Probe density considerations and elongation of self-complementary looped probes where probes are attached to a solid phase
a probe and loop technology, applied in biochemical equipment and processes, specific use bioreactors/fermenters, biomass after-treatment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing specificity, reducing detection sensitivity, and reducing the likelihood of target capture, so as to enhance detection sensitivity, expand the range of stringencies compatible, and enhance detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Homogeneous Beadchip Assay Using Looped Probes
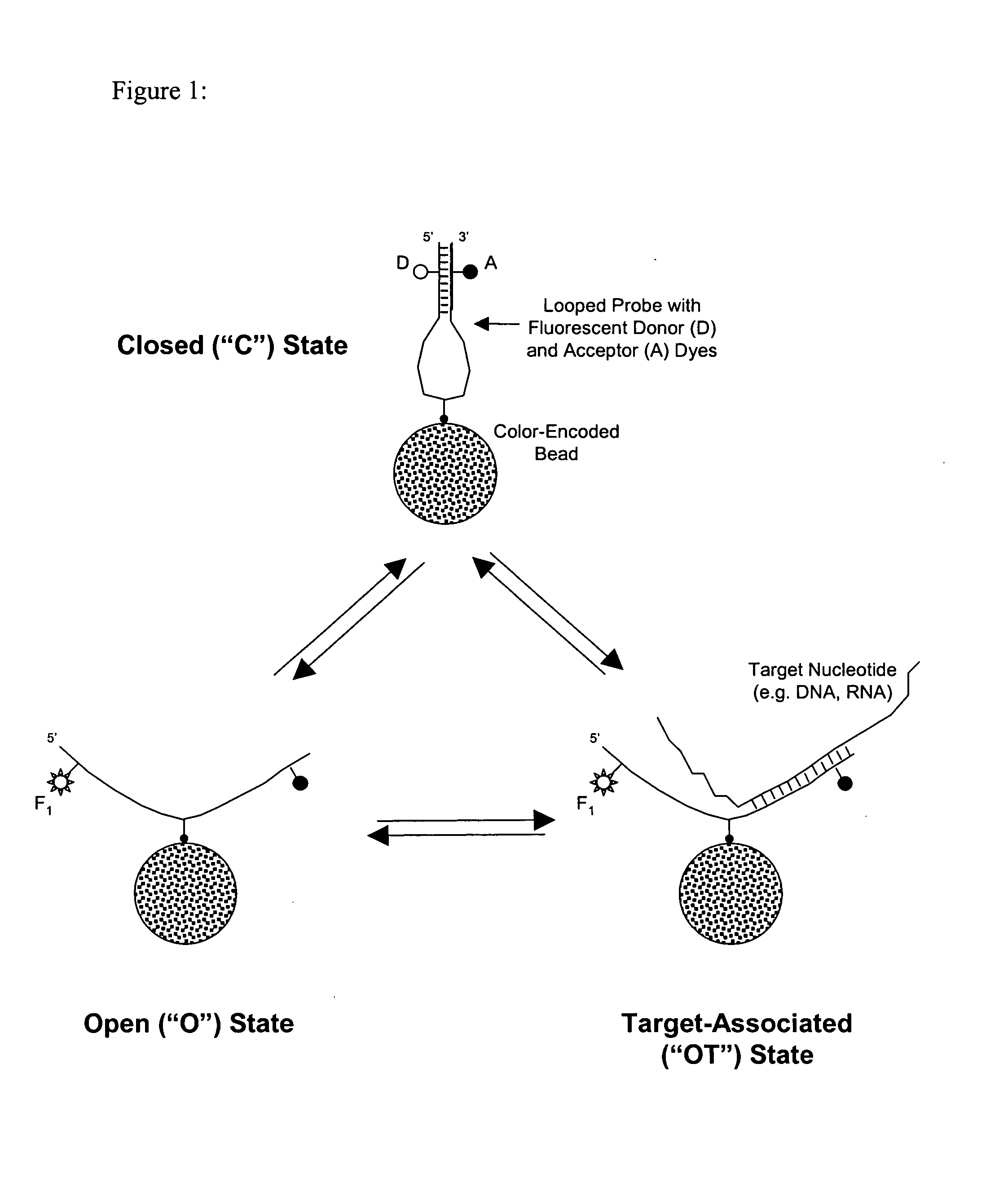
[0057] A homogenous BeadChip assay format, shown in FIG. 1, was implemented by providing a variable gap configuration set to a large value during target capture and a smaller value during recording of assay images from a random encoded array of beads displaying self-complementary probes as well as positive and negative controls. The reaction volume was sealed by encapsulation of the reaction with mineral oil (from Sigma-Aldrich).
