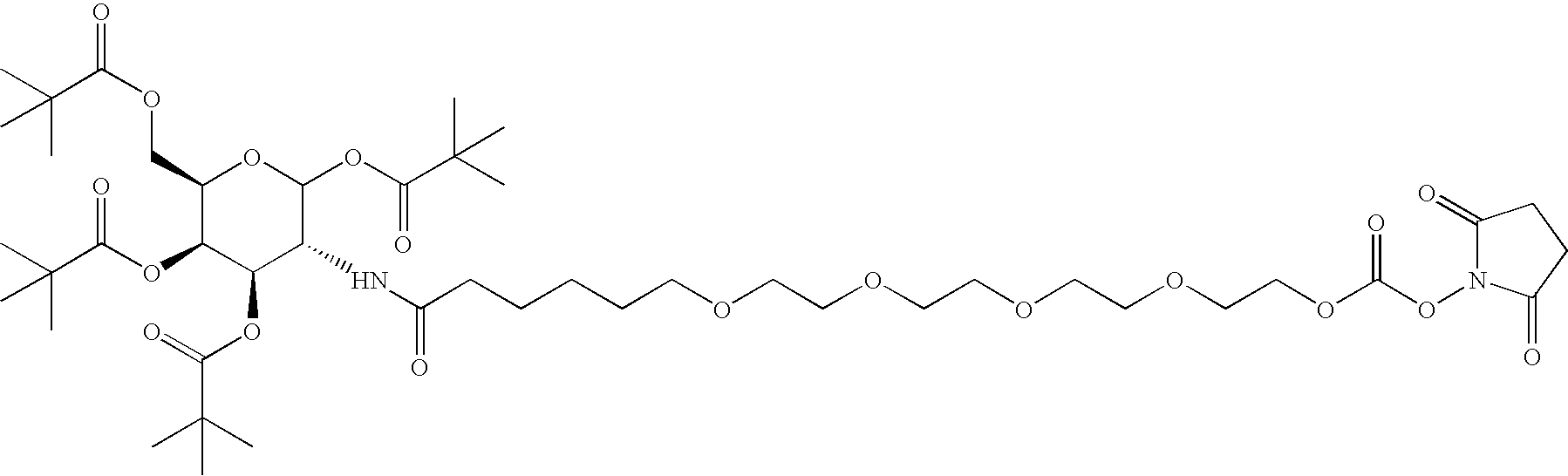
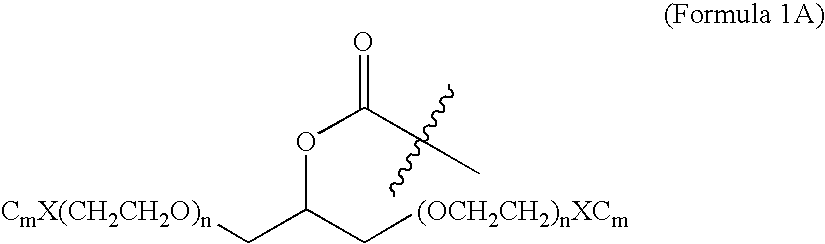
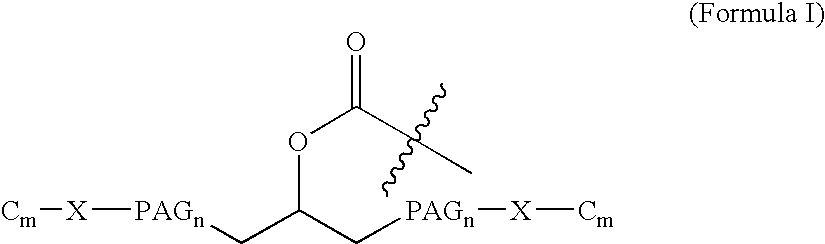[0015] The present invention broadly comprises variant and modified forms of several naturally occurring natriuretic peptides, proteins, analogs, and chemical conjugates of these natriuretic peptides that possess one or more advantages over their naturally occurring counterparts. By way of example, some of these advantages include an increased resistance to
proteolytic degradation, an improved time of persistence in the bloodstream, and / or an improved ability to
traverse cell membrane barriers.
[0017] In some cases, the natriuretic compound conjugate is characterized at least in part by its increased resistance to
enzymatic degradation, such as
proteolysis, relative to a corresponding unconjugated form of the native natriuretic compound. These compound conjugates may be even further characterized by a retained therapeutically significant percentage of
biological activity, such as cGMP stimulating activity, relative to the corresponding unconjugated natriuretic compound. The retained cGMP stimulating activity is typically at least 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 90%, 95%, or even greater than 99% or 100% of the cGMP activity of an unconjugated form of the
natriuretic peptide as measured
in vitro. Other examples of improved characteristics of the natriuretic compound conjugates of the invention having a modifying
moiety, relative to unmodified (unconjugated) natriuretic compound, include improved ability of the natriuretic compound to pass through the GI tract and enter the
blood stream; improved hydrophilicity, hydrophobicity, or amphiphilicity of the natriuretic compound;
improved solubility of the natriuretic compound in aqueous environments or organic solvents; improved ability of the natriuretic compound to cross
cell membranes; improved ability of the natriuretic compound to
traverse the blood-brain barrier; improved ability of the natriuretic compound to target a certain
receptor,
cell, tissue, or organ; and improved pharmacokinetic profile of the natriuretic compound. In a preferred embodiment, the degradation of the biologically
active agent component of the natriuretic compound is less than the degradation of unmodified (unconjugated) biologically active natriuretic compound, at a pH of about 2 for less than about 2 hours. The natriuretic compound component of the natriuretic compound can, for example, be more stable as a component of the natriuretic compound conjugates than the unconjugated natriuretic compound in the presence of
plasma,
proteases, liver homogenate, acidic conditions and / or basic conditions.
[0018]
Natriuretic peptide conjugates of the invention may induce the anti-hypertensive, cardiovascular, renal, and / or endocrine effects that are associated with the native
peptide. In some embodiments, the modification of the
natriuretic peptide will protect the
peptide, such as hBNP, from
proteolysis and facilitate delivery into the
systemic circulation through the gut wall, resulting in natriuresis,
diuresis, and / or
vasodilation.
Natriuretic peptide conjugates of the invention can therefore be effectively delivered as an oral formulation (instead of by continuous intravenous infusion for days in a
hospital setting). This
advantage is expected to reduce hospital costs associated with other CHF therapies by enabling
self administration, which has not heretofore been possible, and is expected to expand the therapeutic use of
natriuretic peptide, especially hBNP, to include early stage (e.g., class 1) and chronic CHF as well as acute CHF. A preferred embodiment of the present invention is a non-
immunogenic peptide conjugate that has increased resistance to degradative enzymes and is suitable for oral delivery and transport across the
intestinal epithelium.
[0028]“Amphiphilic” means the ability to dissolve in both water and lipids and / or having hydrophilic and lipophilic characteristics, and the terms “amphiphilic
moiety” and “
amphiphile” mean a moiety which is amphiphilic and / or which, when attached to a polypeptide or non-polypeptide
drug, increases the amphiphilicity of the resulting conjugate, e.g., PEG-
fatty acid oligomer,
sugar fatty acid oligomer.
[0033]“Lipophilic” means having an affinity for fat, such as chemicals that accumulate in fat and fatty tissues, the ability to dissolve in lipids and / or the ability to penetrate, interact with and / or
traverse biological membranes, and the term, “lipophilic moiety” or “lipophile” means a moiety which is lipophilic and / or which, when attached to another chemical entity, increases the
lipophilicity of such chemical entity.
 Login to View More
Login to View More