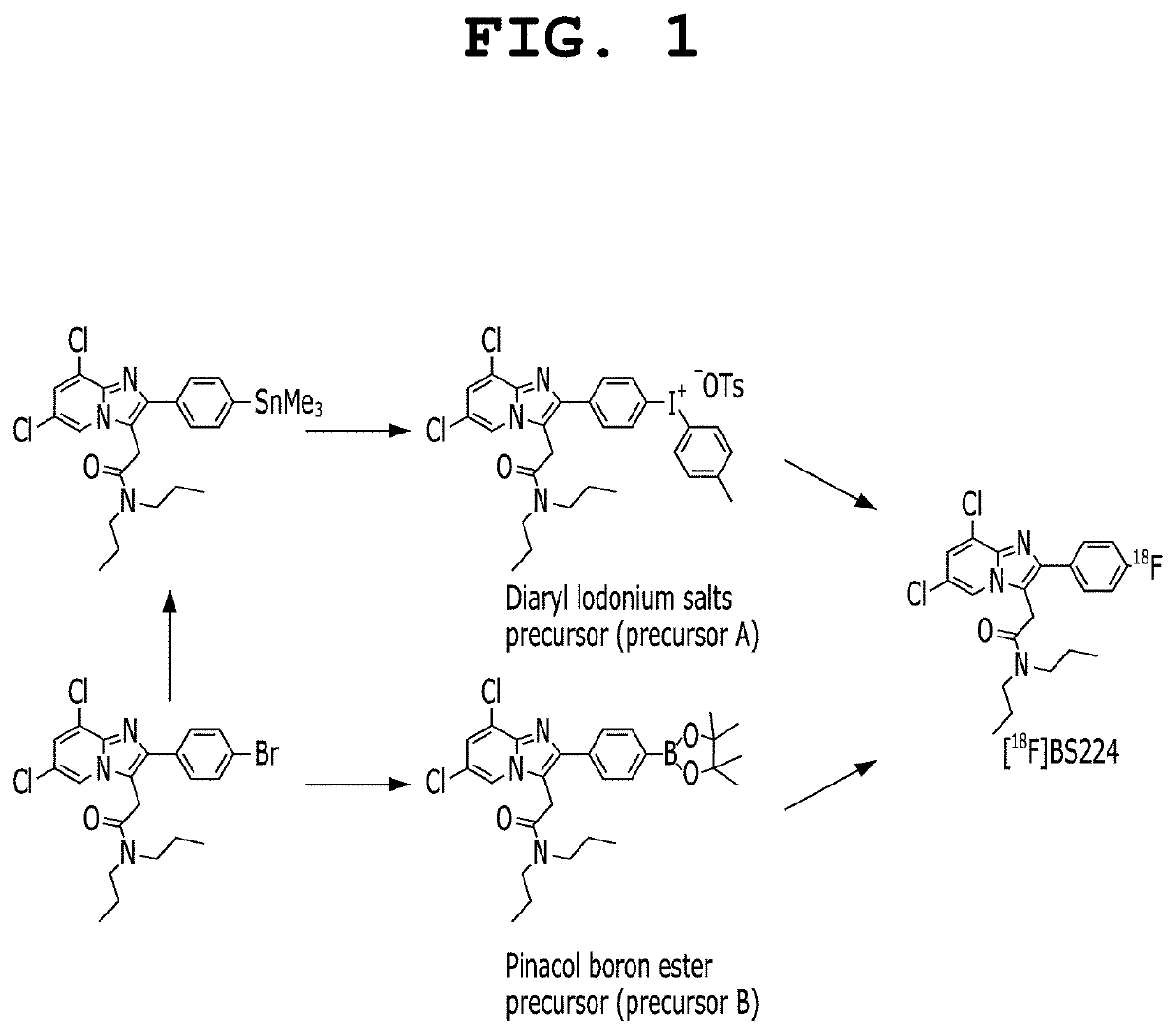
Positron emission tomography radiotracer for diseases associated with translocator protein overexpression, translocator protein-targeting ligand for fluorescence imaging-guided surgery and photodynamic therapy, and production methods therefor
a translocator protein and radiotracer technology, applied in the field of fluorine-18labeled positron emission tomography radiotracer, can solve the problems of low tspo-specific signal, limited signal-to-noise ratio, and limited use of [sup>11/sup>c] pk11195, and achieve the effect of increasing the fluorine-18 labeling reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation examples
Preparation of Starting Material for Producing Iodonium Salt or Boron Ester Precursor
preparation example 1
-dichloro-2-(4-(trimethylstannyl)phenyl)-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N,Nr-dipropylacetamide
[0082]
(Step 1): Preparation of 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxo-B;N-dipropylbutanamide
[0083]3-(4-bromobenzoyl)propionic acid (2.0 g, 7.8 mmol) and 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole (1.4 g, 8.6 mmol) were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (THF, 50 ml) and stirred for 30 minutes. After 30 minutes, N,N′-dipropylamine (1.2 mL, 8.6 mmol) and triethylamine (1.3 ml, 9.4 mmol) were added thereto, followed by stirring for 3 hours. After the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, a 0.1 N aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride was added thereto, followed by extraction with ethyl acetate. The extracted organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate and filtered, and the remaining organic solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by column chromatography to afford the desired compound.
