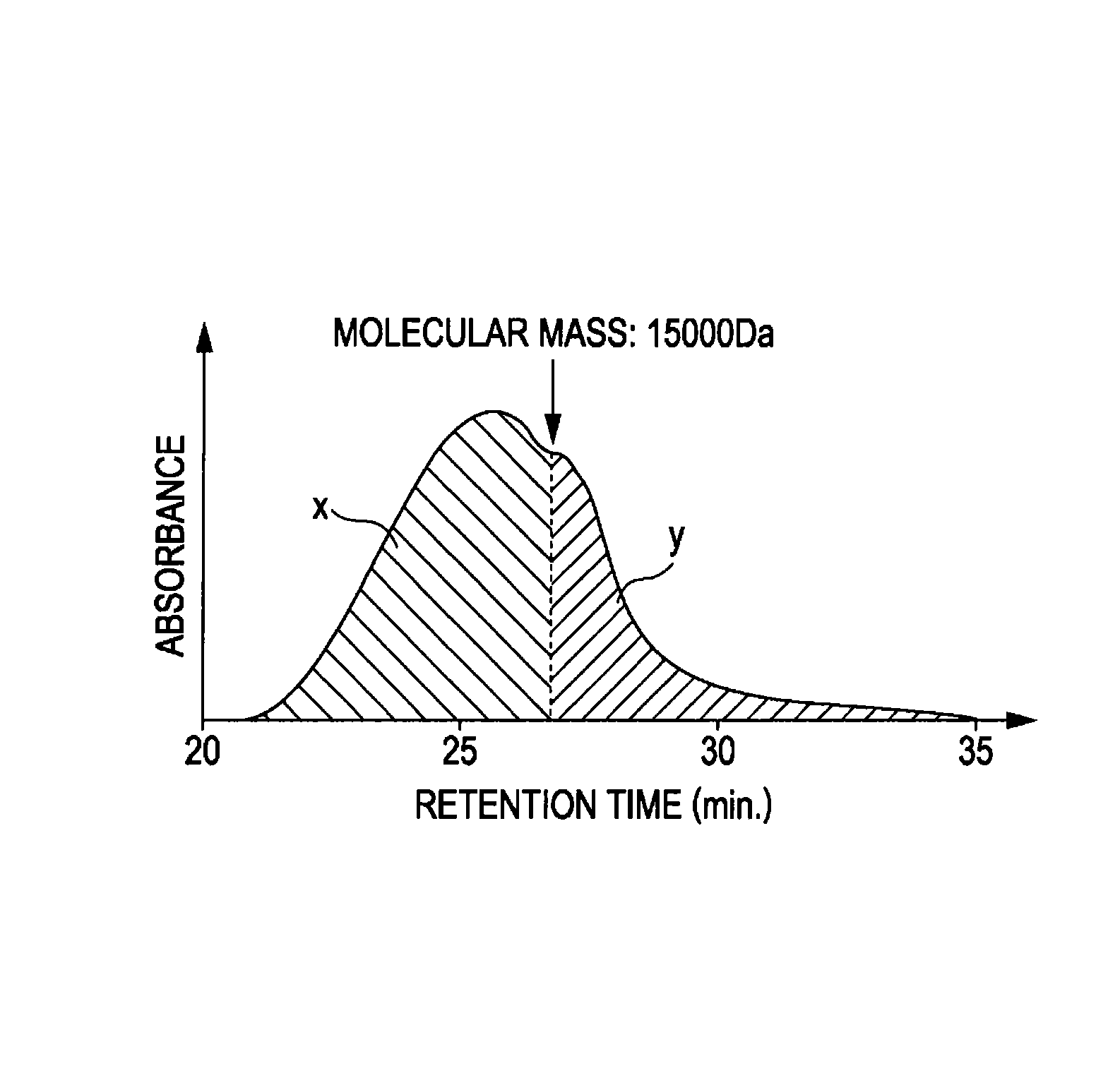
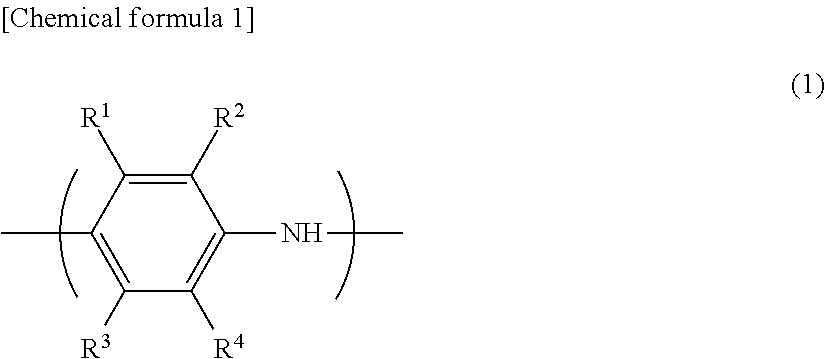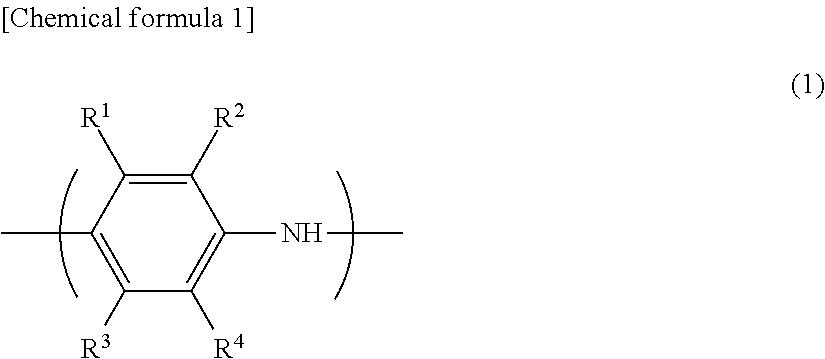Conductive aniline polymer, method for producing same, and method for producing conductive film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0090]In this embodiment, a polymerization step (Z1) shown below is used as the polymerization step (Z).
[0091]The method for producing a conductive aniline polymer of the embodiment includes a polymerization step (Z1) of polymerizing an aniline derivative (A) in a solution containing a basic compound (B), a solvent (C), and an oxidizing agent (D) at a liquid temperature lower than 25° C.
[0092]Hereinafter, each component used in the polymerization step (Z1) will be specifically described.
Aniline Derivative (A)
[0093]An aniline derivative (A) used in the polymerization step (Z1) of the embodiment is a compound represented by the following formula (2). Specifically, the aniline derivative (A) is preferably a compound selected from the group consisting of an acidic group-substituted aniline, an alkali metal salt, an alkaline earth metal salt, an ammonium salt, and a substituted ammonium salt thereof.
[0094]In the formula (2), R5 to R9 are each independently —H, a linear or branched alkyl ...
second embodiment
[0221]In the embodiment, a polymerization step (Z2) shown below is used as the polymerization step (Z).
[0222]A method for producing a conductive aniline polymer (P) of the embodiment includes a polymerization step (Z2) of adding an aniline derivative (A) represented by the formula (2) and an oxidizing agent (D) to a solution in which a conductive aniline polymer (P-1) having a repeating unit represented by the formula (1) is dissolved in a solvent (C) or a dispersion in which the conductive aniline polymer (P-1) is dispersed in a solvent (C) to polymerize the aniline derivative.
