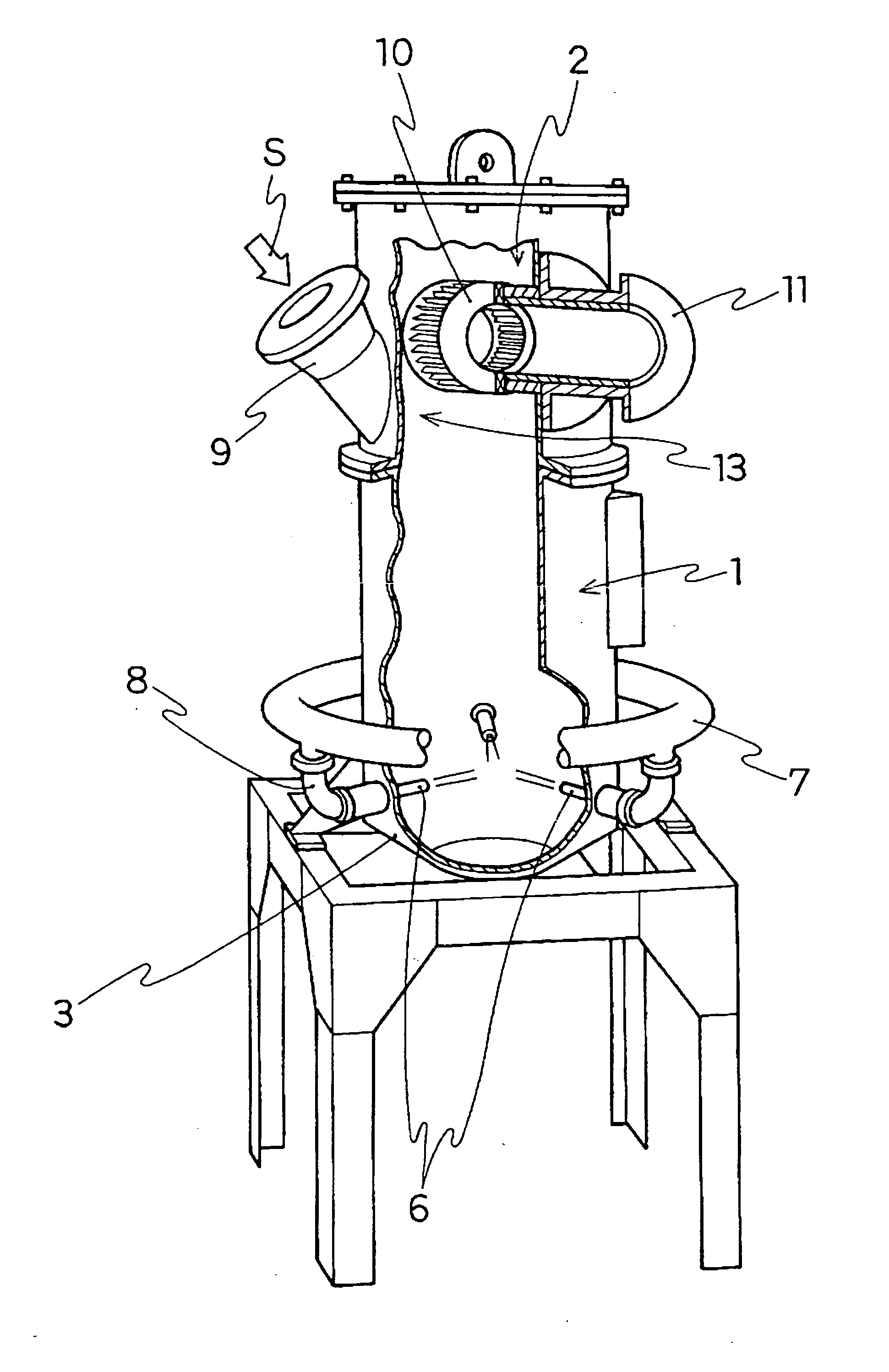
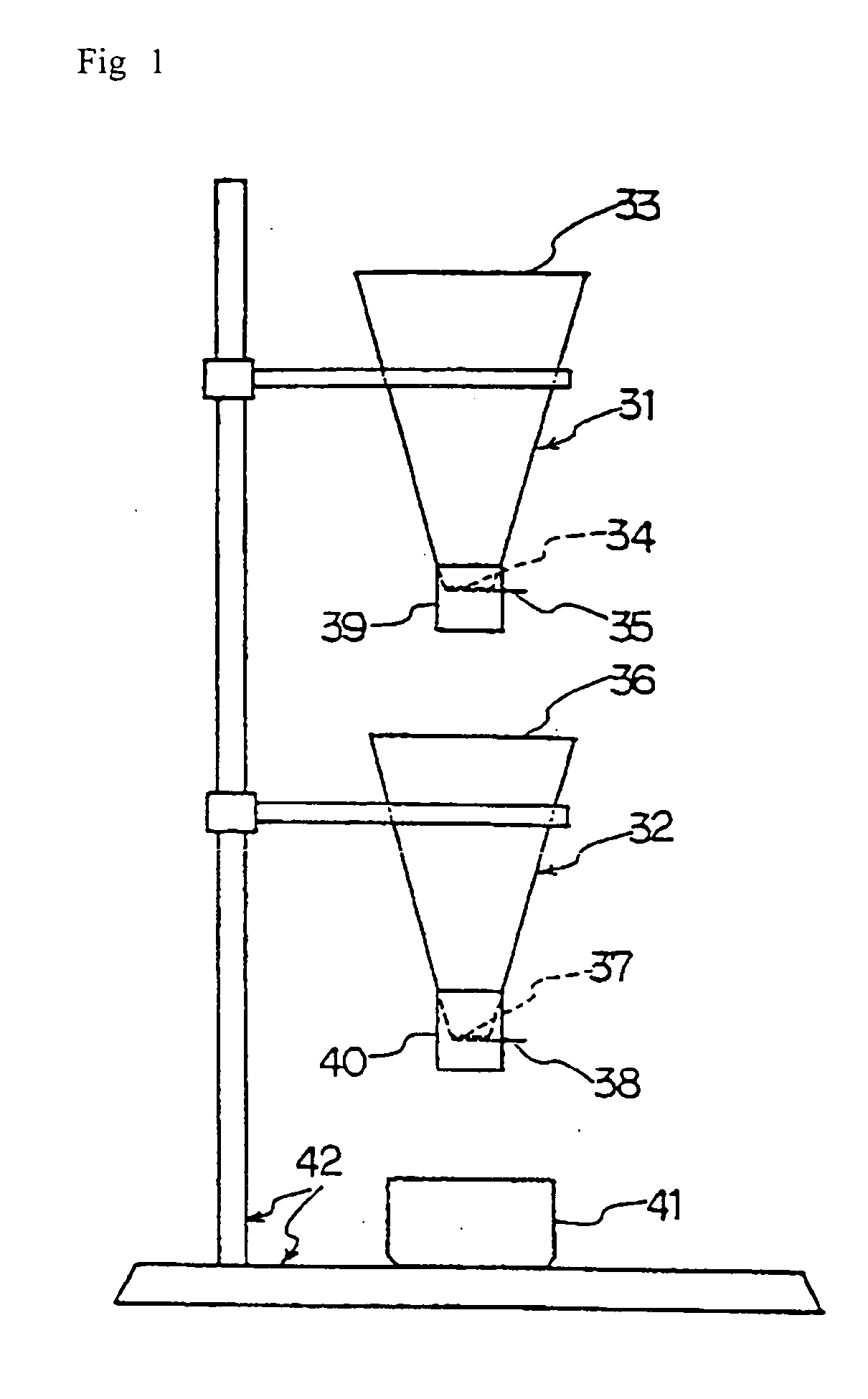
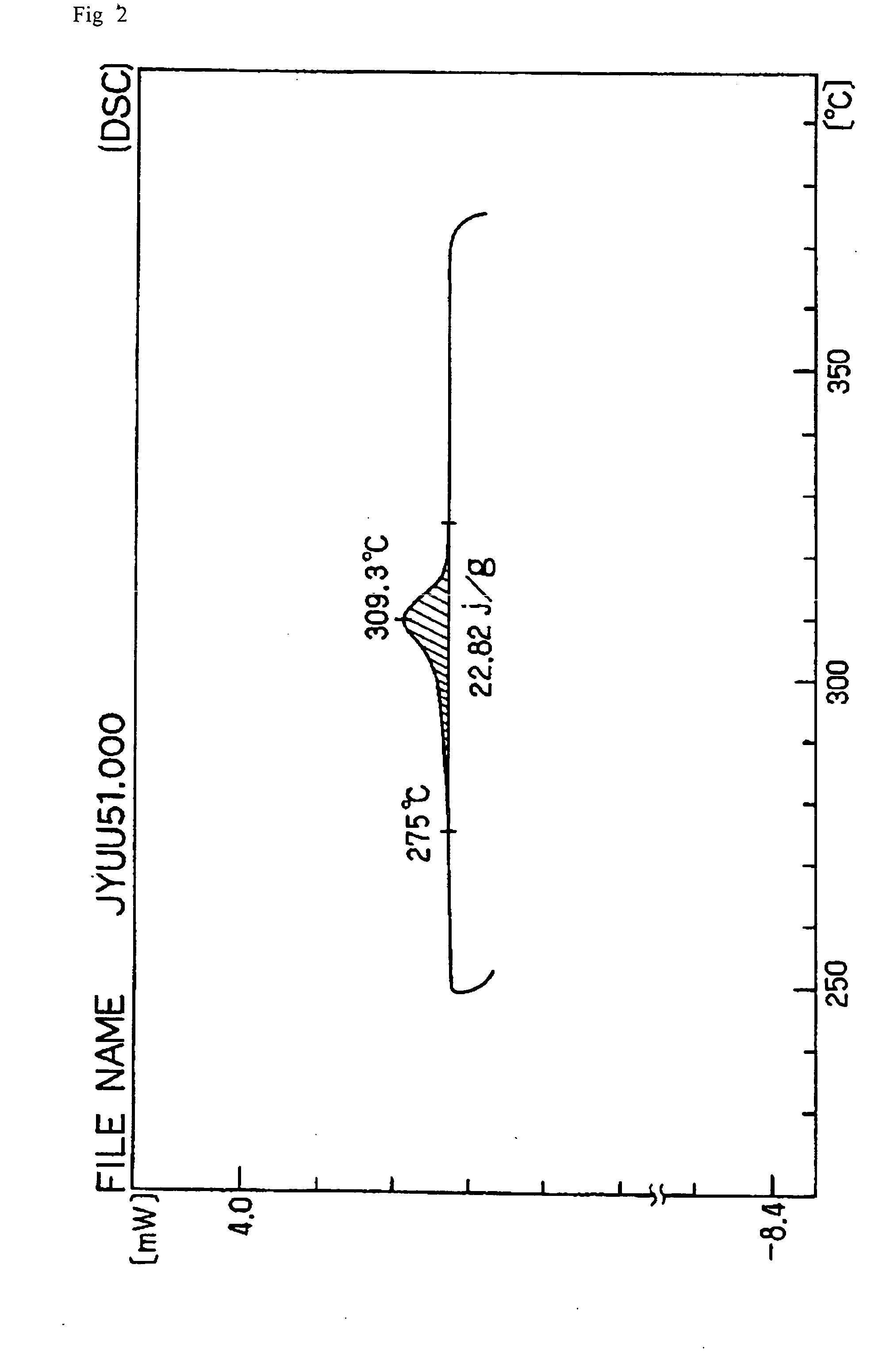
Ptfe powder and method of producing ptfe powder for molding
a technology of polytetrafluoroethylene and ptfe powder, which is applied in the field of polytetrafluoroethylene powder, can solve the problems of reducing the tensile strength of the cylinder, the inability to mold the resin, and the inability to meet the requirements of the mold or cylinder, so as to/or tensile elongation, improve the surface roughness ra, and improve the tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
production example 1
Production of PTFE Powder (I) not Reduced in Size
A 2,000-liter stainless steel autoclave equipped with a stirrer was charged with 1,600 liters of deoxygenated pure water, and the air in the autoclave was purged with nitrogen, which was in turn substituted with tetrafluoroethylene. Then, while maintaining the inside temperature at 30° C., tetrafluoroethylene was pressed into the autoclave until an internal pressure of 4 atmospheres, (NH4)2S2O8 was added as a polymerization initiator, and the polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene was carried out with stirring. As the polymerization progresses, the