[0058] BeadChips were prepared to contain a random array composed of 4,000 beads of four types of color-encoded microparticles (“beads”) on a 375-μm thick n-type Silicon substrate. Color-coding was achieved by staining the beads in accordance with a solvent tuning method described in U.S. application Ser. No. 10 / 348,165 (incorporated by reference). Stained beads were functionalized by covalent attachment of streptavidin to permit subsequent attachment of biotinylated self-complementary (“looped”) probes, illus...
example 2
Homogenous Assay in Suspension of Encoded Beads
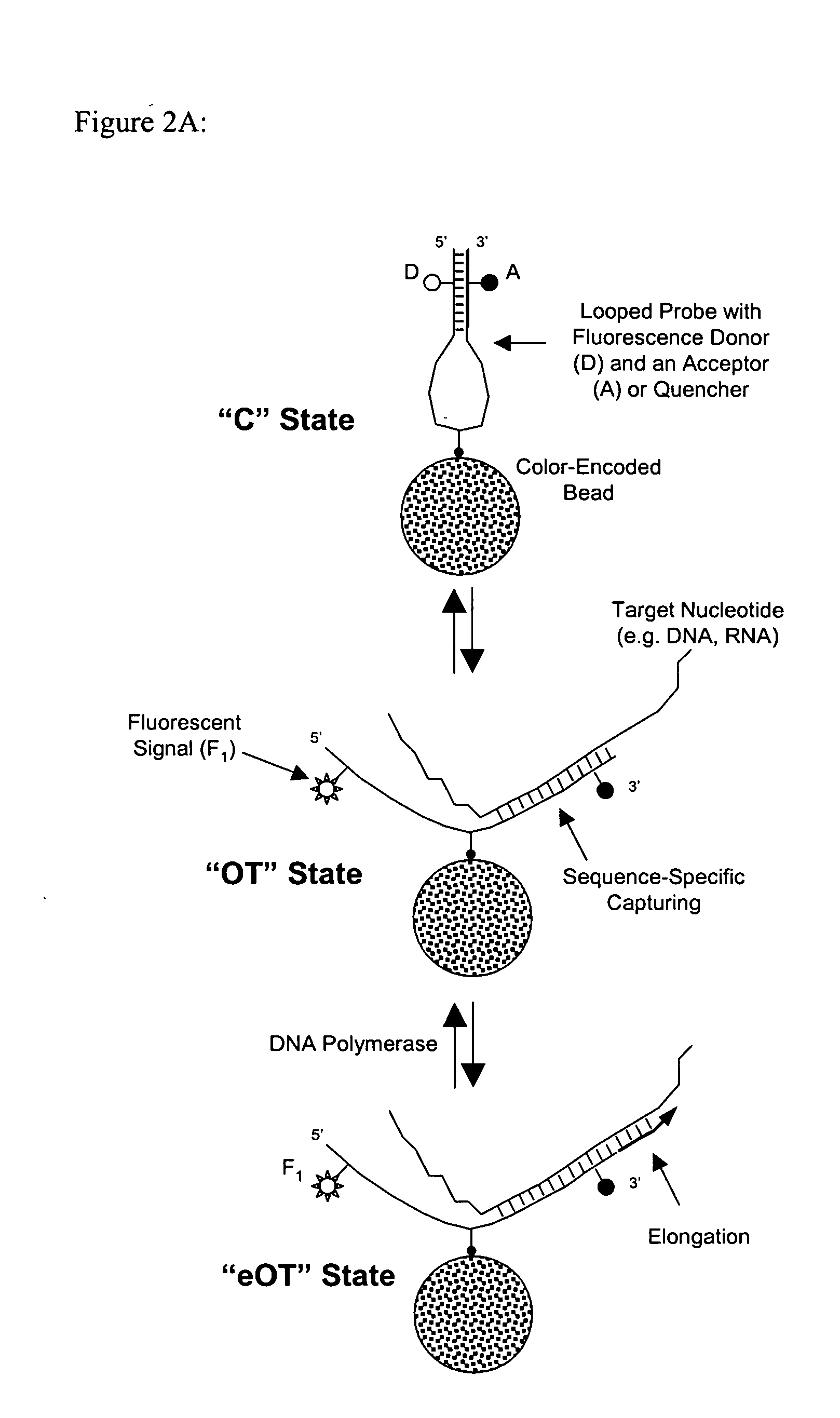
[0062] The looped-probe design also can be used in a homogenous format with encoded beads in suspension, as described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,251,691; U.S. application Ser. No. 10 / 204,799 (incorporated by reference). As shown in FIG. 9, a reaction mixture in a sealed incubation chamber, or cartridge, may contain T7-tagged DNA template, components for in-vitro transcription reaction such as a T7 RNA polymerase, well known in the art, and looped-probe functionalized color-coded beads, each color corresponding to a unique capture probe sequence. Preferably, encoded magnetic beads are used (see U.S. application Ser. No. 11 / 218,838), and a random array of such beads is assembled in real time following completion of the assay, as described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,251,691; U.S. application Ser. No. 10 / 204,799.
