Polishing composition and use thereof
a technology of polishing composition and composition, applied in the field of aqueous chemical formulation, can solve the problems of limited shelf life of products and great challenge of chemical mechanical planarization, and achieve the effects of good planarity, excellent colloidal stability, and absence of corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0046] The following composition is made by missing the following components in the concentrations listed bellowed. The pH of the slurry is 2.5:
Concentrations in ppmPoliEdge 2001 silica128571Benzotriazole6500Tetrabutyl ammonium hydroxide4000Phosphoric acid4488Deionized waterBalance
[0047] To this slurry, hydrogen peroxide is added as an oxidizer to oxidize the metallic layers to be polished. Dilution for polishing is 70 parts by volume of slurry: 29 parts by volume of deionized water: 1 part by volume of 30% hydrogen peroxide.
[0048] Polishing is performed on a IPEC 472 CMP tool. The polishing parameters are: [0049] Pressure: 3 psi [0050] Platen Speed: 90 RPM [0051] Carrier Speed: 30 RPM [0052] Back-pressure: 2 psi [0053] Slurry Flow rate: 200 ml / min [0054] Polish Pad: k-grooved IC 1000 [0055] Polish time: 60 seconds
[0056] The removal rates of the metal films are calculated based on the changes in thickness upon polishing as measured by sheet resistance measurement technique with ...
example 2
[0059] A 8″ patterned wafer containing 9000A deep trenches patterned inside a TEOS dielectric. The trenches are filled with a metallization stack consisting of 200 A Ta / 100A Ru / 250A NiFe / 100A Ru / 9000A Cu. The copper film deposited on the regions outside the trenches is first removed using a copper CMP process using a slurry with Cu:Ta removal rate selectivity of more than 100. This results in a wafer with copper restricted to the trenches. The remaining wafer is still covered with the Ta / Ru / NiFe / Ru metallization layer. The slurry described in example 1 along with the hydrogen peroxide dilution also described in example 1 is used to remove these metallic layers. CMP polish parameters except for the polish time are identical as in example 1.
[0060] The following table tabulates the dishing topography for 100 micron lines for wafers polished at different stages. This topography is measured using VEECO AFP. After the initial 45 seconds, the wafer is mostly free from all the metallic lay...
example 3
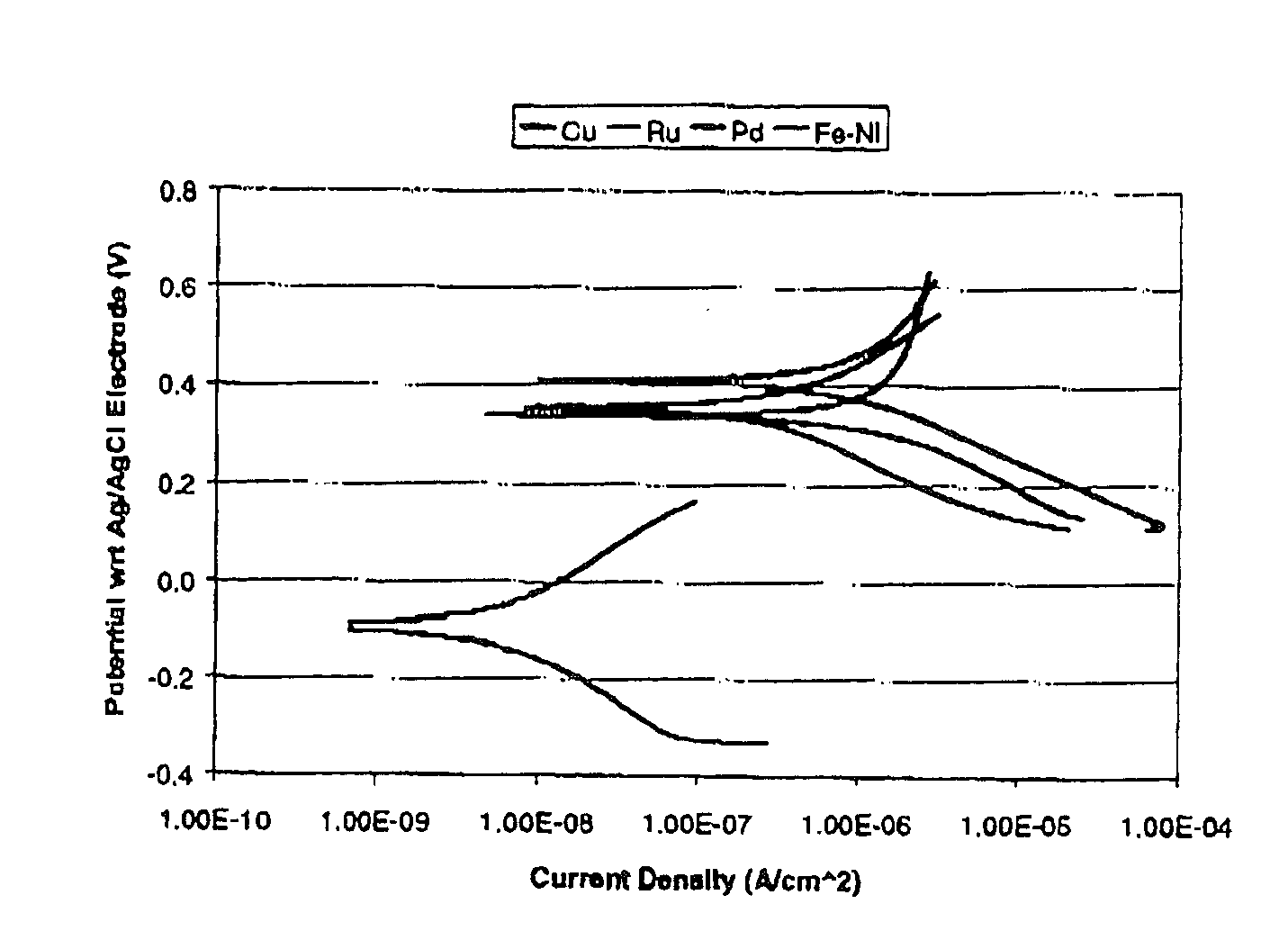
[0062] Electrochemical polarization characteristics of different film types in the slurry described in example 1 and diluted with hydrogen peroxide as shown in example 1 are measured using EG&G M263 potentiostate / galvanostat controlled by SofetcorrII corrosion software. The Scan rate is 0.25 mV / s. FIG. 1 show the Electrochemical polarization curves.
[0063] The electrochemical polarization curves in the FIGURE show that the copper corrosion potential in the slurry mixed diluted as described in example 1 is anodic with respect to ruthenium and Fe—Ni alloy. So in case of a galvanic coupling formed between copper and any of these materials, copper will be thermodynamically favored to be protected. This would result in superior corrosion protection for copper lines / structures.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com