Targeted Thrombolysis for Treatment of Microvascular Thrombosis
a thrombolytic and microvascular technology, applied in the field of medicine and pharmacy, can solve the problems of organ damage, multi-organ failure with lethal consequences, obstructing the microvasculature with life-threatening consequences, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
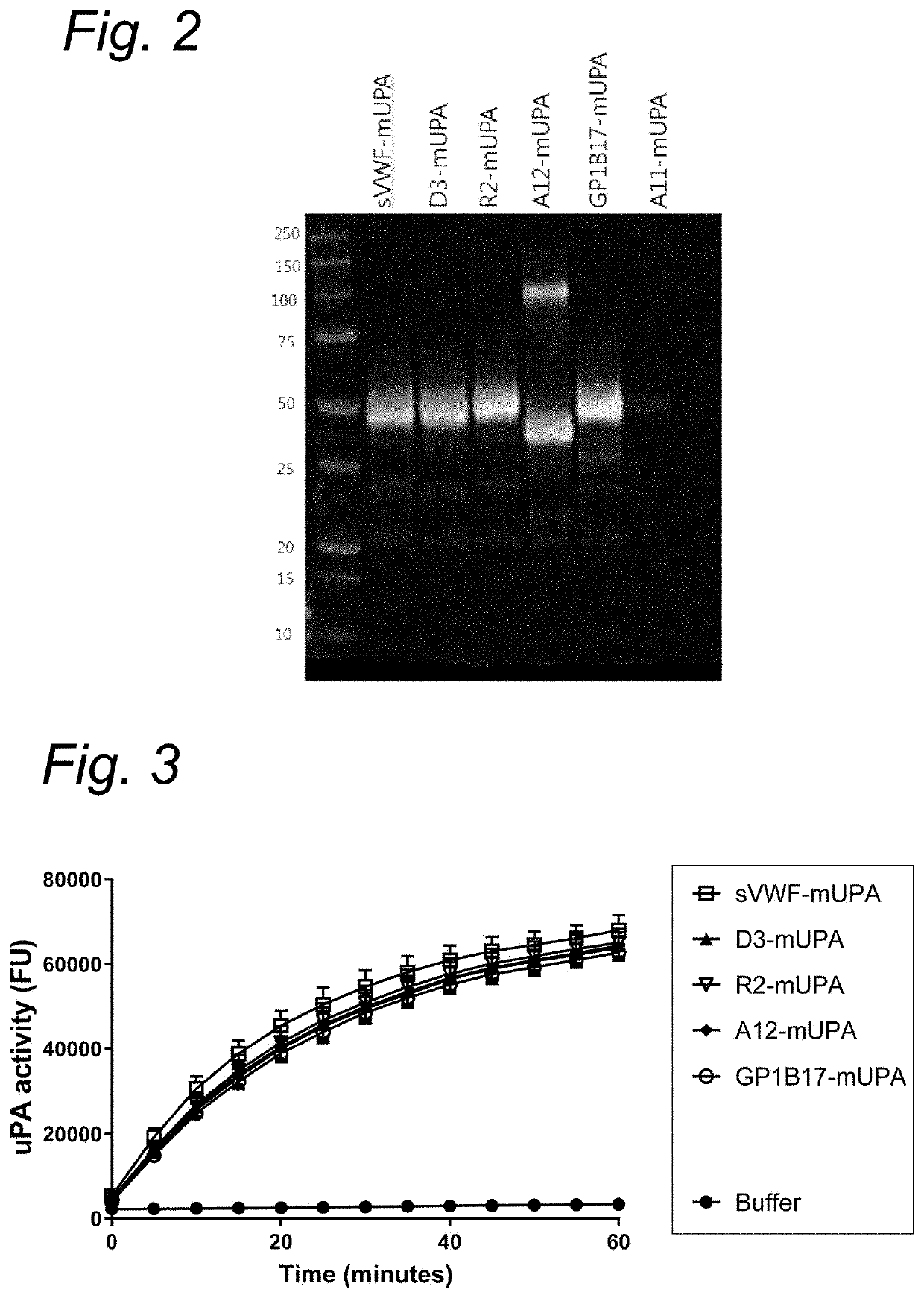
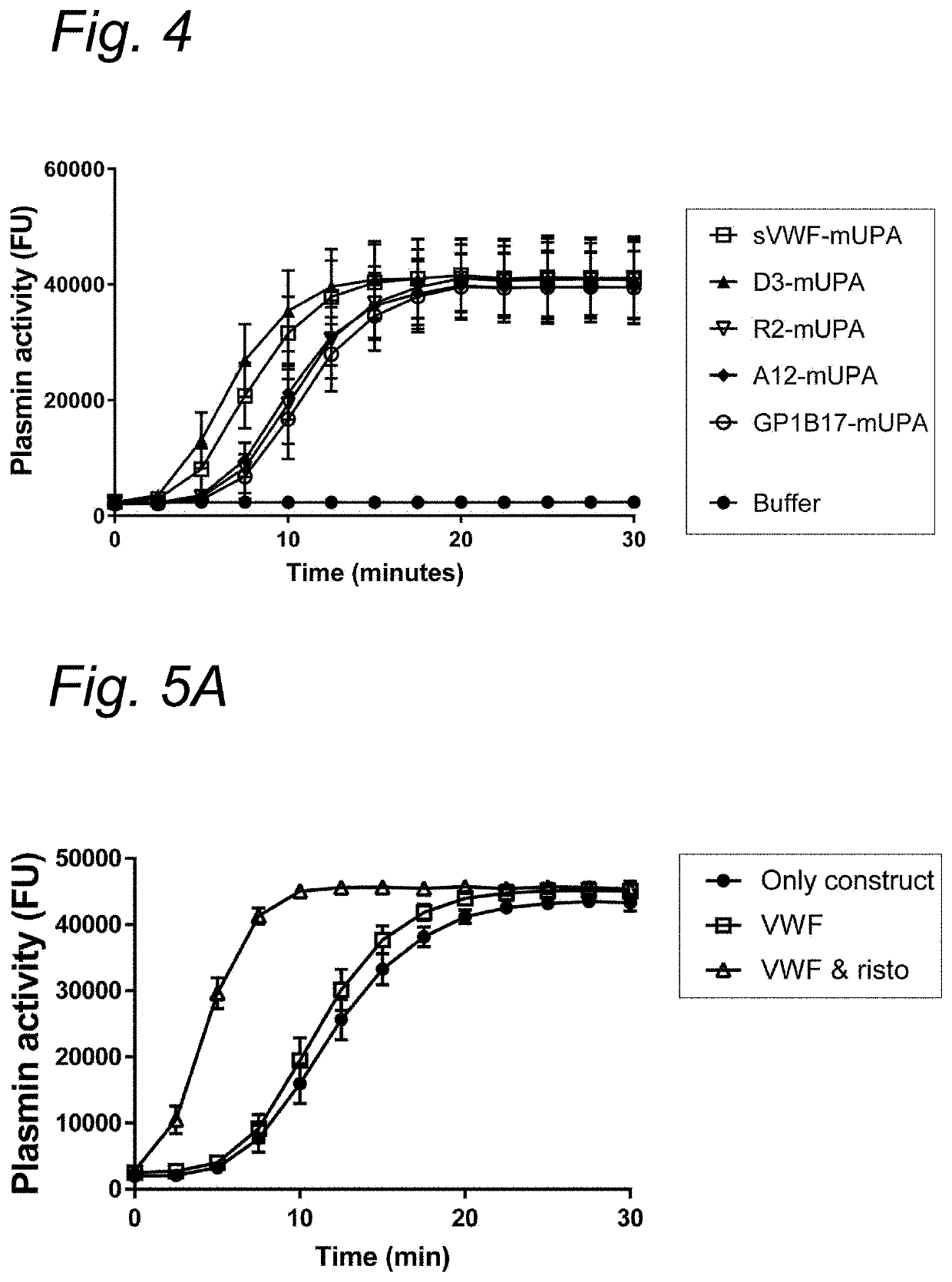
Examples
example 1
Methods and Materials
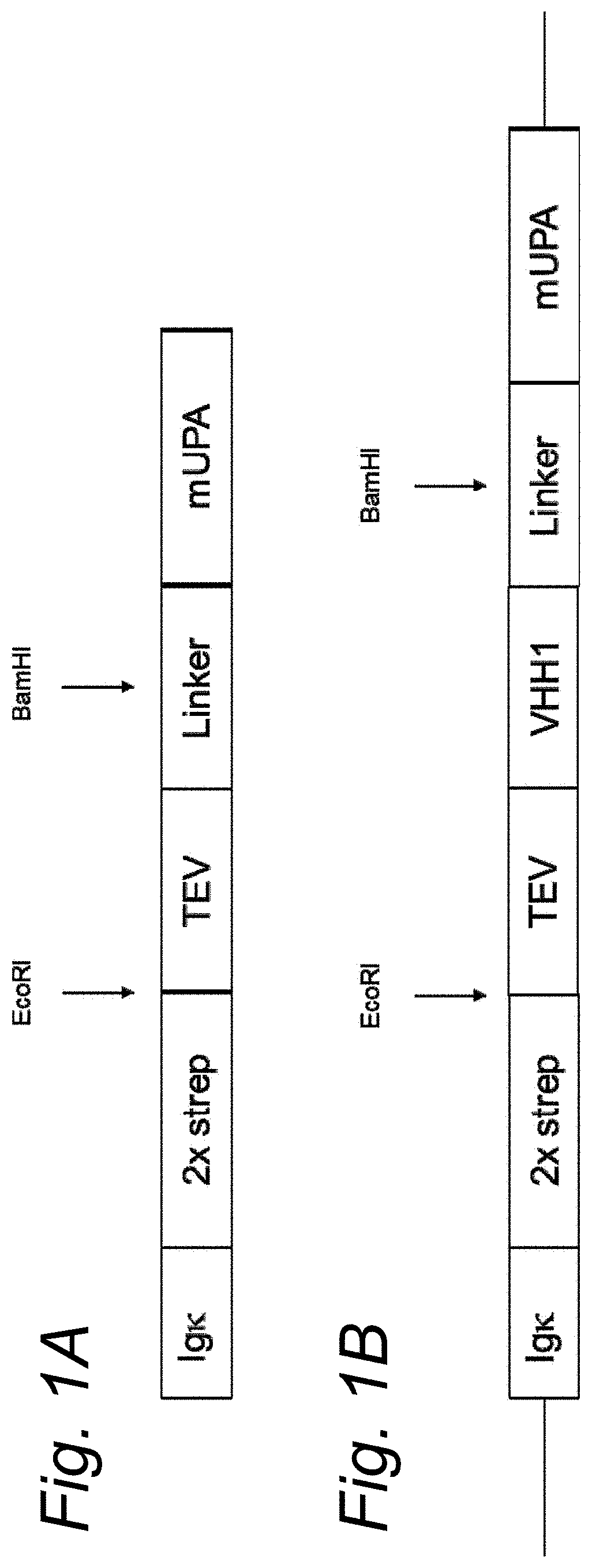
[0118]Nanobody-mUPA construction
[0119]The cDNA sequence for both human and mouse urokinase (PLAU) was obtained from the NCBI database (NM_002658.4 and NM_008873.3 respectively). The sequence for the signal peptide, EGF-like and Kringle domain were removed as well as the first part of the connecting peptide. To the remaining connecting peptide and S1 peptidase domain (Catalytic domain) a N-terminal sequence coding for a Tobacco Etch Virus cleavage site followed by an GGGGS linker was added. In the GGGGS linked a Pstl and BamHI digestion site were incorporated without disturbing the amino acid sequence. At the 5′ side an EcoRl digestion site was added and at the 3′ side and Notl digestion was added after the STOP codon of PLAU. The construct was obtained from IDT (Integrated DNA Technologies, Leuven, Belgium) as a custom gene construct.