[0063] Two sets of magnetic beads (Spherotech, 4.10 μm in diameter, ρ˜1.13 g / ml), one encoded with a green dye by solvent-tuning (REF—Solvent Tu...
example iii
Homogeneous Binding Assay in Suspension Using Looped Probes Immobilized on Magnetic Beads
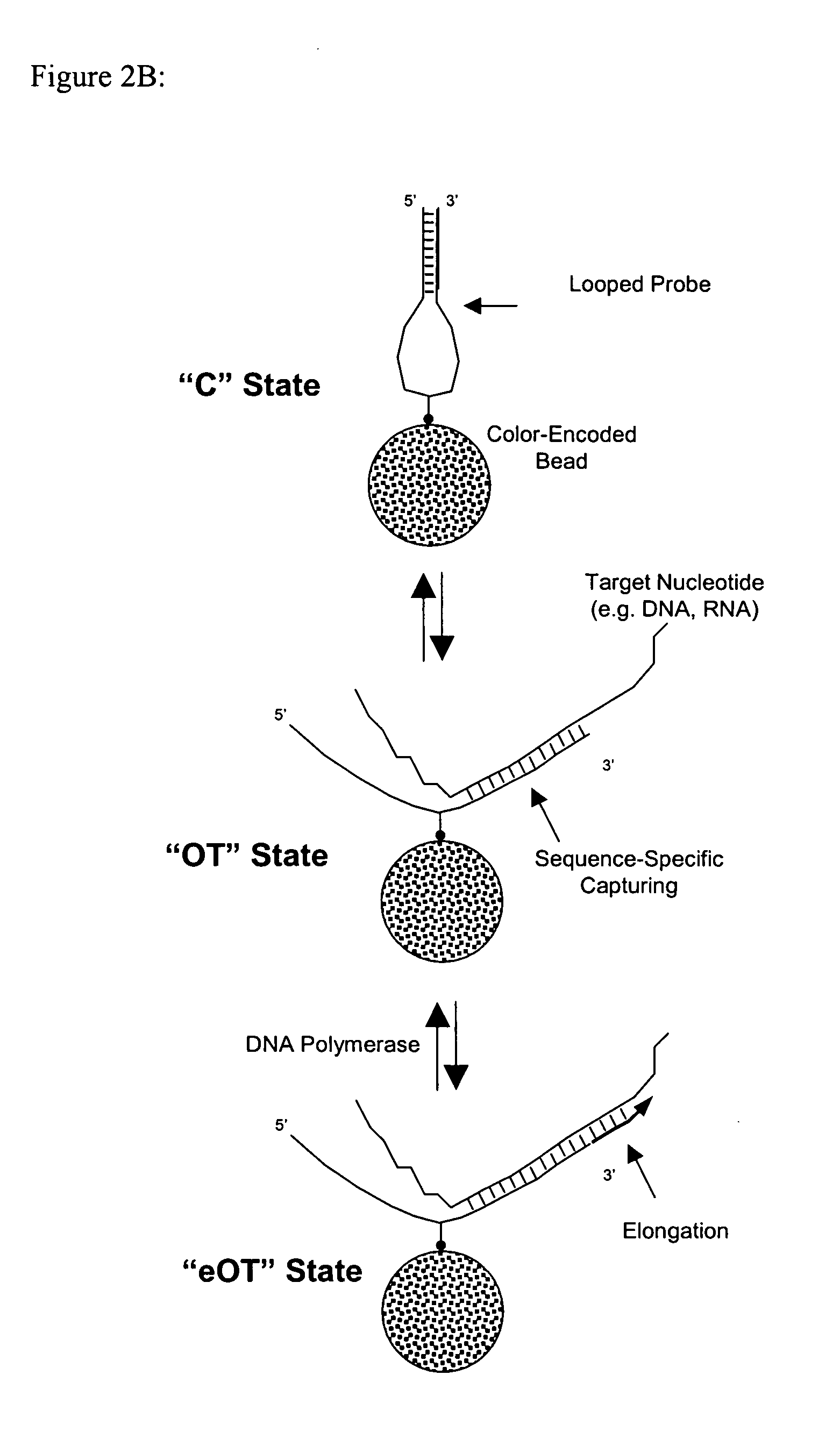
[0067] Looped probes were immobilized on color-encoded magnetic microparticles (“beads”) for use in a homogeneous binding assay. Briefly, magnetic beads of ˜4 micron diameter were synthesized by standard methods and color-encoded as set forth in U.S. application Ser. No. 10 / 348,165, incorporated by reference. Next, encoded beads were modified by covalent attachment of Neutravidin to epoxy groups on the beads to permit: attachment of a “perfect-match (PM)” biotinylated looped probe, a “no-match (NM)” biotinylated looped probe, and a biotinylated positive control, in the form of a Cy3-labeled oligonucleotide.
[0068] As in the previous examples, looped-probes contain a donor dye and an acceptor dye at their respective 5′ and 3′ ends. Aliquots of probe-decorated, encoded magnetic beads were pooled in one test tube for determination of RNA target concentrations.
[0069] To determine the response of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Ionic strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com