Method for preparing metallic lithium using electrolysis in non-aqueous electrolyte
a technology of electrolysis and metallic lithium, applied in the field of non-aqueous electrolysis, can solve the problems of reducing reducing the potential of potassium having a higher standard electrode, and inability to use battery applications, etc., and achieves the effect of improving the electrolytic efficiency of lithium and improving the stability of metallic lithium deposits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Electrolytic Reduction of Lithium
[0046]In order to determine the reduction of lithium according to the present invention, the following tests were performed.
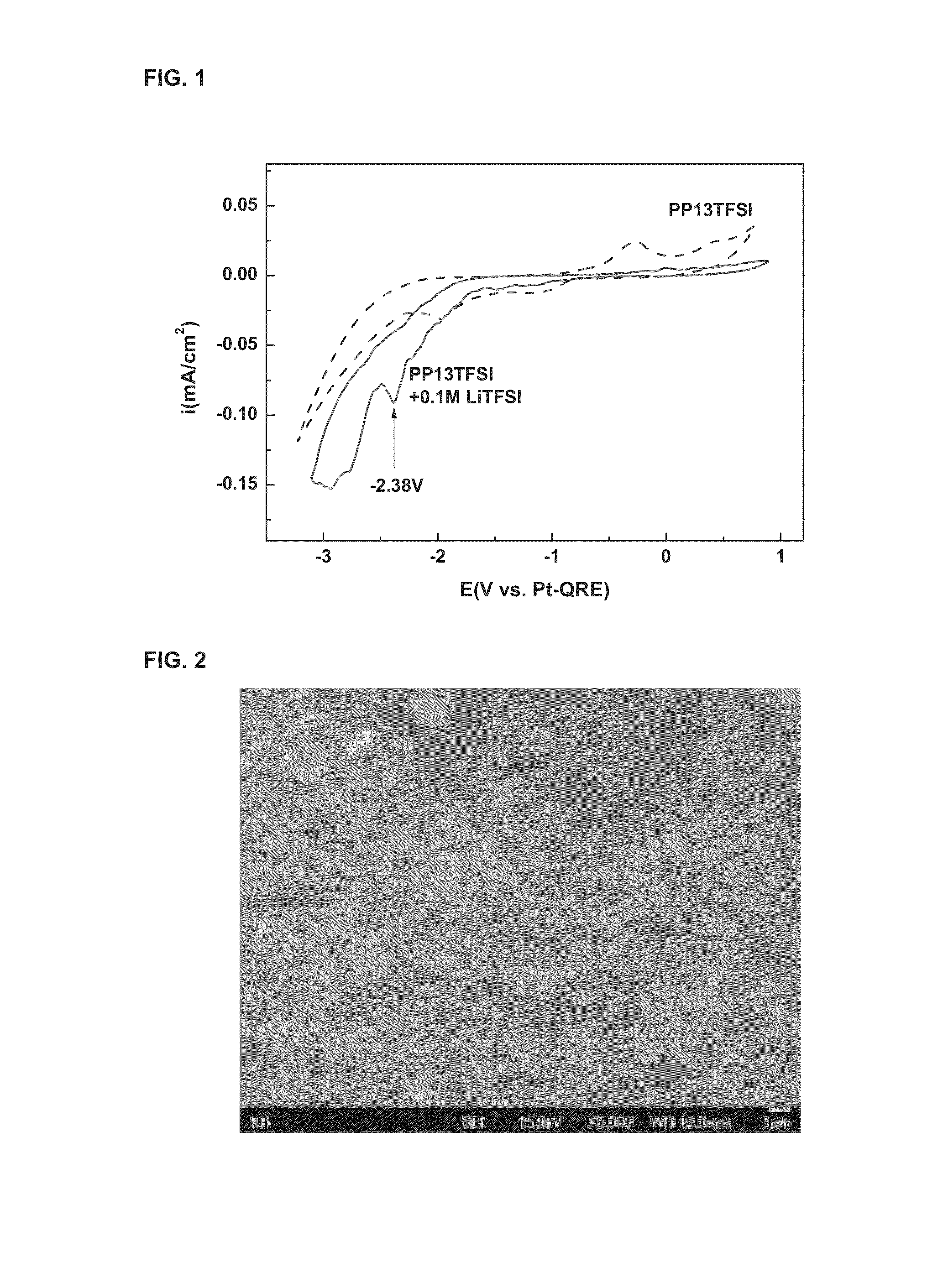
[0047]An electrolytic cell with a ternary electrode system was used for the electrolytic reduction of lithium, in which a working electrode was gold and an opposite electrode was platinum. An electrolyte with LiTFSI dissolved in PP13TFSI was used as a non-aqueous conductive solvent. The ternary electrode system refers to the structure in which a reference electrode for precisely monitoring the voltage applied to a cathode is added to an electrolytic cell comprising a working electrode and a relative electrode.
[0048]Before the tests, all the electrodes and the electrolytic cell were washed with a mixed solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) at a mixed ratio of 50:50 vol %, and all the non-aqueous solvents were dried at a 100° C. vacuum oven for 24 hours and used for the electrolysis.
