cm) on 1.2% agarose gel, using PhiX174 / HaeIII and lambda / HindIII size markers. The 100-300 bp fraction was eluted onto NA45 strips (Sc...
example 4
Neutralizing Activity of Anti-3.2(M) Antibody
[0190] A. In vitro Infection
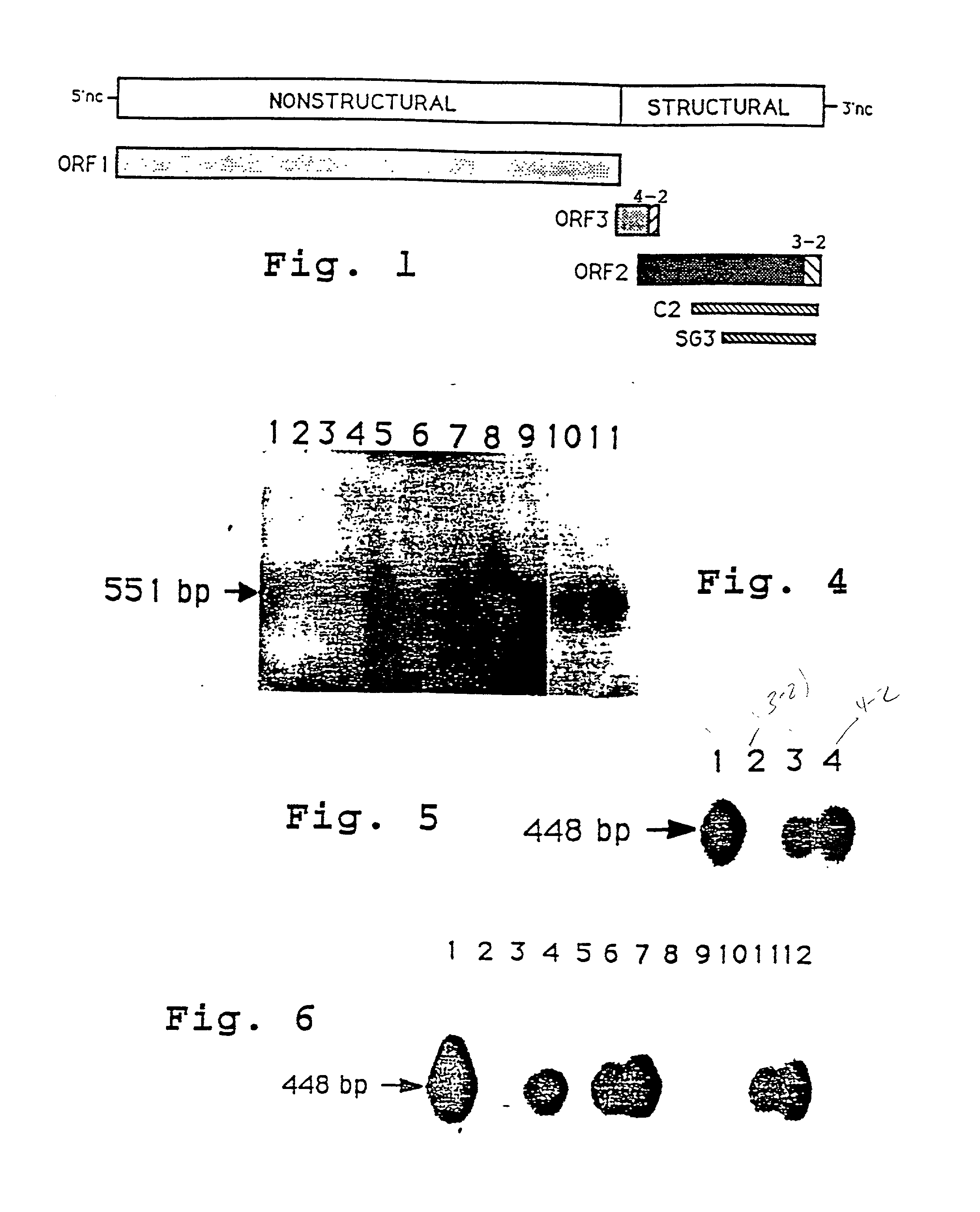
[0191] To prove that primary human hepatocytes were permissive for HEV infection and replication, cells were exposed to either normal human serum (NIH normal human serum pool) or HEV-infected cynomolgus macaque stool preparation (cyno#73). Fourteen days postinfection, total cellular RNAs were prepared for reverse-transcription (RT) / polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays to evaluate the infectability of primary human hepatocytes with HEV. The results indicated that primary human hepatocytes were capable of supporting HEV propagation (FIG. 4).
[0192] Although quantitative PCR was not applied, total cellular RNA isolated from HEV-infected primary human hepatocytes would indicate a high level of virus replication as suggested by the extent of hybridization with the .alpha.-.sup.32P-dCTP labeled HEV-specific probe (lane 5). There was no evidence of HEV in total cellular RNA isolated from primary human hepatocytes tre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com