[0084]1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.86 (t, J=7.4 Hz, 3H, CH3), 0.95 (t, J=7.4 Hz, 3H, CH3), 1.53 (q, J=7.4 Hz, 2H, CH...
example 3
n of 2-(6,8-dichloro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N,N-dipropylacetamide
[0102]
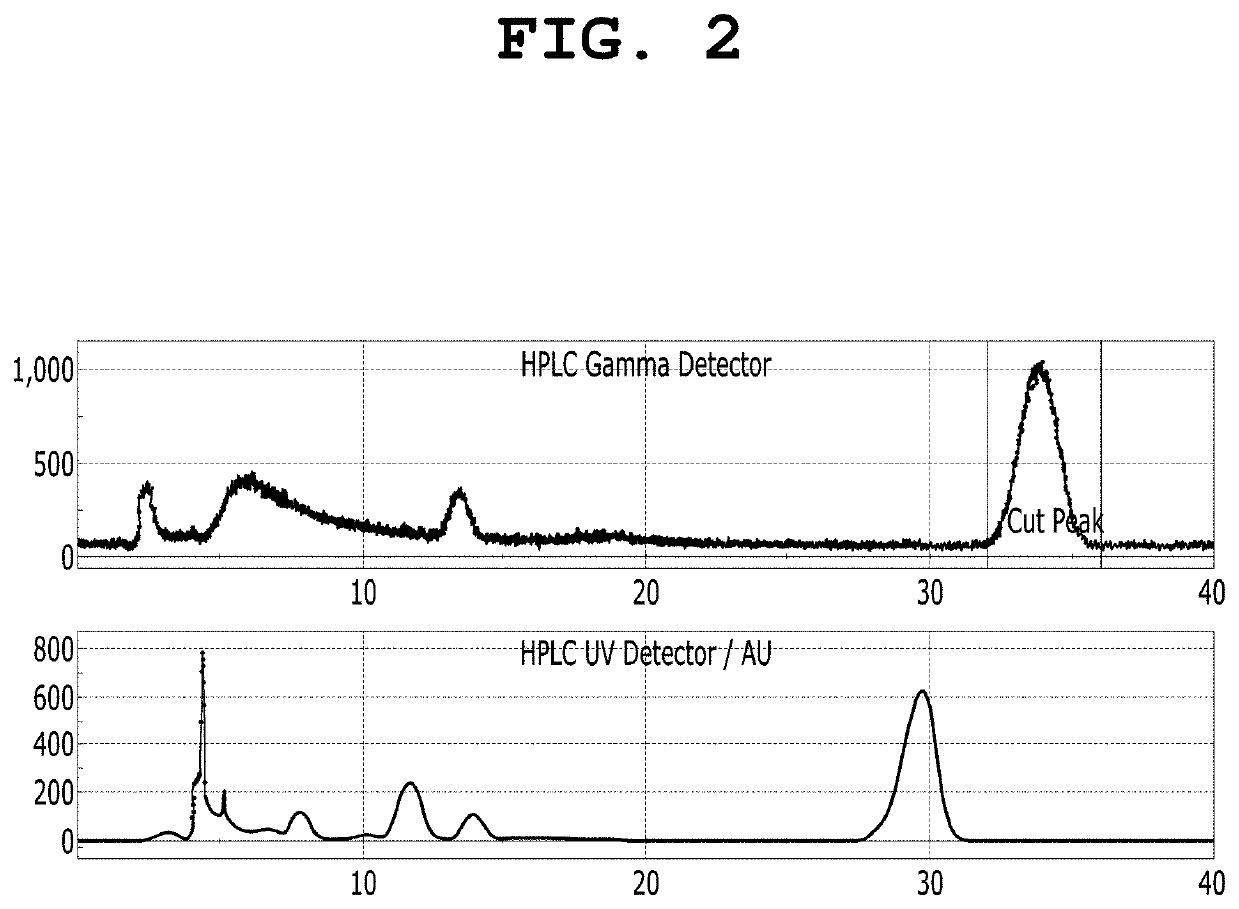
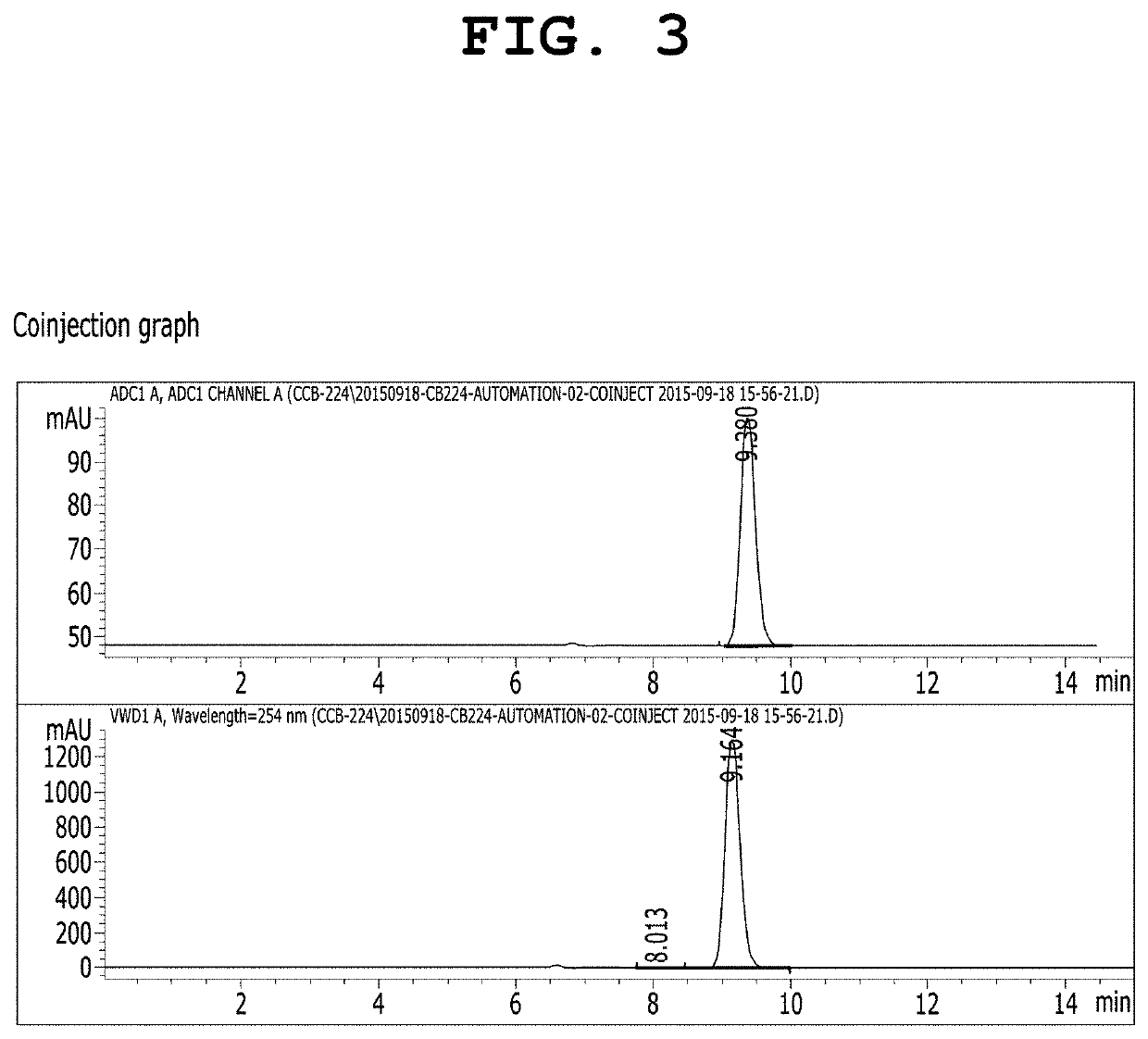
[0103]To a solution of 18-crown-6 (25.0 μmol) in acetonitrile (0.3 mL), a solution of cesium fluoride (25.0 μmol) in water (10 μL) was added. The solvent was completely evaporated by azeotropic distillation while the solution was heated at 90° C. under nitrogen. To the remaining material, a solution of (4-(6,8-dichloro-3-(2-(dipropylamino)-2-oxoethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-2-yl)phenyl) (p-tolyl)iodonium tosylate in acetonitrile (0.3 ml) was added, followed by heating at 80 to 140° C. for 1 hour with stirring. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was purified using an HPLC system (Waters, Xterra Semi-preparative C18 column, 10×250 mm, 10 μm; 50% acetonitrile-water, 254 nm, flow rate: 5.0 mL / min) equipped with a 254 nm UV detector and a radioisotope gamma-ray detector, and 2-(6,8-dichloro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N,N-dipropylacetamide (BS224) was isolate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Nanoscale particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com