[0120]Coding sequences for nanobodies (also known as VHH) were codon optimized via IDT for expression in a human host cells. At th...
example 2
Micro-Thrombolysis of VWF-Platelet on Endothelial Cells in Flow Perfusion Materials and Methods
Human Vascular Endothelial Cell (Huvecs) Culture on Cover Glasses
[0134]Huvecs (passage 0) stored in liquid nitrogen were thawed at 37° C. and added to medium 1:10 (EBM-2 Lonza or Promocel supplemented with huvec growth factors EGM2) and spun down 100 g for 5 minutes. Supernatant was discarded and cells were taken up in 5 mL medium and cultured in T25 flasks at 37 degrees Celsius, 5% CO2. The following day the cells were passed to 3× T75 flasks. On day 6 the cells are passed 1:6 to the cover glasses pre-treated with 1,25% glutaraldehyde in HT-buffer pH 7.4 (HEPES Tyrode buffer: 10 mM HEPES, 0.5 mM Na2HPO4, 145 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1 mM MgSO4).
[0135]To coat cover glasses with glutaraldehyde, coverglasses were rinsed with demi water and with ethanol. Cover glasses were then incubated in HCL 37% : methanol (1:1) for 30 minutes followed by a rinse with demi water for 5 minutes. Next cover glasses...
example 3
Methods and Materials
Caplacizumab Production
[0142]Caplacizumab (a bi-valent variant of the Cablivi VHH) was produced in E.coli and purified via HIS-tag affinity chromatography. The Caplacizumab protein sequence was derived from its EMA assessment report (EMA / 490172 / 2018; Procedure No. EMEA / H / C / 004426 / 0000) and codon optimized for E.coli expression via the integrated DNA technologies (IDT) codon optimized tool. N-terminal BamHl and C-terminal Notl digestion sites were added to the constructs and ordered as a double stranded DNA fragment from IDT (SEQ ID NO:40).
[0143]The DNA fragment were dissolved in 5 mM Tris-buffer (pH=8.5) and heated at 50° C. for 20 minutes. Hereafter the DNA fragment was ligated into the pJET1.2 vector (CloneJET PCR Cloning Kit; Thermo Fisher) according to manufacturer instructions. The ligated product was transformed into chemically competent E.coli TOP10 (Thermo Fisher) via heat shock according to manufacturer instructions. Transformed bacteria were cul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com