[0049]The redox current...
experimental example 1
CV Measurement Depending on Working Electrodes
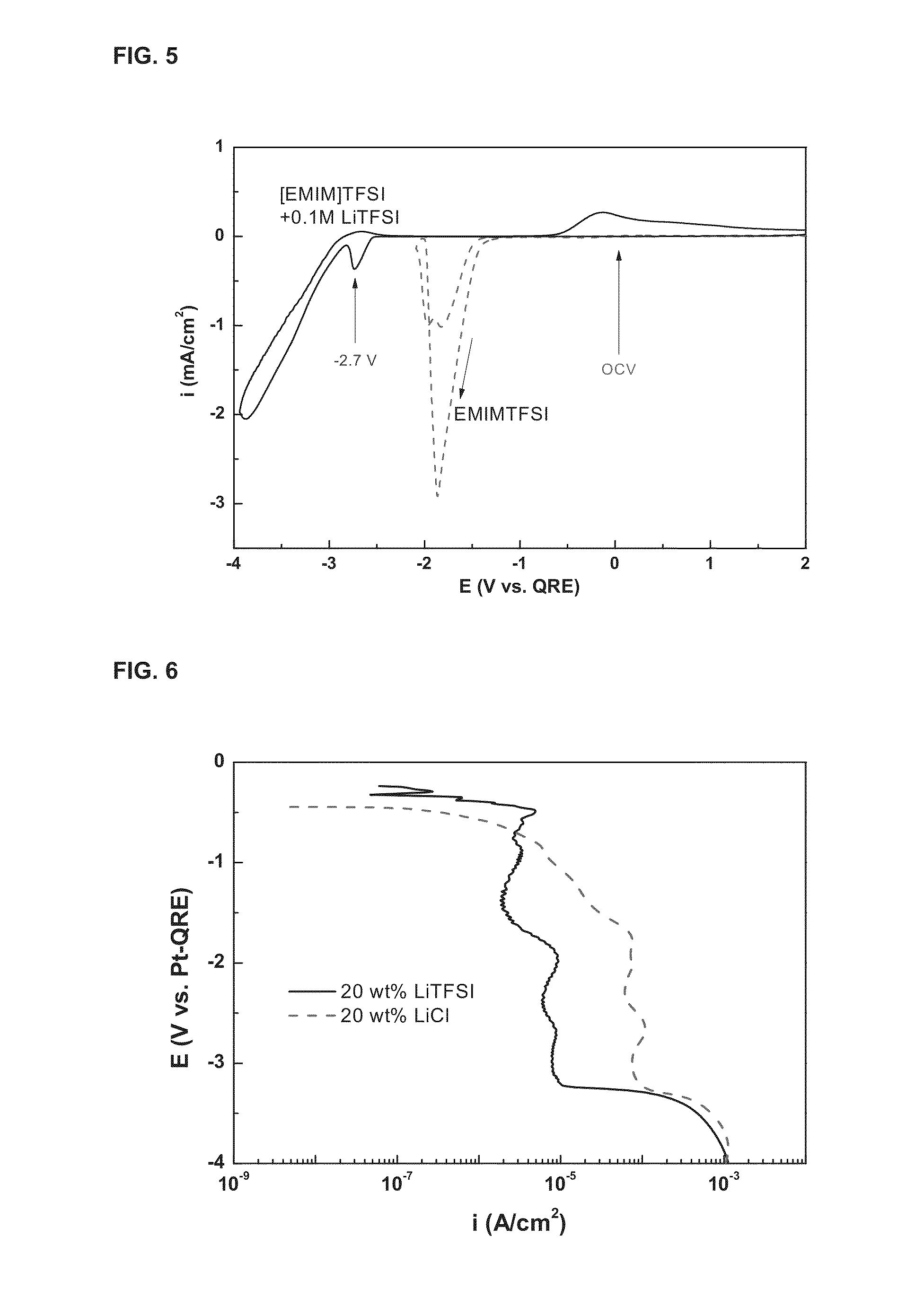
[0055]The CV results measured when platinum was used as the working electrode in the same electrolytic cell and electrolyte as those in Example 1 are shown in FIG. 3.
[0056]As shown in FIG. 3, the peak interpreted as the reduction of lithium was observed at −1.85 V (vs. Pt-QRE), and the peaks interpreted as the oxidation and reduction of ionic liquids were also observed, and thus it was found that the stability of PP13TFSI as the solvent was very low.
[0057]Moreover, the CV results measured using copper as the working electrode in the same electrolyte are shown in FIG. 4.
[0058]As shown in FIG. 4, it can be seen that the stability of PP13TFSI is similar to the position of the voltage (−2.18 V vs. Pt-QRE) at which the lithium is reduced, but the reduction current is lower than that of gold, indicating that the catalytic performance of gold is most excellent in the electrolytic reduction of metallic lithium.
experimental example 2
Replacement of Non-Aqueous Conductive Solvents
[0059]The electrolytic properties of lithium when gold was used as the working electrode in the same electrolytic cell as that in Example 1 and [EMIM]TFSI with a dissolved lithium salt was used as the conductive electrolyte were measured by cyclic voltammetry. The measurement results of electrochemical properties in [EMIM]TFSI are shown in FIG. 5.
[0060]As shown in FIG. 5, it can be seen that the reduction peak of lithium is −2.7 V which is slightly lower than −2.4. V in PP13TFSI, indicating that other non-aqueous conductive solvents capable of dissolving the lithium salt can be used for the recovery of metallic lithium. Moreover, it can be seen that the stable reduction region of [EMIM]TFSI was shifted from about −2 V to about −3 V in the negative direction by the addition of LiTFSI. However, the cations of the solvent, which determine the cathode limit potential, had the lowest stable cathode potential in EMIM, and the cathode reactivit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com