pressure lowered. Therefore, tetrafluoroethylene was added continuously so that the internal pressure might be maintained at 4 atmospheres. After 5 hours, stirring was discontinued, the unreacted tetrafluoroethylene was recovered, and the autoclave contents were taken out. The product polymer, namely the virgin polymer of a PTFE-based polymer with an average particle diameter of 5 to 7 mm,...
production example 2
Production of PTFE Powder (III) not Reduced in Size
A 170-liter autoclave was charged with a solution of 3.3 g of ammonium carbonate in 54.8 liters of pure water, and the solution was stirred using an anchor impeller at 110 rpm. After deaeration, tetrafluoroethylene was charged into the autoclave until a gauge pressure of 0.5 kgf / cm2G. After three repetitions of this procedure, perfluoro(propyl vinyl ether) was pressed into the autoclave using tetrafluoroethylene and, after raising the reaction system temperature to 50° C., tetrafluoroethylene was fed to the autoclave under pressure until a reaction system internal pressure of 8 kgf / cm2 G. Thereto was added ammonium persulfate to initiate the polymerization. While continuously feeding tetrafluoroethylene under pressure to maintain the reaction system internal pressure at 8 kgf / cm2 G, the polymerization was carried out until the tetrafluoroethylene consumption amounted to 30% by weight relative to the weight of the aqueous medium. T...
production example 3
Production of PTFE Powder (II) not Reduced in Size
A 170-liter autoclave was charged with a solution of 3.3 g of ammonium carbonate in 54.8 liters of pure water, and the solution was stirred using an anchor impeller at 110 rpm. After deaeration, tetrafluoroethylene was charged into the autoclave until a gauge pressure of 0.5 kgf / cm2 G. After three repetitions of this procedure, perfluoro(propyl vinyl ether) was pressed into the autoclave using tetrafluoroethylene and, after raising the reaction system temperature to 70° C., tetrafluoroethylene was fed to the autoclave under pressure until a reaction system internal pressure of 8 kgf / cm2 G. Thereto was added ammonium persulfate to initiate the polymerization. While continuously feeding tetrafluoroethylene under pressure to maintain the reaction system internal pressure at 8 kgf / cm2 G, the polymerization was carried out until the tetrafluoroethylene consumption amounted to 22.5% by weight relative to the weight of the aqueous medium....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com