[0223]In the polymerization step (Z2), a basic compound (B) may be further added to a solution or a dispersion of the conductive aniline polymer (P-1) to polymerize the aniline derivative, if necessary.
Conductive Aniline Polymer (P-1)
[0224]A conductive aniline polymer (P-1) used in the polymerization step (Z2) of the embodiment has a repeating unit represented by the formula (1).
[0225]The conductive aniline p...
example 1-1
[0307]First, 200 mmol of ammonium peroxodisulfate and 1.0 g of sulfuric acid were dissolved in 150 mL of a mixed solvent of water and acetonitrile (volume ratio: 1:1) cooled to 0° C. in an ethylene glycol bath at a stirring power of 0.7 kw / m3 to give a solution (polymerization initiation temperature: reaction solution temperature, 1.5° C.). Next, to the solution, a solution of 200 mmol of 2-aminoanisole-4-sulfonic acid and 200 mmol of triethylamine in 150 mL of a mixed solvent of water and acetonitrile (volume ratio: 1:1) was added dropwise at 200 mmol / hr. After completion of the dropwise addition, the reaction solution was kept for 2 hours under stirring at a stirring rotation speed of 200 rpm while the temperature of the refrigerant was adjusted so that the temperature (retention temperature) of the reaction solution was 0° C. (polymerization step (Z1)). The maximum temperature of the reaction solution in the polymerization step (Z1) was 8° C. when the amount of the added monomer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap